Bible Stele, Tablets, Inscriptions, Manuscripts, Scrolls, Codex
|
Babylonian furnace of fire tablet: Book of Daniel: 605 BC |
||
|
|
Daniel’s furnace of fire: 594 BC A Babylonian tablet dating from the time of Nebuchadnezzar decreed that if you offend the gods, you will be cast into a commercial oven like a brick kiln. This directly confirms the story of Daniel 3 where Shadrach, Meshach and Abed-nego where cast into a brick kiln in the spring of 594 BC. This proves Daniel was written in the 6th century BC, not 150 BC as the skeptics suggest because execution in an industrial kiln was unknown during the Hasmonean era. Babylonian furnace of fire tablet
|
|

|
Origin of the Philistines from Crete 1. Egyptian Reliefs at the mortuary temple of Medinet Habu in Thebes of Rameses III that document the world uprising of the Philistines in 1177 BC. 2. Sling stones excavated in Israel 3. Philistine Pentapolis at the time of Moses
|

|
Origin of Synagogues in 280 BC in Alexandria Egypt |
||
|
|
Origin of Synagogues “The Septuagint was Synagogue seed” See also: How the Septuagint gave birth to Synagogues in 280 BC
|
|
|
Pharaoh’s of the Babylonian Captivity: 690 – 526 BC |
||||
|
Psamtik I (Psammetichus I) |
Neco II |
Psamtik II (Psammetichus II) |
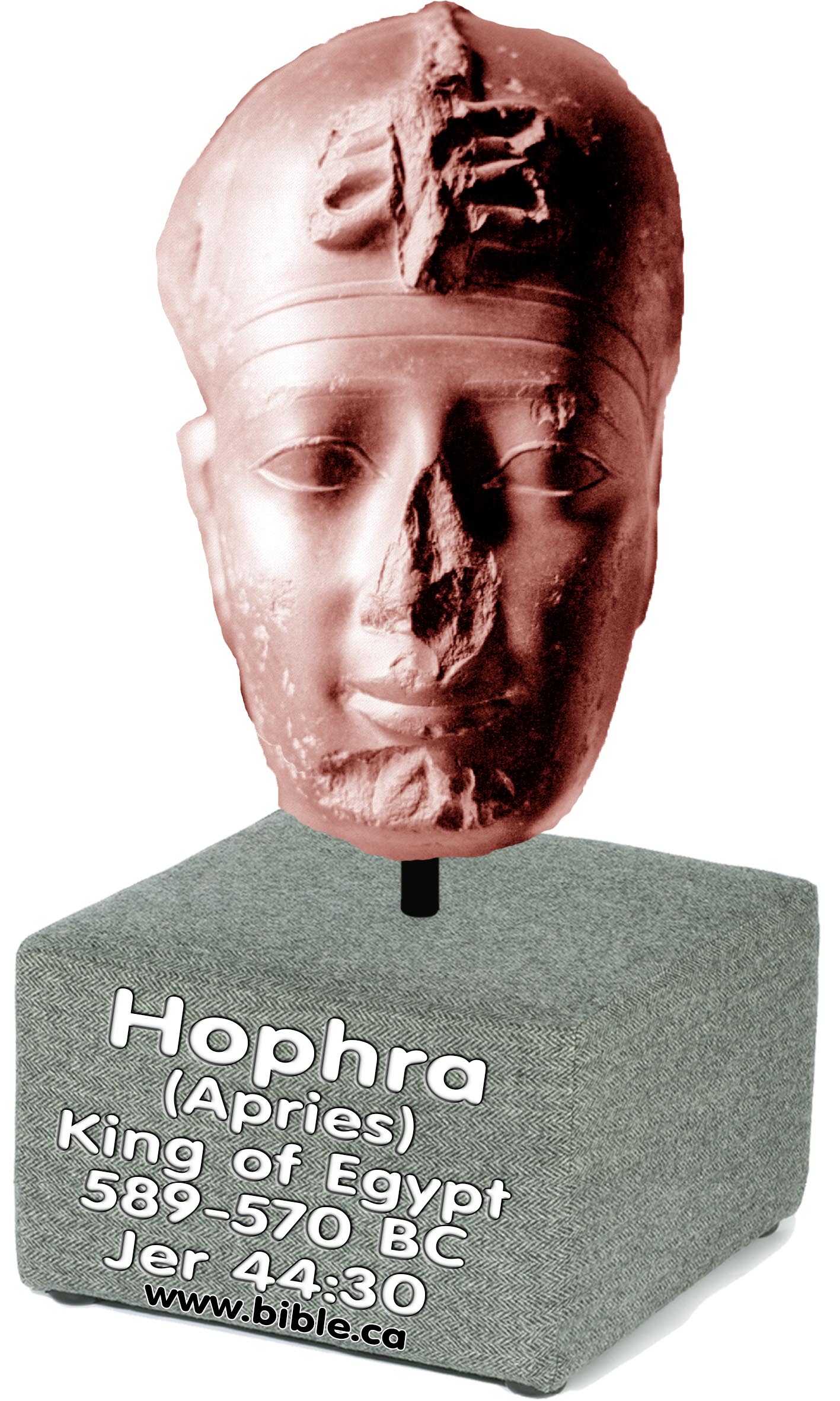
Hophra (Apries) |
Amasis II (Amoses) |
|
664-610 BC |
610-595 BC |
595-589 BC |
589-570 BC |
570-526 BC |
|
Victory Stele of Esarhaddon: 671 BC |
||
|
|
Victory Stele of Esarhaddon: 671 BC The victory Stele of Esarhaddon dates to 671 BC which is contemporary with Pharaoh Taharaqa (Isa 37:9) and Manasseh, king of Judah (695-642 BC) Several scriptures speak of Assyrian kings deporting Judeans with ropes attached to lip hooks and shackles. Outline: Victory Stele of Esarhaddon
|
|
|
Archeology of the Exodus |
||
|
|
Archeological evidence of the Exodus Survey of Archeological evidence from the recently translated Sinai inscriptions, stone carvings, stele and papyri. |
|
|
HEBREW: THE WORLD’S OLDEST ALPHABET |
||
|
|
The Four Hebrew Alphabet Scripts: Hebrew is the world’s oldest alphabet from which English is derived.
Its official! The world’s first authentic inscription that names Moses of the Exodus! |
|
|
|
|
|
Melqart Stele of Ben-Hadad II, king of Aram: 860-841 BC |
|
|
Melqart Stele of Ben-Hadad II Contemporary with Ahab, Naaman, Elisha, Hazael 1 Kings 20,22; 2 Ki 5-8
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bible Inscriptions of Shalmaneser III Ahab, Jehu, Omri, Ben-Hadad II, Hazael, Tyre, Sidon King of Assyria 858-824 BC |
||
|
Start here: Detailed outline on Shalmaneser III |
||
|
Start here: Detailed outline on Shalmaneser III |
||
|
Start here: Detailed outline on Shalmaneser III |
||
|
Start here: Detailed outline on Shalmaneser III |
||
|
|
|
|
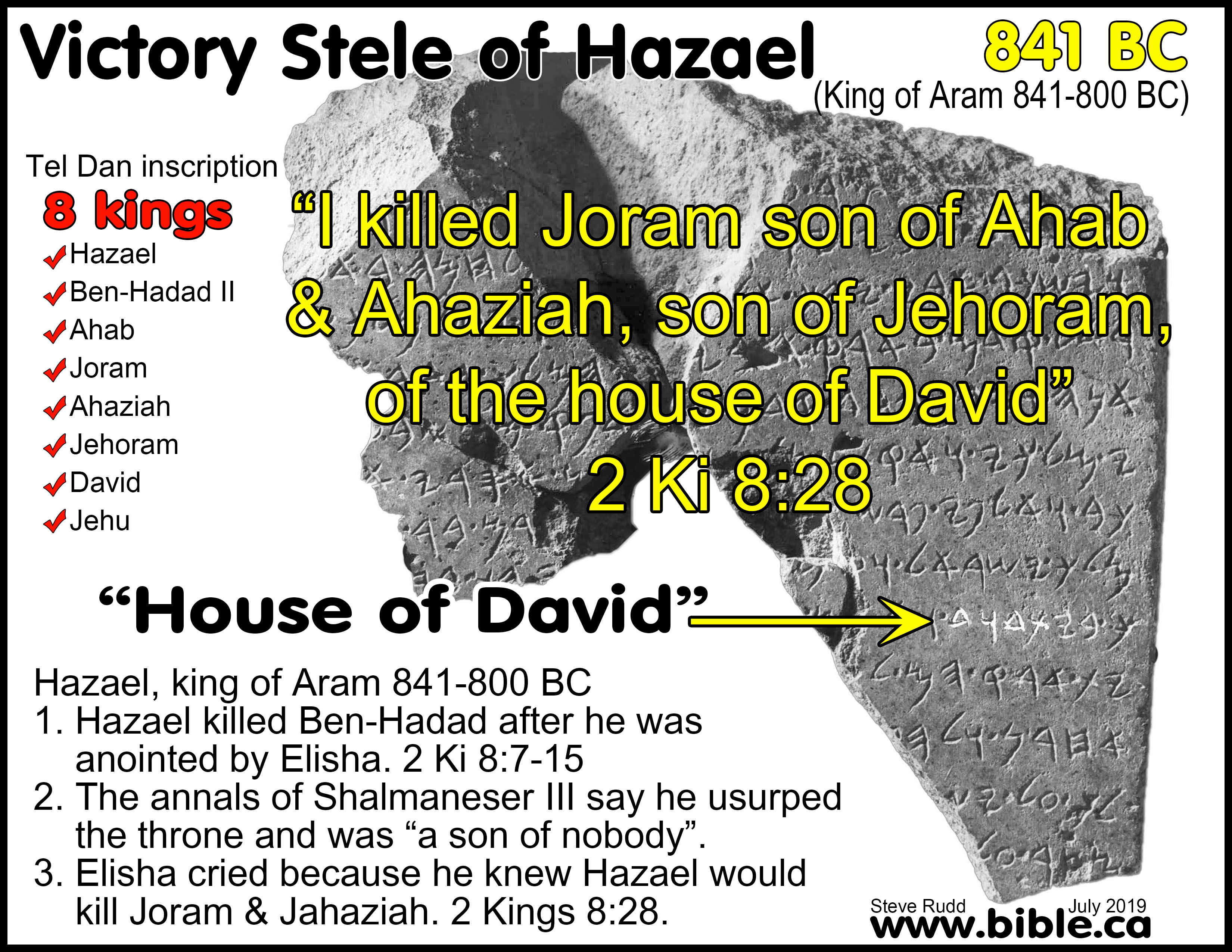
Stele of 841 BC: Hazael Stele and Mesha Stele |
|
|
Hazael Stele (Tel Dan Stele) |
Mesha Stele (Moabite Stone) |
|
“House of David” inscription
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stele of Adad-nirari III, king of Assyria: Joash, Omri, Ben Hadad III |
|
|
A collection of 6 stela, tablets and statues A stunning collection of six (6) stela, statues and inscriptions fully document how God used Assyrian king Adad-Nirari III, as the one who delivered Josiah, king of Israel, out of the hand of the Ben-Hadad III, king of Aram at Damascus in 2 Kings 13:4-5. 796 BC
Josiah, Omri, Ben-Hadad III Stela of Adad-Nirari III, King of Assyria (810-783 BC) |
|
|
|
|
|
2 Kings 13:5 |
||
|
"YHWH gave Israel King Jehoahaz & Joash (Israel) |
a deliverer King Adad-nirari III (Assyria) |
they escaped Aram" King Ben Hadad III (Aram) |
|
Conquest Stela of Adad-Nirari III (810 - 783 BC) Detailed outline on Adad-Nirari III . |
||
|
Religious and dynastic Stela of Adad-Nirari III (810 - 783 BC) |
||
|
|
|
|
Stele of Zakkur, king of Hamath: Hazael, Ben Hadad III |
|
|
Stele of Zakkur, king of Hamath A war between Hamath and Ben-Hadat III (Mari), son of Hazael, and a coalition of 17 kings. |
|
|
|
|
28 Elephantine Papyrus letters
Persian letters Dating to 471-410 BC
|
|
|
|
3 featured Elephantine papyrus 1. Temple of YHWH burned (Sanballat, Bagohi Governor) 2. Document of wifehood (bride price, divorce causes) 3. Passover regulations (unleavened wine and bread) |
|
|
|
|
Manuscripts of the Bible
New Testament and Old Testament manuscripts
|
|
|
|
Bible Manuscripts |
Scrolls, Codex, Papyrus, Vellum, Dead Sea scrolls The Bible is the most historically verified book on earth with over 5000 manuscripts and fragments. |
|
|
|
Septuagint scroll of the Greek Twelve Minor Prophets written in 50 BC
|
Dating to 50 BC, this is a Greek (Septuagint) translation of the 12 minor prophets by Jews before Christ was born. This proves that the Entire Old Testament (Tanakh) was translated into Greek before the Christian Era. The text reads essentially the same as the modern text we use (Masoretic) proving the Bible has not been lost, altered or corrupted over time. YHWH is written in Mosaic Hebrew as the name of God. Read full outline and see 5 ultra high resolution plates of the scroll. |
|
|
|
|
Septuagint LXX Fouad #266 (dated 100 BC) Deut 31:28-32:7 Commissioned by Ptolemy II (282BC)
YHWH (red) was added later in blank space left by scribes.
E-book outline on the Septuagint
“The Septuagint was Synagogue seed” See also: How the Septuagint gave birth to Synagogues in 280 BC |
|
|
DEAD SEA SCROLLS FROM QUMRAN |
|
||
|
Jewish Expectation of the Messiah in the Dead Sea Scrolls: Mt 2:23
Two different scrolls, Testimonia and Florilegium quote messianic Old Testament scripture in the fever of messianic expectation at the time of Christ. |
|
||
|
Dating to 30 BC, the famous Psalms scroll that highlights the feelings of the Jews while in sitting by the rivers in Babylonian after the captivity of 587 BC in Ps 137. It also demonstrates responsive singing in Ps 145 where the phrase “Blessed be Yahweh, and blessed be his name forever!” is added after each statement where is does not exist in the bible. This proves the first century singing style including the church, was responsive. |
|
||
|
Dating to 30 BC, this is the oldest extant copy of the book of Lamentations on earth that documents the feelings of the Jews in the aftermath of the Babylonian Captivity of 587 BC |
|
||
|
Beatitudes Dead Sea Scroll: 4Q525 Prototype of the Book of Revelation. Historical insight: Jesus patterned his beatitudes after the well-known poetic style of his day with 8 short beatitudes followed by an 9th longer one. Like saying, "knock, knock" or "Roses are Red…" today, everyone sitting on the north shore of the Sea of Galilee was familiar with the format and listened curiously to the Nazarene's own variation on the poetic form. Jesus used known cultural paradigms so his message was: revolutionary, relevant and refreshing. |
|
||
|
Songs of Sabbath Sacrifice Angelic Liturgy: 4Q402, MAS1K Prototype of the Book of Revelation. And First century Jewish song book. Historical insight: John patterned Revelation after the well-known apocalyptic genre of his day. Like saying, "knock, knock" or "Roses are Red…" today, the Christians in Jerusalem immediately recognized the format and read intently to this new variation of a well known poetic form. The H.S. used known cultural paradigms so John’s warning to flee Jerusalem, echoing Mathew 24 and Luke 21 was: revolutionary, relevant and authentic.
|
|
||
|
BM 10012 Lahun Egyptian Chronology Papyrus |
|
Heliacal rising of Sirius: 1830 BC El-Lahun Berlin Museum Papyrus 10012 and the 12th Dynasty, Year 7 of Pharaoh Sesostris III |
|
The Story of Sinuhe: |
|
And Edomite chief Jeush, son of Esau named in Gen 36:5,18 |
|
Sanballat bulla, papyri from the Cave of Wadi-Daliyeh: |
|
Wadi-Daliyeh and Sanballat II (408 BC) Sanballat II, son of the famous adversary of Nehemiah and is named in the papyri and sealed with his bulla. |
Steve Rudd: Contact the author for comments, input or corrections.