Solved: Chronology of Elijah and Elisha
Elisha as a Type of Christ
By Steven Rudd
Elijah as a Type of John the Baptist
A list of 40 similarities
Comparison Chart of Elisha/Christ Shadows, Types, Antitypes and similarities
1 Kings 17-2 Ki 10:10; 2 Chron 21:12; Mal 4:5;
Mt 11:14; 16:14;
Mt 17:3; 27:47-49; Lk 1:17; Jn 1:21-25; Rom 11:2; Jas 5:17
Edited by Julia Page
Updated December 2024
|
Quick links in this document: I. 40 ways Elisha as a type of Christ: Elijah as a type of John the Baptist II. Snapshots of 10 Bible kings and characters of the 9th century BC III. Notable Quotables from bible texts from 900-800 BC IV. Solved: Detailed Chronology of Elisha and Elijah V. Master List of 25 Wars of the 9th Century BC VI. A. Asa king of Judah: 911-870 BC VII. B. Asa and Josiah Parallels VIII. Kings of Aram IX. 25 Archeological confirmations of the Bible: inscriptions, stele |
See also:
Introduction:
1. How to teach this chronological outline and special features:
a. The detailed chronological table is your sequential guide that integrates bible readings, literary references, archeological finds and types/antitypes associated with each story.
b. Printing the entire outline on full colour 8.5x11 for each member is recommended.
c. The master map and Master chronological chart are best printed 11x17 full colour, double sided. One sheet with the map on one side and the chronological chart on the other. It needs to be large and in full colour. It makes a central references for dates and geography.
d. To prepare to teach this monograph read it thoroughly several times, look up all bible verses chronologically and study it for several weeks.
e. After teaching introductory material and acquainting the audience with the maps, archeological references etc, you can then move onto the main sequence of teaching the material.
f. A detailed chronological list of the life of Elijah and Elisha.
g. Archeological information from the inscriptions and stele of Assyrian Kings like Shalmaneser III give us additional information and confirm the historical accuracy of the Bible.
h. A list of 40 similarities between Elisha as a type of Christ and Elijah as a type of John the Baptist. These are included in green text in the chronology beginning with TYPE:
i. A list of 25 wars.
2. Elisha’s three prophet’s Schools:
a. In 1200 BC Deborah was judging Israel at her “tree” between Ramah and Bethel: "Now Deborah, a prophetess, the wife of Lappidoth, was judging Israel at that time. She used to sit under the palm tree of Deborah between Ramah and Bethel in the hill country of Ephraim; and the sons of Israel came up to her for judgment." (Judges 4:4–5)
b. In 1025 BC, David fled from Saul and went to Samuel’s prophet’s school called “Naioth” at Ramah: 1 Sam 19:18-20:1.
c. In 842 BC, the three prophet’s schools of Elijah: Gilgal, Bethel and Jericho. 2 Kings 2:1ff and 2 Kings 4:38
d. There seemed to be a regular “cycle” that Elijah and Elisha would travel between these cities of Ephraim.
e. The day Elijah is taken to heaven in a tornado (whirlwind) 50 prophets from these three prophet’s schools accompany Elijah and Elisha but wait on the western shore of the Jordan river.
f. Elisha replaces Elijah as the “master” of these three prophet schools.
3. The same crossing point on the Jordan River with parted waters:
a. See also detailed outline on the Jordan River and this crossing/baptism site of John the Baptist.
b. Joshua’s crossing point of the Jordan on dry ground in 1406 BC during the conquest where the waters parted when the priest’s feet touched the water.
c. Elijah parted the Jordan and crossed on dry ground at same spot as Joshua: 2 Kings 2:8
d. Elisha parted the Jordan and crossed on dry ground at same spot as Joshua: 2 Kings 2:14
e. John Baptized Jesus in AD 29, at the same spot Joshua crossed in 1406 BC and Elijah and Elisha crossed in 842 BC: John 1:28
f. Jesus was baptized at the identical crossing point of Joshua, Elijah and Elisha.
g.
You can visit this exact place today in Israel and even
be baptized in the Jordan River for the remission of your sins and be born
again! (Mk 16:16; Acts 2:38; 22:16, Jn 3:3-5)

4. The confusion of duplicate and alternate names of kings of Judah and Israel for 50 years between 853-796 BC.
a. We have meticulously added “king of Judah or King of Israel” after each of these names to solve the confusion.
b. Not only do most of the kings have alternate names, but kings of Judah and Israel often ruled at the same time with the same names!
c. Ahaziah, Azariah were names of kings of Judah and Israel but not at the same time.
d. Jorah, Jehoram were names of kings of Judah and Israel at the same time.
e. Joash, Jehoahaz, Jehoash were names of kings of Judah and Israel at the same time.
5. The contrast, shock and awe of the 9th century BC (900-800 BC)
a. The 9th century BC is the golden age of the divided kingdom period of Judah and Israel.
b. The 9th century BC illustrates in the clearest terms, God’s blessings for worshipping him and God’s destruction for worshipping idols.
c. The contrast of living conditions during this most ideal period of the two kingdoms of Judah and Israel are clear and plain for all to see.
d. While Israel is suffering famine, Judah enjoys prosperity
e. There were 25 Bible related wars between Judah, Israel, Philistines, Assyria, Aram, Edom, Moab, Ammon, Ethiopia, Arabs
f. While Israel is practicing idolatry, Judah is worshipping YHWH.
g. While Baasha is building pagan altars in Israel, Asa is tearing them down in Judah: 2 Chronicles 14:3
h. While Baasha is having huge pagan festivals, Asa is exuberantly celebrating Passover and Pentecost to worship YWHW: 2 Chronicles 15:10
i. While Elijah is killing the 850 false prophets of Baal on Mt. Carmel and flees Jezebel queen of Israel to Mt. Sinai thinking he is the last righteous man on earth, Jehoshaphat king of Judah sends priests and Levites with the Book of the Law of Moses to be read in all his cities and to teach the people about YHWH.
j. While Jehorah king of Israel is teaching his subjects to sin in idol worship, Jehoshaphat is personally teaching the law of Moses from city to city in the last 5 years of his life in an effort to bring his subjects closer to the one true God.
k. While Ahab is building the House of Baal for his pagan wife Jezebel, Elijah restored the altar of YHWH on Mt. Carmel for this great showdown with the prophets of Baal.
l. While Israel is almost under constant attack from outside nations, Judah enjoys only two wars with the Ethiopians and Aram during a 56-year time of peace (900-844 BC) during the reigns of Righteous Asa and his son Jehoshaphat. In both cases God fought the victory for Judah!
m. While God is working to defeat the kings of Israel (except when it bugged God that Ben-Hadad II said YHWH was only the “God of the hills or valleys”), he is working to defeat the enemies of Judah.
n. While Elijah and Elisha, who work exclusively within the then northern tribes of Israel, perform some of the greatest miracles in the Old Testament, the Israel and Aramean kings who were often first-hand witnesses to the miracles, continue to practice Baal worship.
6. God rebukes Judean kings for their allegiances with Israel and Aram
a. In 896 BC, Asa throws Hanani the prophet into prison because he condemned him for relying on Ben-Hadad I to defeat Baasha: (2 Chr 16:7-10)
b. In 853 BC, Jehoshaphat is condemned by the prophet Jehu son of Hanani over his allegiance with Ahab against Ben-Hadad II in the Battle of Ramoth-Gilead I in spite of the fact that Micaiah son of Imlah, predicts the death of Ahab:1 Ki 22: 2 Chr 19:2; Why Jehoshaphat would ask for a true prophet of YHWH, then reject the word of God that it will be defeated and therefore DO NOT GO, is a mystery. With the rebuke of Jehu, Jehosphaphat got the message it was wrong to join the battle after the prophet Micaiah said don’t go, so he begins to personally travel Judea, teaching the law to restore his subjects to true worship of YHWH.
c. In 852 BC, God destroys the armies of Moab and Ammon in the Battle of Engedi for Jehoshaphat, who then enters into a joint ship building venture at Ezion-Geber with Ahaziah, the wicked king of Judah. Eliezer immediately condemns Jehoshaphat for this ship building allegiance and God destroys the ships either by the Edomites (who were getting increasingly hostile) or a natural storm: 2 Chron 20:36
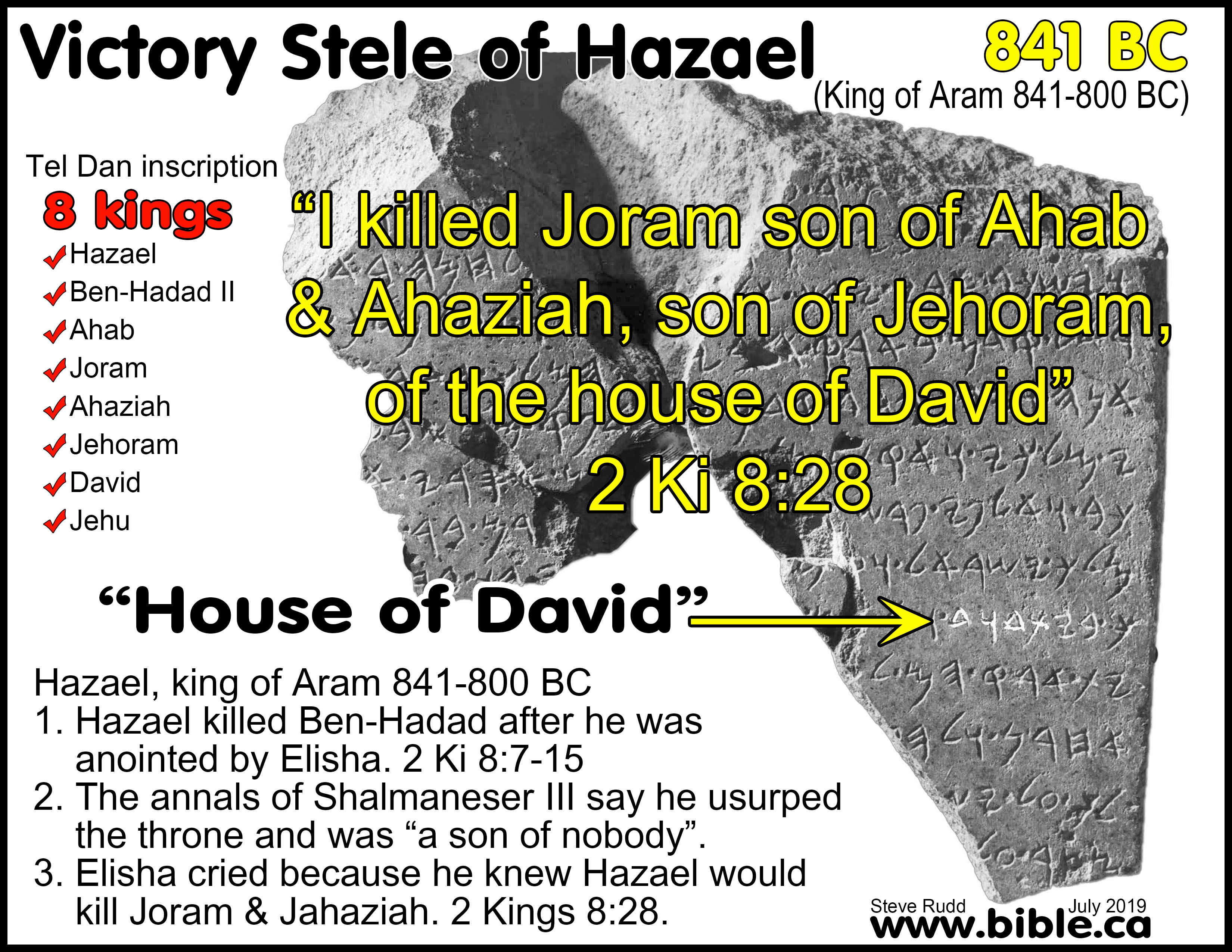
d. In 849 BC, in the Battle of Moab I, during the first year of the 7-year drought, Jehoshaphat king of Judah, Jehoram king of Israel and Edom decide to attack Mesha king of Moab. Moab had rebelled after the death of Ahab king of Israel in 853 BC. Jehoshaphat had just defeated Moab in 852 BC in the Battle of Engedi when Moab and Ammon attacked Judah in the Battle of Engedi three years earlier. Jehoshaphat was rebuked twice for his allegiances with two previous kings of Israel (Ahab in the battle of Ramoth-gilead I and Ahaziah in the shipbuilding venture at Ezion-geber). It is a puzzle why Jehoshaphat would AGAIN agree to another military cooperation with a wicked king of Jehoram of Israel who 7 years later issues a death edict against Elisha in 843 BC. Perhaps Jehoshaphat’s victory against Moab in the Battle of Engedi gave him confidence that such an allegiance was approved by God. Elisha is called and he miraculously commands the holes of the land of Edom to be filled with water during drought and they win the battle against Mesha. Later in 841 BC, Mesha will record this successful rebellion against Judah in his famous “Mesha Stone.”
7. Prayer is as powerful as all the miracles of Elijah: This is a key application point regarding Elijah, John the Baptist and Christians today.
a. John the Baptist performed no miracles, yet he came in the “spirit and power” of Elijah:
i. How can John come in the “power of Elijah” if he never performed any miracles?
ii. “It is he who will go as a forerunner before Him in the spirit and power of Elijah, to turn the hearts of the fathers back to the children, and the disobedient to the attitude of the righteous, so as to make ready a people prepared for the Lord.”" (Luke 1:17)
iii. "Many came to Him and were saying, “While John performed no sign, yet everything John said about this man was true.”" (John 10:41)
iv. John was a prophet, yet performed no miracles.
b. Elijah performed some of the greatest miracles in the Bible like raising the dead, yet was a man with a nature exactly like ordinary ungifted Christians, who also can accomplish much through prayer:
i. "The effective prayer of a righteous man can accomplish much. Elijah was a man with a nature like ours, and he prayed earnestly that it would not rain, and it did not rain on the earth for three years and six months. Then he prayed again, and the sky poured rain and the earth produced its fruit." (James 5:16-18)
c. Christians today, who are not empowered with supernatural gifts of the Holy Spirit as Elijah was, can like John the Baptist, “come in the spirit and power of Elijah” through prayer.
i. Christians today function as prophets like John the Baptist and Elijah.
ii. We have the inspired scripture of the Holy Spirit that informs us of the mind of God and future events like the second coming, judgement, heaven and hell.
iii. Christians are commanded to preach the gospel of salvation to every creature and pray in the spirit and power of Elijah. (Mt 28:18)
d. Jesus told his disciples that they would “perform greater WORKS than Christ”
i. "Believe Me that I am in the Father and the Father is in Me; otherwise believe because of the works themselves. “Truly, truly, I say to you, he who believes in Me, the works that I do, he will do also; and greater works than these he will do; because I go to the Father." (John 14:11–12)
ii. These greater works were not miracles, but like John the Baptist, were proclaiming salvation and repentance to lost souls.
e. Evangelism by Christians today is truly a greater work than all the miracles of Elijah and Christ combined.
i. Miracles do not save souls
ii. Telling someone about Jesus so they believe does save souls.
iii. The gospel is simple: Believe, repent, confess and be immersed in water for the remission of your sins and become born again!
f. Prayer is more powerful and more important than any miracle.
8. 10 miracles of resurrection from the dead in the Bible: 3 Old Testament, 7 New Testament
a. Elijah: Widow of Zarephath's Son: 1 King 17:17-24
b. Elisha: Shunammite Woman's Son: 2 Kings 4:18-37
c. Elisha: Israelite Man who touched the bones of Elisha: 2 Kings 13:20-21
d. Widow of Nain's only Son: Luke 7:11-17
e. Jairus' only Daughter: Mark 5:38-43; Luke 8:40-56
f. Lazarus: John 11:1-44
g. Jesus Christ: Matthew 28:1
h. Jerusalem saints when Christ died: Matthew 27:50-54
i. Tabitha or Dorcas: Acts 9:36-42
j. Eutychus: Acts 20:7-12
9. Elisha’s “double measure” or double portion of Elijah’s ministry is seen in:
a. Elijah had a 35-year ministry and Elisha 70 year ministry.
b. Elijah predicted a 3.5-year drought and Elisha predicted a 7-year drought.
c. Elijah raised one person from the dead and Elisha two: 1 Ki 17:17; 2 Ki 4:32; 13:20. One man was raised by the dead body of Elisha (who had the double portion) but many were raised by the dead body of Jesus who had the messianic double portion: Mt 27:52. Then at the last day every man on earth will be raised from the dead.
d. The Messiah (like Elisha) was prophesied to get double portion: Isa 61:1-7. In Luke 4:18-28, Jesus quoted Isa 61 in his hometown synagogue in Nazareth and said He had fulfilled it. The Jews would know the text well and recognize that Jesus was claiming the “double portion” of Elisha upon himself in performing miracles. They requested miracles to prove his claim. Jesus’ answer by directly named Elijah and Elisha in Lk 4:25-27. There is a direct tie between the double portion of Elisha and Jesus.
10. See also: Excavations at Tel Rehov where the Elisha ostraca was found in 2013 AD
|
|
I. 40 ways Elisha was a type of Christ: Elijah as a type of John the Baptist:
A. Use of the number 3 ½, 3 and 7 by Elijah and Elisha as source for Daniel and Revelation
1. It is no coincidence that the church began exactly “7” weeks after Christ was crucified: Passover to Pentecost was 49 days or 7 x 7 weeks.
2. Messianic connection of Elijah and Elisha:
a. Elijah was seen as a central messianic figure and this may be where the first century Jews traced the a major part of the meaning of the numbers 3 ½, 3 and 7 back to.
b. Elijah starts his ministry at the beginning of his 3.5-year famine in 870 BC and is taken up to heaven in a whirlwind at the end of Elisha’s 7-year famine in 842 BC.
c. See Messianic expectation in Dead Sea Scrolls and Judean coins.
d. We know that in the Dead Sea Scrolls, the Songs of Sabbath Sacrifice and the books of Daniel and Revelation, that the numbers “times, time and half a time” (3.5 years) 3 and 7 are widely used.
3. The number 3.5: Elijah, Daniel, Revelation:
a. Elijah had a 35-year ministry from 877 – 842 BC. (Elisha had a 70-year ministry because of his double measure)
b. The famous drought of Elijah was 3 ½ years: Jas 5:17
c. The number 3.5: and Daniel/Nero/Revelation: Daniel 7: 3.5 years: The 1260 Days, 42 months: Nero persecution: 64-68 AD
d. The number 3.5: and Daniel/Christ’s Resurrection: Daniel 9: 70x7: The 70 weeks, 490 years ending at Resurrection of Christ
e. The number 3.5: and Daniel/Christ’s Ministry: Daniel 12: 3.5 years + 1 month: The 1290 Days, 43 months: Ministry of Christ up to between the Ascension and Pentecost.
4. The number 3:
a. Elijah “stretched himself upon the child three times” when he raised the widow of Sidon’s son from the dead: 1 Kings 17:21
b. Elijah poured four buckets of water over the alter, three times, for a total of 12 buckets of water: 1 Kings 18:34
c. The three prophet’s schools of Elijah: Gilgal, Bethel and Jericho. Three times Elijah told Elisha to remain in at each prophet’s school: 2 Kings 2:1ff and 2 Kings 4:38
d. Men searched in vain for three days for Elijah after he was taken to heaven: 2 Kings 2:17
e. Ahaziah sent three sets of 50 solders to arrest Elijah, who killed the first two sets of 50: 2 Ki 1:9-13
5. The number 7 in the Elijah and Elisha stories:
a. Elijah prayed 7 times for it to rain again after the 3.5-year drought: 1 Kings 18:43
b. Elisha performed the miracle of water on the 7th day of the Battle of Moab in 849 BC: 2 Kings 3:9-20
c. Elijah was told by God that there were 7000 righteous men in addition to himself: 1 Kings 19:18 (Ahab defeated Ben-Hadad II with an army of 7000 men: 1 Kings 20:15)
d. Elisha raised the Shunammite’s son from the dead by laying on him 7 times and the boy sneezed 7 times before he woke up. Note. There is a variant between the MT and the LXX. The LXX is probably correct:
i. LXX: "He turned and went in the house up and down. He ascended and bent down over the boy for seven times, and the boy opened his eyes." (4 Kingdoms 4:35, Greek Septuagint, LXX)
ii. MT: “Then he returned and walked in the house once back and forth, and went up and stretched himself on him; and the lad sneezed seven times and the lad opened his eyes." (2 Kings 4:35, Hebrew Masoretic Text, MT)
e. Elisha told Naaman to dip in the Jordan 7 times: 2 Kings 5:10
f. Elisha caused a 7-year drought (double portion of Elijah’s power: 3.5-year drought of Elijah = 7 year drought of Elisha): 2 Kings 8:1
g. Elisha’s ministry lasted exactly 70 years from 865-795 BC
6. The “three-day pattern” of the Old Testament:
a. Abraham received Issac back from the dead: Genesis 22:3-4 + Hebrews 11:17-19
b. Cupbearer and baker restored and executed in 3 days: Genesis 40:9–22
c. In 1446 BC during the Exodus, darkness fell upon Egypt for three days: Exodus 10:22
d. Three days of preparation at Mt. Sinai to receive law on Pentecost: Exodus 19:10–14
e. An animal was killed for the salvation of the people, but the body had to be burned on the third day: Leviticus 7:17–18
f. Three days preparation to prepare to cross the Jordan: Joshua 1:11; 3:2
g. Sinful Benjamin defeated on the third day: Judges 20:30
h. Jonah raised from the dead after three days: Jonah 1:17
i. David learned he was king three days after Saul Died: 2 Samuel 1:1–2
j. Rehoboam asked the people to return after three days: 1 Kings 12:12
k. Hezekiah healed on the third day at the temple: 2 Kings 20:4-13
l. “He will raise us up on the third day: Hosea 6:1–2
m. In 515 BC the temple was completed on the third day of the month: Ezra 6:15
n. In 483 BC Esther prayed three days for deliverance: Esther 4:16–17
o. Palm Sunday and Triumphal entry one week before crucifixion: Luke 13:32
p. Jewish expectation was that Jesus would rise from the dead on the third day: Luke 24:21
7. The number 3, 7 and 10 in Daniel used in important historical events:
a. 10 kings – 3 kings = 7 kings: A core of 7 kings is computed when 3 kings are “subdued/removed” from the 10 kings: "‘As for the ten horns, out of this kingdom ten kings will arise; and another will arise after them, and he will be different from the previous ones and will subdue three kings." (Daniel 7:24)
b. "Then Nebuchadnezzar was filled with wrath, and his facial expression was altered toward Shadrach, Meshach and Abed-nego. He answered by giving orders to heat the furnace seven times more than it was usually heated." (Daniel 3:19)
c. Nebuchadnezzar was stricken in a mental illness for 7 years: "“Let his mind be changed from that of a man and let a beast’s mind be given to him, and let seven periods of time pass over him." (Daniel 4:16)
8. Seven miraculous signs predicted by Jesus fulfilled in AD 65-66 at Jerusalem as recorded by Josephus Wars 6:288-300 and Eusebius Ecclesiastical History 3.8.1–6. It is noteworthy that these miraculous signs began on Passover AD 65 and ended on Passover AD 66, which was 18 days before the First Jewish War was started when the local Greeks in Caesarea defiled the Jewish Synagogue by placing an upside down clay jar of dead birds that had been sacrificed to idols on the entrance to the Synagogue.
a. SIGN #1: YEAR LONG COMET: Duration: 1 year. Wed, 3rd April AD 65 (6 days before Passover) to Passover, Mon 28th April AD 66.
b. SIGN #2: YEAR LONG SWORD STAR: Duration: 1 year. Wed, 3rd April AD 65 (6 days before Passover) to Passover, Mon 28th April AD 66.
c. SIGN #3: TEMPLE/ALTAR SHINE: Duration: Lasted ½ hour at 3 AM on Wednesday, 3rd April AD 65 (6 days before Passover)
d. SIGN #4: COW’S VIRGIN BIRTH OF LAMB: Duration: On Passover (Nisan 14) Tuesday, 9th April AD 65
e. SIGN #5: EASTERN IRON GATE OPENED ON ITS OWN: Duration: On Passover (Nisan 14) Midnight Tuesday, 9th April AD 65
f. SIGN #6: ANGELIC CHARIOT ARMIES: Duration: Before sunset, Thursday, 16th May AD 65
g. SIGN #7: EARTHQUAKE & MYRIAD OF ANGEL VOICES IN TEMPLE: Duration: Pentecost: After sunset, Sunday, 2nd June AD 65
9. The First Jewish War lasted almost exactly 7 years: AD 66-73
a. Started at Caesarea synagogue: Sabbath 17th May AD 66.
b. Ended with mass suicide at Masada: Monday 12th April AD 73.
10. The number 70:
a. The Babylonian captivity lasted 70 years from 605-536 BC.
b. The 70 weeks of Daniel lasted from 458 BC – AD 33.
11. The messianic relationship between the numbers 3.5 and 7
a. Elisha had a “double portion” of power of Elijah: 2 Kings 2:9
b. Isaiah 61:1-7 speaks of a double portion of the Messiah and his followers.
c. Elijah predicted a 3.5-year drought
d. Elisha predicted a 3.5 x 2 = 7-year drought: 2 Kings 8:1
12. Elijah and Elisha are the primary source for the numbers 3, 3.5, 7 in ancient Jewish writings:
a. The book of Daniel: see details on Daniel draws on the numbers from Elijah.
b. First century Jewish synagogue songbook: see details: Songs of Sabbath Sacrifice. Every synagogue used a songbook called “The Songs of Sabbath Sacrifice” that used the number 7 to the point of obsession. It was a collection of 13 songs, sung acapella, (because instrumental music was banned in synagogues), consecutively in a 13-week cycle. The outstanding feature of its use of the number 7 was as familiar to every first century Jew as “Jesus Loves Me” is to Christians today. There are striking similarities with Revelation including the extensive use of the number 7, seven-word descriptors (Rev 5:12 = DSS 4Q403 Frag. 1 i:4), war in heaven, myriads of angels singing in heaven, a climactic detailed throne scene complete with thunder and lightning, detailed description of a beautiful, multi-coloured heavenly temple, judgement followed by silence in heaven, Rev 8:1 = DSS 4Q400 Frag. 1 ii:1-21.
c. As early as 90 BC, Dead Sea Scroll 11QMelchizedek is evidence that the Jews were long using the number 7 as an organizing numeric framework in their literature.
13. The number 7 in the Amarna Tablets: 1406-1350 BC
a. The 382 Amarna tablets are cuneiform clay letters of correspondence between the city-kings being conquered by Joshua and the pharaoh in Egypt. The Amarna letters are one of the greatest archeological proofs that the history of the Bible and the conquest under Joshua of the promised land is true. The story of the conquest of Joshua as told by the Amarna Tablets.
b. Many of the Amarna tablets record a ritual of showing submission to pharaoh, king of Egypt. The Canaan city-state kings would stand before pharaoh then fall to the ground on their face, then rolling over on their back, then get up and repeat it a total of 7 times. This shows that the number 7 had special divine meaning among the pagan gentiles at the time of the Exodus.
c. Amarna Letter EA215: Storyline: Bayawa begs pharaoh to send Yanhamu, an Egyptian ambassador or provincial overseer, to help within the year or the entire land of Canaan will be lost to the Hebrews. Full text translation of Tablet: "To the king, my lord, my Sun, my god: Message of Bayawa, your servant. I fall at the feet of the king, my lord, my Sun, my god, 7 times and 7 times, on the stomach and on the back. 9–17 Should Yanḫamu not be here within this [year, a]ll the lands are [lo]st to the ˓Apiru. So give life to your lands." (The Amarna letters, W. L. Moran, introduction, 1992 AD, EA 215)
d. Amarna Letter EA288: Full text translation of EA288: "Say [t]o the king, my lord, [my Su]n: [M]essage of ˓Abdi-Ḫeba, your servant. I fall at the feet of the king, my lord, 7 times and 7 times. 5–10 Behold, the king, my lord, has placed his name at the rising of the sun and at the setting of the sun. It is, therefore, impious what they have done to me. Behold, I am not a mayor; I am a soldier of the king, my lord. 11–15 Behold, I am a friend of the king and a tribute-bearer of the king. It was neither my father nor my mother, but the strong arm of the king that [p]laced me in the house of [my] fath[er].3 16–22 [ … c]ame to me. … [ … ]. I gave over [to his char]ge 10 slaves. Šuta, the commissioner of the king, ca[me t]o me; I gave over to Šuta˒s charge 21 girls, [8]0 prisoners, as a gift for the king, my lord. 23–28 May the king give thought to his land; the land of the king is lost. All of it has attacked me. I am at war as far as the land of Šeru and as far as Ginti-kirmil. All the mayors are at peace, but I am at war. 29–33 I am treated like an ˓Apiru, and I do not visit the king, my lord, since I am at war. I am situated like a ship7 in the midst of the sea. 34–40 The strong hand (arm) of the king took the land of Naḫrima and the land of Kasi, but now the ˓Apiru [Hebrews] have taken the very cities of the king. Not a single mayor remains to the king, my lord; all are lost. 41–47 Behold, Turbazu was slain in the city gate of Silu [Shiloh]. The king did nothing. Behold, servants who were joined to the ˓Api[r]u smote Zimredda of Lakisu [Lachish], and Yaptiḫ-Hadda was slain in the city gate of Silu [Shiloh]. The king did nothing. [Wh]y has he not called them to account? 48–53 May the king [pro]vide for [his land] and may he [se]e to it tha[t] archers [come ou]t to h[is] land. If there are no archers this year, all the lands of the king, my lord, are lost. 54–61 They have not reported to the king that the lands of the king, my lord, are lost and all the mayors lost. If there are no archers this year, may the king send a commissioner to fetch me, me along with my brothers, and then we will die near the king, our lord. 62–66 [To] the scribe of the king, my lord: [Message] of ˓Abdi-Ḫeba, (your) servant. [I fa]ll a[t (your) feet]. Present [the words that I hav]e offered to [the king, my lord]: I am your servant [and] your [s]on." (The Amarna letters, W. L. Moran, introduction, 1992 AD, EA 288)
|
Amarna Letter EA288 Storyline: Abdi-Heba, mayor of Jerusalem warns Pharaoh that all cities except his are lost to the Hebrews (Habiru). Strangely, he asks why pharaoh allowed Zimredda of Lachish and Yaptiḫ-Hadda of Shiloh (Silu) to be killed without taking any action. Zimredda is a traitor! The Hebrews killed Zimredda of Lachish, even though he had supplied them with oil and food. Likely, Zimredda was discovered to be a traitor to the Hebrews. He was likely claiming submission to both Egypt and Joshua, while seeking total control for himself. Paraphrase of Tablet: "From Abdi-Heba, mayor of Jerusalem to king Pharaoh: The Habiru have taken all the cities. Not a single mayor remains. Turbazu & Yaptih-Hadda were slain in the city gate of Silu (Shiloh). Habiru killed Zimredda of Lachish The king did nothing. Why?" |
14. So, when Revelation was structured around the numbers 3 ½ and 7, Revelation had the “feel” of “Jewish literature” that the Jews in Jerusalem would be familiar with. This enhanced their acceptance of the message in Revelation to “leave it all behind” and flee Jerusalem or die.
15. Elijah and Elisha are the primary source for the numbers 3, 3.5, 7 in
a. First century Jewish synagogue songbook: see details: Songs of Sabbath Sacrifice
b. the book of Daniel: see details on Daniel
c. the Book of Revelation: see details on Revelation
B. 40 Antitypes of Elijah and John the Baptist, Elisha and Jesus:
|
40 Antitypes Elijah and John the Baptist Antitypes Elisha and Jesus Antitypes |
|||||
|
|
Elijah |
Elisha |
John (Baptist) |
Jesus |
|
|
1. Hairy with leather belt |
"They answered him, “He was a hairy man with a leather girdle bound about his loins.” And he said, “It is Elijah the Tishbite.”" (2 Kings 1:8) |
2 Kings 9:11 described the prophet who anointed Jehu king of Israel as “crazy or mad”. This indicates that like Elijah and John the Baptist, the prophets from the three prophet’s schools of Gilgal, Bethel and Jericho dressed in peculiar ways that were contrary to the norms of the day. Jehu answered, “You know very well the man and his talk” meaning, his odd dress was a known way the prophets dressed during this period. |
Mt 3:4; Zech 13:4. John the Baptist dressed in a costume worn by prophets of the 9th century BC. His dress was as distinct, recognizable and historic as the Jewish Hassidic dress today. The black hats, shirt and pants and beards with a long twirl of hair is a costume that imitates 18th century Germany. |
||
|
2. Prophet |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Luke 24:19 |
|
|
3. Double portion |
Single portion |
Double portion: 2 Kings 2:9 |
|
Christ and his disciples had double portion: Isaiah 61:1-7. Cf. Luke 4:18-28 |
|
|
4. Control over weather |
3.5 year drought: 1 Ki 17; Lk 4:25; James 5:17 |
Elisha caused 7 year famine: 2 Ki 6:31; 8:1-3 (double portion of Elijah’s 3.5 year famine) |
|
Calmed the storm |
|
|
5. Asks gentile woman for water |
1 Kings 17:10 |
|
|
Jn 4:7 Samaritan |
|
|
6. Multiply bread “How can we feed so many… They shall eat and have some left over” |
1 Kings 17:14 |
2 Kings 4:42–44 |
|
Luke 9:17; John 6:9,13 |
|
|
7. Raise dead |
1 Kings 17:17 |
2 Kin 4:34 |
|
Mark 5:39 Only daughter |
|
|
8. Raised only son of widow |
1 Kings 17:17 |
|
|
Luke 7:12 |
|
|
9. “How long will you hesitate between two opinions?” |
1 Kings 18:21 (also said by Joshua 24:15) |
|
|
money or God Matt 6:24 |
|
|
10. “God who answers by fire” |
1 Kings 18:24, 38 |
|
|
Acts 2 Jesus sends tongues of fire |
|
|
11. 12 pitchers of water over the 12 stones of the altar |
1 Kings 18:34 |
|
|
12-18 measures of water into 6 stone vessels John 2:7-9 |
|
|
12. Miracle of supernatural transportation |
1 Kings 18:46 |
|
|
John 6:21 |
|
|
13. Enemies issue death threat |
Jezebel issues death threat to Elijah: 1 Ki 19:2 |
Ben Hadad II tries to arrest or kill Elisha: 2 Ki 6:12-14; Jehoram king of Israel issued death threat because Elisha caused 7 year famine: 2 Ki 6:31; 8:1-3 (double portion of Elijah’s 3.5 year famine) |
|
John 19:7 |
|
|
14. Flees into wilderness after death threats |
1 Kings 19:3 |
|
|
John 11:53-54 |
|
|
15. Angels served him in wilderness when physically exhausted |
1 Kings 19:5-7 |
|
|
Matthew 4:11 |
|
|
16. fasted for 40 days in wilderness |
Angel gave food at the start of 40 days then he didn’t eat until reaching Sinai: 1 Kings 19:5-7 |
|
|
Fasted for 40 days then angels gave him food: Matthew 4:2 |
|
|
17. Angels encouraged him in time of emotional distress |
1 Kings 19:7 |
|
|
Luke 22:43 |
|
|
18. Plowing then say goodbye to family |
|
Elijah found Elisha plowing who asked to say goodbye: 1 Kings 19:20–21 |
|
Jesus did not accept Elisha’s excuse: Luke 9:61-62 |
|
|
19. Murder to gain possession of vineyard |
Naboth’s vineyard: 1 Kings 21 |
|
|
Parable of the vineyard: Luke 20:14–15 |
|
|
20. Pay debt |
|
With oil 2 Kings 4:1-7 |
|
With coin from mouth of fish |
|
|
21. Others prepared an upper room |
|
In Shunem: 2 Ki 4:10-11 |
|
In Jerusalem for Jesus to sleep and the last supper: “Where is MY guest room”: Mk 14:13-15 |
|
|
22. Miraculous conception |
|
Conception after menopause: “she has no son and her husband is old”: 2 Ki 4:13-17 |
Conception after menopause: Luke 1:7,18 |
Virgin birth: Mt 1:18 |
|
|
23. Person falls at feet crying, wanting miracle, disciples of master dissuade |
|
Shunamite falls at feet of Elisha over dead son, Gehazi objects: 2 Kings 4:27 |
|
Jarius falls at feet of Jesus, disciples object: Mark 5:22,35 Mary at feet of Jesus over Lazarus who died: John 11:32 |
|
|
24. Disciples of the master could not perform miracle |
|
Gehazi unable to raise child from dead, Elisha raises child: 2 Kings 4:29-37 |
|
Jesus’ disciples unable to cure boy: Mt 17:14–20 |
|
|
25. Immune from poison |
|
2 Ki 4:38-41 eat poisonous stew |
|
Mark 16:18 |
|
|
26. Leprosy cured at a distance without physical contact |
|
Naaman cured by Elisha who struck dishonest Gehazi with leprosy 2 Ki 5:27 |
|
Mt 8:1-13: Jesus cured the leper: Mt 8:2; Mk 14:3. Then in Mt 8:8, Jesus cured the centurion’s servant at a distance. Also the ten lepers and the Samaritan leper: Luke 17:17 |
|
|
27. Lying, faithless, traitorous money-grubbing, materialistic, servant for silver money/coins |
|
Gehazi betrayed for silver money: 2 Ki 5:23; lied: 2 Ki 5:25, money: 2 Ki 5:26. The first coins in Israel date to 378 BC. Gehazi’s leprosy: Gehazi was faithless and unable to raise the dead Shunammite’s son. Gehazi was a faithless traitor, liar and thief just like Judas. |
|
Judas betrayed for silver coins: Mt 26:15-16 |
|
|
28. Defy gravity |
|
Iron axe-head float: 2 Kings 6:6 |
|
Jesus and peter walk on water: Matthew 14:25-29 |
|
|
29. Opened eyes of disciples to see glory of God on the mountain |
|
Elisha showed angel chariots that protected the mountain: 2 Ki 6:17 |
|
Jesus showed glorified Moses and Elijah on the mountain: Mt 17:1-3; 72,000 angels protect Jesus: Mt 26:53 |
|
|
30. Sinful captives released in mercy when others wanted to condemn and kill |
|
Jehoram, king of Israel wanted to kill the “blinded Aram army” but Elisha set them free: 2 Ki 6:22 |
|
Woman caught in adultery: Jn 8:11; “he has sent me to proclaim release to the captives, and recovery of sight to the blind” Lk 4:18 |
|
|
31. Disguised himself so not to be recognized |
|
One of the prophets asked to be injured then covered his eyes for Ahab: 1 Kings 20:41 |
John was “not recognized” as Elijah: Mt 17:12 |
Road to Emmaus: Luke 24:16; Mary: John 20:14; Disciples on beach: Jn 21:4 |
|
|
32. Three sets of men sent, first two killed |
|
Ahaziah king of Israel sent three sets of 50 to Elisha: 2 Kings 1:9-16 |
|
Parable of the landowner: Matthew 21:34-37 |
|
|
33. Same starting location of ministry at Jordan |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
34. Itinerant miracle workers |
Yes |
Yes |
No. yet John came in the “power and spirit of Elijah” Jn 10:41 |
Yes |
|
|
35. Blindness, sight |
|
Strikes Aram army with blindness |
|
Restores site of blind man: Jn 9 |
|
|
36. Angels at disposal |
|
The Battle of Dothan: 2 Ki 6:17. |
|
Jesus at the temptation: Mt 4:6-7. Jesus at his arrest could have called 12 legions of angels: Mt 26:53. |
|
|
37. Joshua’s crossing point of the Jordan on dry ground |
Elijah crossed on dry ground at same spot as Joshua: 2 Kings 2:8 |
Elisha crossed on dry ground at same spot as Joshua: 2 Kings 2:14 |
John Baptized at the same spot Joshua crossed: John 1:28 |
Jesus was baptized at the crossing point of Joshua, Elijah and Elisha. You can visit this exact place today in Israel. |
|
|
38. Living waters |
|
Elisha purified the death of the spring waters of Jericho into waters of life forever: 2 Kings 2:21. Today you still drink of this same pure spring water at Jericho. |
|
Living water at Samaritan well: John 4:10; John 7:38 |
|
|
39. Dead raised at death |
|
Body thrown onto Elisha’s bones was resurrected: 2 Ki 13:21; Josephus Ant. 9.183 |
|
Jerusalem saints resurrected from tombs at death of Christ: Mt 27:52 |
|
|
40. Life and death |
Elijah confronted Ahab of his sin and a death decree was issued. 1 Ki 20:42-43. |
|
John the Baptist confronted Herod of his sin Mt 14:4 and was beheaded then buried in Samaria beside Ahab’s ancient palace at the Byzantine church of John the Baptist that marks the original grave spot. |
|
|
|
|
II. Ten Character Snapshot of Kings of the 9th century BC:
1. Unrebukable fair-weather Asa: 911-870 BC: Asa was one of the most righteous kings in the Bible in removing idolatry from Judah and promoting true faith in YHWH. When God rebuked him for his allegiance with Ben-Hadad I (king of Aram) to stop Baasha from fortifying Ramah, he imprisoned the prophet 894 BC and stopped seeking God’s input. 22 years later, Jehu contracted a severe disease in his feet in 872 BC and still would not seek Gods help and healing. As long as God was praising his good works, Asa was happy but the first time he is criticized he gives up on God and gets angry.
2. Ahab the Wicked Wuus: 873-853 BC: That Ahab was a wicked wuus is best illustrated in his sulking over Naboth’s vineyard then walking joyfully on its earth without regard that a man was murdered. Ahab sulked when he couldn’t have a forbidden thing: Naboth’s vineyard. He built a house for Baal for his wicked, dominant wife Jezebel while she murdered the righteous prophets of YHWH. Ahab defeated Ben-hadad II in the Battle of Aphek and should have killed him, but instead believed his crocodile tears and let the Aramean king go with a worthless peace treaty, only to have this same king 3 years later kill Ahab in the Battle of Ramoth-gilead I. In that battle, Ahab the king disguised himself a commoner and that was one of his rare moments of truth.
3. Jezebel the pagan prostitute priestess: 873-841 BC: Jezebel is considered the most wicked woman in the Bible and is described three ways: “harlotries/prostitute, witchcrafts/sorcerer, prophetess/priestess”. (2 Kin 9:22; Rev 2:20). At her death she sat in her customary window in the tower of the city gate of Jezreel and painted her eyes and fixed her hair. (2 Kings 9:30). This picture of her as representing herself as “the woman in the window” was no mistake. Many archeological examples of the “woman in the window” as the Egyptian goddess Isis and the cult of Astarte, have been found both in Samaria and in Assyria of the same exact period. Ahab built his ivory palace in Samaria and the Phoenician ivory motifs excavated from the palace where Jezebel lived, invoke of the goddess Astarte who also lived in a Phoenician palace as a sacred prostitute. Jezebel’s actions of painting her eyes while she sat in the window was a failed ploy to save her life by reminding everyone of her high spiritual status and the thought of harming her would create fear of drawing the wrath of the pagan gods. That Ahab married Jezebel, the daughter of Ethbaal king of the Sidonians was strictly forbidden by Moses: Deut 7:1-5. As soon at Ahab became king, Jezebel built a “House of Baal” and started killing the true prophets of God. Elijah was alive to witness this and begins his ministry by predicting a 3.5 year famine. At the end Elijah kills Jezebels 850 false prophets on Mt. Carmel. "Surely there was no one like Ahab who sold himself to do evil in the sight of the LORD, because Jezebel his wife incited him." (1 Kings 21:25)
4. Evangelist Jehoshaphat: 872-848 BC: Jehoshaphat took “great pride” in spiritual matters and sent his royal officials, priests and Levites from city to city with a copy of the Book of the Law of Moses. (2 Chron 17:6-10) This is the same Book of the Law that was lost then found by Josiah in 623 BC. Amazingly, this all was happening in Judah at the same time Elijah claimed at Mt. Sinai to be the “last believer on earth” after he killed the 850 false prophets of Baal on Mt. Carmel. Jehoshaphat’s major failure was his allegiance with Ahab after Micaiah the prophet said “don’t go” or Ahab will die in the Battle of Ramoth-gilead I in 853 BC. (2 Chronicles 18:1-34; 1 Ki 22:28; Josephus Antiquities 8.414) Josephus said it was Naaman who was previously cured of Leprosy who shot the arrow that killed Ahab. The prophet Jehu son of Hanani condemns Jehoshaphat for his allegiance with Ahab in the Battle of Ramoth-gilead I. Unlike Asa, “Evangelist Jehoshaphat”, takes the rebuke of God to heart and during the last 5 year of his life, Jehoshaphat travels personally throughout Judah personally teaching them the bible. During this time, we know that Jehoram his son was coregent with him for these last 5 years of his life. While Jehoram takes over the official state matters and Jehoshaphat in his old age becomes an itinerant evangelist of the Mosaic Law from city to city. (2 Chron 19:4-11) It is no coincidence that the 7 year drought of Elisha begins the year Jehoshaphat dies in 849 BC. (2 Kings 8:1-2)
5. The conversion of Pagan Naaman, army general of Ben-Hadad II of Aram: 854 BC: In 854 BC, Naaman comes to Elisha to be healed of his leprosy. Naaman said, “If not, please let your servant at least be given two mules’ load of earth; for your servant will no longer offer burnt offering nor will he sacrifice to other gods, but to the LORD." (2 Kings 5:17) Perhaps Naaman was familiar with: "‘You shall make an altar of earth for Me, and you shall sacrifice on it your burnt offerings and your peace offerings, your sheep and your oxen; in every place where I cause My name to be remembered, I will come to you and bless you." (Exodus 20:24). Notice the direct parallel with Mt 8:1-13, where Jesus cured the leper, then cured the centurion’s servant at a distance.
6. Carnally obedient Jehu: 841-814 BC: Jehu was obedient to God in killing Jehoram king of Israel, Ahaziah king of Judah, Jezebel and prophets of Baal to selfishly secure his own throne. Although he “eradicated Baal from Israel” it was for carnal selfish reasons rather than faith. We know this because he continued to worship Jeroboam’s two golden calves at Bethel and Dan. So to Jehu, his pagan god of choice was a golden calf not Baal: 2 Kings 10:29-31
7. The conversion of Pagan Ben-Hadad II king of Aram (860-841 BC): 841 BC: In 850 BC, the king of Aram issued a death decree against Elisha in the Battle of Dothan because Elisha miraculously kept telling the top secret battle plans of Ben-Hadad II to Ahab king of Israel. He found Elisha in Dothan but his army was blinded, marched to Samaria, given food, then mercifully released. 8 years later in 842 BC, Ben-hadad II shows no mercy in sieging Samaria in the last year of a 7-year famine but is miraculously defeated by God. We do not know if he was injured in that battle or got sick, but within a year Ben-Hadad was on his death bed and who does he ask to see? The same Elisha whom Ben-Hadad tried to kill 9 years earlier. The same Elisha who miraculously told his secret battle plans to Ahab. For the next 24 hours until Hazael killed him, Ben-Hadad II may have been praising and thanking YHWH for the false hope generated through the lie of Hazael that he would live. At least his last 24 hours were filled with peace, joy and thankfulness. While the kings of Israel were seeking the worthless gods of Aram for advice, Ben-Hadad II realized at the end of his life that YHWH, the God of Elisha, was the one true God.
8. Filicidal Idolatrous Queen Athaliah (aka Jezebel #2): 841-835 BC: Athaliah was the daughter of Ahab and Jezebel of Israel. Athaliah was the wife of Jehoram, the son of Jehoshaphat. Athaliah was the mother of wicked King Ahaziah, whom Jehu killed and the granddaughter of Omri king of Israel. (2 Ki 11:1-3; 2 Chro 22:10-12) Like Jezebel her mother, Athaliah built a house of Baal, except this was in Judah. (2 Chro 23:17) She stole the sacred things from Solomon’s temple and used them for Baal worship: 2 Chron 24:7. Like Jezebel, Athaliah was a ruthless murderer of all her own royal children just to secure the throne for herself for six short years. The influence that Athaliah was the granddaughter of pagan king Omri of Israel outweighed her marriage to a king of Judah (Jehoram). She was killed by the righteous high priest Jehoiada who became the spiritual force in young Joash’s life as king of Judah.
9. Joash: The faithless teenager who was forced to attend church by his parents but was never obedient from the heart: Joash (Jehoash) king of Judah: 835-796 BC: In 835 BC Joash became king at age 7 but it was the high priest, Jehoiada, who ran the kingdom of Judah as a shadow monarch until the king grew up. He immediately got the people of Judah to recommit their lives to YWHW and tore down the House of Baal that Queen Athaliah had built. In 815 BC High Priest Jehoiada persuades Joash king of Judah to repair Solomon’s temple but the priests are simply not interested in repairing the temple and any monies collected are stolen by the priests for themselves: 2 Ki 12:1; 2 Chro 24:1. The following year in 814 BC, Jehoiada collects money in a secure chest to pay workers to fix Solomon’s temple: 2 Ki 12:6; 2 Chron 24:6. When the people of Judah learn that their money will actually be spent on repairing the temple, rather than enriching the corrupt temple priests, they give generously. Workers are hired and the temple is restored. But when Jehoiada the high priest dies in 808 BC at age 130 years old (2 Chro 24:15-16) the wicked temple priests convince Joash king of Judah, now 34 years old, to abandon Solomon’s temple and begin worshipping idols. God sends many prophets to warn the king and in 805 BC the prophet Zechariah, (son of Jehoiada the high priest who recently died) condemns king Joash for idolatry. Joash king of Judah murders the prophet rather than listen to him: 2 Chr 24:20 (see also Mt 23:35). In the Battle of Gath (804 BC) Hazael king of Aram attacks and captures Gath then threatens Jerusalem. Joash king of Judah pays Hazael tribute: 2 Ki 12:17;2 Chr 24:23. However, Joash king of Judah is severely injured in the Battle of Gath and is bedridden until death 8 years later: 2 Chro 24:25. In 796 BC the sickly and bedridden Joash is murdered by his Ammonite and Moabite servants in his bed: 2 Chro 24:25; 2 Ki 12:20. Joash therefore, was like a teenager who obediently followed the religion of his parents (Jehoiada, the high priest) until he grew up and was then free to become what he really was: an idol worshipper. Very few kings of Judah were involved in restoring Solomon’s temple. It is shocking that the newly restored temple was abandoned the year Jehoiada died. Many teens attend church with their parents until they become independent and are “out on their own”. Those who were obedient from a true heart of inward faith follow the proverb, “train up a child in the way he should go, and when he is old, he will not depart” (Proverbs 22:6). Those who are merely “putting on a show” because they “have to go to church” while living at home, are "A foolish son is a grief to his father and bitterness to her who bore him." (Proverbs 17:25).
10. Schizophrenic double-minded Amaziah king of Judah: 796-767 BC: Although Edom had been controlled by Judah as far back as king David, in 847 BC Edom rebelled and appoints a king for themselves: 2 Chro 21:8-10. In 793 BC (54 years after Edom rebelled) Amaziah king of Judah wanted to bring Edom once again into submission. In spite of the many warnings from God to form no allegiances with Israeli kings (10 northern tribes) Amaziah hires 100,000 Israeli warriors and pays them 1 talent of silver each for a total of 100,000 talents of silver. However God sends a prophet who condemns the alliance and assures defeat if he proceeds. Amaziah heeds the warning from God and dismisses the warriors, telling them to keep their pay. God tells Amaziah not to worry about the lost money because, “The LORD has much more to give you than this.” (2 Chro 25:9) Jesus tells us to give up the riches of this world for the greater riches of heaven! The 100,000 Israeli mercenaries are insulted and proceed to loot Judean cities and kill 3000 Judeans on route home to Samaria. In the Battle of Kadesh Barnea (793 BC), Amaziah attacks Edom in the “valley of salt” which is located at the south end of the Salt Sea, then travels south to capture the city of ancient Kadesh Barnea (Petra), which at this time was called “Sela”. Shockingly, Amaziah brings back and worships the gods of Edom: 2 Chro 25:14. God sends a prophet to Amaziah and says, “Why have you sought the gods of the people who have not delivered their own people from your hand?” (2 Chr 25:15). Instead of snapping to his senses, Amaziah threatened to kill the prophet of God. (This is exactly what Asa king of Judah had done in 894 BC when he threw Hanani the prophet into prison for condemning Asa for relying on Ben-Hadad I to defeat Baasha king of Israel. 2 Chr 16:7-10) Three years later in 790 BC, Amaziah king of Judah was still angry that the 100,000 soldiers had looted the cities of Judah and killed 3000 Judeans. In schizophrenic reasoning, he figured if God condemned the alliance with idol worshipping Israel to defeat Edom, he would surely defeat Israel, in spite of the fact that he is now also worshipping the idols of Edom! Amaziah king of Judah is not only defeated in the Battle of Beth Shemesh he is captured by Joash king of Israel who proceeds to tear down 225 meters of the walls of Jerusalem, loot Solomon’s temple and the King’s palaces. Joash releases Amaziah after taking several hostages to assure safe passage home to Samaria. Amaziah appoints his son Uzziah as coregent king of Judah in 790 BC after the devastating loss in the Battle of Beth Shemesh. From that point forward Amaziah was under the condemnation of God and for the next 15 years he was finally forced to flee Jerusalem to Lachish because his own staff conspired against him. He was captured at Lachish and killed and lost his soul to the devil. The life of double-minded Amaziah with his delusional schizophrenic reasoning is truly a puzzle.
|
|
III. Notable Quotables from 900-800 BC:
1. 896 BC: Asa’s great prayer at Meresha when he faced an army of 1 million from Ethiopia: "Then Asa called to the Lord his God and said, “Lord, there is no one besides You to help in the battle between the powerful and those who have no strength; so help us, O Lord our God, for we trust in You, and in Your name have come against this multitude. O Lord, You are our God; let not man prevail against You.”" (2 Chronicles 14:11)
2. 896 BC: Just after Asa defeated the 1-million-man army from Ethiopia: "Now the Spirit of God came on Azariah the son of Oded, and he went out to meet Asa and said to him, “Listen to me, Asa, and all Judah and Benjamin: the Lord is with you when you are with Him. And if you seek Him, He will let you find Him; but if you forsake Him, He will forsake you. “For many days Israel was without the true God and without a teaching priest and without law. “But in their distress they turned to the Lord God of Israel, and they sought Him, and He let them find Him. “In those times there was no peace to him who went out or to him who came in, for many disturbances afflicted all the inhabitants of the lands. “Nation was crushed by nation, and city by city, for God troubled them with every kind of distress. “But you, be strong and do not lose courage, for there is reward for your work.” Now when Asa heard these words and the prophecy which Azariah the son of Oded the prophet spoke, he took courage and removed the abominable idols from all the land of Judah and Benjamin and from the cities which he had captured in the hill country of Ephraim. He then restored the altar of the Lord which was in front of the porch of the Lord. He gathered all Judah and Benjamin and those from Ephraim, Manasseh and Simeon who resided with them, for many defected to him from Israel when they saw that the Lord his God was with him." (2 Chronicles 15:1–9)
3. 872 BC: "It came about, as though it had been a trivial thing for him to walk in the sins of Jeroboam the son of Nebat, that he married Jezebel the daughter of Ethbaal king of the Sidonians, and went to serve Baal and worshiped him." (1 Kings 16:31)
4. 868 BC: Note: Elijah’s great showdown on Mt. Carmel happened in Israel as this happened in Judah: "Jehoshaphat took great pride in the ways of the LORD and again removed the high places and the Asherim from Judah. Then in the third year of his reign he sent his officials, Ben-hail, Obadiah, Zechariah, Nethanel and Micaiah, to teach in the cities of Judah; and with them the Levites, Shemaiah, Nethaniah, Zebadiah, Asahel, Shemiramoth, Jehonathan, Adonijah, Tobijah and Tobadonijah, the Levites; and with them Elishama and Jehoram, the priests. They taught in Judah, having the book of the law of the LORD with them; and they went throughout all the cities of Judah and taught among the people. Now the dread of the LORD was on all the kingdoms of the lands which were around Judah, so that they did not make war against Jehoshaphat." (2 Chronicles 17:6–10)
5. 867 BC: "Elijah came near to all the people and said, “How long will you hesitate between two opinions? If the LORD is God, follow Him; but if Baal, follow him.” But the people did not answer him a word." (1 Kings 18:21)
6. 867 BC: The God Who answers by fire: “Then you call on the name of your god, and I will call on the name of the LORD, and the God who answers by fire, He is God.” And all the people said, “That is a good idea.”" (1 Kings 18:24)
a. Moses on Sinai: "And to the eyes of the sons of Israel the appearance of the glory of the Lord was like a consuming fire on the mountain top. Moses entered the midst of the cloud as he went up to the mountain; and Moses was on the mountain forty days and forty nights." (Exodus 24:17–18)
b. “For the LORD your God is a consuming fire, a jealous God." (Deuteronomy 4:24)
c. Nadab and Abihu: Lev 10:1-3
d. Korah’s Rebellion: Numbers 16:35
e. Complaint about manna: Numbers 11:1-6
f. "Sinners in Zion are terrified; Trembling has seized the godless. “Who among us can live with the consuming fire? Who among us can live with continual burning?” He who walks righteously and speaks with sincerity, He who rejects unjust gain And shakes his hands so that they hold no bribe; He who stops his ears from hearing about bloodshed And shuts his eyes from looking upon evil; He will dwell on the heights, His refuge will be the impregnable rock; His bread will be given him, His water will be sure." (Isaiah 33:14–16)
g. Destruction of Solomon’s temple and Jerusalem in 587 BC: "In fierce anger He has cut off All the strength of Israel; He has drawn back His right hand From before the enemy. And He has burned in Jacob like a flaming fire Consuming round about." (Lamentations 2:3)
h. Pentecost: Tongues of Fire: Acts 2:1-4
i. "for our God is a consuming fire." (Hebrews 12:29)
7. 867 BC: Miracles confirm who is speaking truth from God: "At the time of the offering of the evening sacrifice, Elijah the prophet came near and said, “O LORD, the God of Abraham, Isaac and Israel, today let it be known that You are God in Israel and that I am Your servant and I have done all these things at Your word. “Answer me, O LORD, answer me, that this people may know that You, O LORD, are God, and that You have turned their heart back again.” Then the fire of the LORD fell and consumed the burnt offering and the wood and the stones and the dust, and licked up the water that was in the trench. When all the people saw it, they fell on their faces; and they said, “The LORD, He is God; the LORD, He is God.”" (1 Kings 18:36-39)
8. 854 BC: The conversion of Naaman: "When Naaman [healed of Leprosy after dipping 7 times in Jordan] returned to the man of God with all his company, and came and stood before him, he said, “Behold now, I know that there is no God in all the earth, but in Israel; so please take a present from your servant now.” But he said, “As the LORD lives, before whom I stand, I will take nothing.” And he urged him to take it, but he refused. Naaman said, “If not, please let your servant at least be given two mules’ load of earth [sacred ground of YHWH]; for your servant will no longer offer burnt offering nor will he sacrifice to other gods, but to the LORD. “In this matter may the LORD pardon your servant: when my master goes into the house of Rimmon to worship there, and he leans on my hand and I bow myself in the house of Rimmon, when I bow myself in the house of Rimmon, the LORD pardon your servant in this matter.” He said to him, “Go in peace.” So he departed from him some distance." (2 Kings 5:15–19)
9. 853 BC: Jehoshaphat personally goes from city to city in Judah teaching the Law of the Lord in order to turn back and restore the people to God. He also appointed judges in the land in all the fortified cities of Judah, city by city. He said to the judges, "So Jehoshaphat lived in Jerusalem and went out again among the people from Beersheba to the hill country of Ephraim and brought them back to the Lord, the God of their fathers. He appointed judges in the land in all the fortified cities of Judah, city by city. He said to the judges, “Consider what you are doing, for you do not judge for man but for the Lord who is with you when you render judgment. “Now then let the fear of the Lord be upon you; be very careful what you do, for the Lord our God will have no part in unrighteousness or partiality or the taking of a bribe.”" (2 Chronicles 19:4–7)
10. 852 BC: Battle of Engedi: "Then Jehoshaphat stood in the assembly of Judah and Jerusalem, in the house of the LORD before the new court, and he said, “O LORD, the God of our fathers, are You not God in the heavens? And are You not ruler over all the kingdoms of the nations? Power and might are in Your hand so that no one can stand against You. “Did You not, O our God, drive out the inhabitants of this land before Your people Israel and give it to the descendants of Abraham Your friend forever? “They have lived in it, and have built You a sanctuary there for Your name, saying, ‘Should evil come upon us, the sword, or judgment, or pestilence, or famine, we will stand before this house and before You (for Your name is in this house) and cry to You in our distress, and You will hear and deliver us.’ “Now behold, the sons of Ammon and Moab and Mount Seir, whom You did not let Israel invade when they came out of the land of Egypt (they turned aside from them and did not destroy them), see how they are rewarding us by coming to drive us out from Your possession which You have given us as an inheritance. “O our God, will You not judge them? For we are powerless before this great multitude who are coming against us; nor do we know what to do, but our eyes are on You.” All Judah was standing before the LORD, with their infants, their wives and their children." (2 Chronicles 20:5–13)
11. 853 BC: A wife has great influence over her husband:
a. "Surely there was no one like Ahab who sold himself to do evil in the sight of the LORD, because Jezebel his wife incited him." (1 Kings 21:25)
b. "An excellent wife, who can find? For her worth is far above jewels. The heart of her husband trusts in her, And he will have no lack of gain. She does him good and not evil All the days of her life." (Proverbs 31:10–12)
c. "An excellent wife is the crown of her husband, But she who shames him is like rottenness in his bones." (Proverbs 12:4)
d. "House and wealth are an inheritance from fathers, But a prudent wife is from [ie. She is obedient to God] the LORD." (Proverbs 19:14)
e. "The wise woman builds her house, But the foolish tears it down with her own hands." (Proverbs 14:1)
12. 850 BC: "One of his servants said, “No, my lord, O king; but Elisha, the prophet who is in Israel, tells the king of Israel the words that you speak in your bedroom.”" (2 Kings 6:12)
13. 859 BC: A single holy man among sinners is a powerful force of God: "Elisha said, “As the LORD of hosts lives, before whom I stand, were it not that I regard the presence of Jehoshaphat the king of Judah, I would not look at you nor see you [king Joram of Israel]." (2 Kings 3:14)
14. 793 BC: Battle of Kadesh Barnea: "Moreover, Amaziah assembled Judah and appointed them according to their fathers’ households under commanders of thousands and commanders of hundreds throughout Judah and Benjamin; and he took a census of those from twenty years old and upward and found them to be 300,000 choice men, able to go to war and handle spear and shield. He hired also 100,000 valiant warriors out of Israel for one hundred talents of silver. But a man of God came to him saying, “O king, do not let the army of Israel go with you, for the Lord is not with Israel nor with any of the sons of Ephraim. “But if you do go, do it, be strong for the battle; yet God will bring you down before the enemy, for God has power to help and to bring down.” Amaziah said to the man of God, “But what shall we do for the hundred talents which I have given to the troops of Israel?” And the man of God answered, “The Lord has much more to give you than this.”" (2 Chronicles 25:5-9)
15. 793 BC: After winning Battle of Kadesh Barnea: "Now after Amaziah came from slaughtering the Edomites, he brought the gods of the sons of Seir, set them up as his gods, bowed down before them and burned incense to them. Then the anger of the Lord burned against Amaziah, and He sent him a prophet who said to him, “Why have you sought the gods of the people who have not delivered their own people from your hand?” As he was talking with him, the king said to him, “Have we appointed you a royal counselor? Stop! Why should you be struck down?” Then the prophet stopped and said, “I know that God has planned to destroy you, because you have done this and have not listened to my counsel.”" (2 Chronicles 25:14-16)
|
|
IV. Solved: Detailed Chronology of Elisha and Elijah: 873 – 795 BC
A. Keys to decoding and solving the elusive chronology of Elijah and Elisha:
1. “The chronology of the stories of Elijah is extremely difficult to reconstruct.” (Kingdom of priests, Eugene Merril, p362)
2. The “Pre-Bible” beginning of Elijah’s 35 year ministry was in 877 BC when Omri built his palace in Samaria. The Bible recorded ministry begins in 870 BC when the 3.5-year drought coincides with the death of Asa king of Judah. This was also two years after Ahab builds the House of Baal for Jezebel in 872 BC.
a. Elisha with his 70-year ministry, had a double portion of Elijah who from scripture, had a 28 year ministry, but we would expect it to be 35 years.
b. Elijah storms onto the pages of the Bible “out of nowhere” in the great 3.4-year drought in 870 BC but it is clear he had been active before this.
c. It was likely the condemnations of Elijah against the Baal worship of Ahab and Jezebel that triggered Jezebel to kill the prophets of YHWH and cause Elijah to warn of the famine if they did not repent.
d. Obadiah (master of Ahab’s house) had hid the prophets in caves when Jezebel tried to kill them. When Obadiah sees Elijah after the 3.5-year drought, he says, “Is this you, Elijah my master?” Elijah had been hidden away in Zarephath and Ahab was unable to find him. After not seeing Elijah for the entire duration of the drought, Obadiah’s statement proves Elijah had been recognized as a prophet long before the beginning of the drought.
e. When Ahab finally sees Elijah he says, “Is this you, you troubler of Israel?” but Elijah counters: “I have not troubled Israel, but you and your father’s house have, because you have forsaken the commandments of the Lord and you have followed the Baals”. Therefore it is clear that Elijah had been preaching against Ahab and Jezebel long before the 3.5-year drought.
f. Therefore the most logical time for the start of the public ministry of Elijah was when Omri built his palace in Samaria in 877 BC.
g. This means that Elijah was active in ministry a full 7 years (877 BC) before the first record in scripture where he proclaims the famine in 870 BC.
3. The annals stele of Shalmaneser III give a year by year diary of events and record several of the battles recorded in the Bible.
a. This provides a synchronism between the Bible chronology and Assyrian kings.
b. The two chronologies (Bible numbers and Assyrian annals) are in perfect harmony.
4. Reversing the order of chapters 20 and 21 in 1 Kings:
a. Reversing the order of 1 Kings 20 and 21 puts the murder of Naboth before the three Aram wars, which are now a single continuous unit.
b. “The Septuagint reverses 1 Kings 20 & 21. “The Greek [ie. Septuagint] arrangement is superior, however, because it keeps all the stories about Elijah and Ahab together.” [J. D. Shenkel, Chronology and Recensional Development in the Greek Text of Kings]. Burney concurs, stating that the Septuagint is “no doubt correct in placing this narrative immediately after ch. 19.” [C. F. Burney, Notes on the Hebrew Text of the Book of Kings, p210, 1903 AD] (New American Commentary, p 225, 1995 AD)
c. The Septuagint (LXX) was translated from the earliest Hebrew manuscripts in 280 BC.
d. The Masoretic Text (MT) of the Old Testament that underlies most of our Bibles dates to 1008 AD.
5. When was Elijah taken to heaven in a whirlwind?
a. To Letter of Elijah to Jehoram King of Judah dates to 845 BC: 2 Chron 21:12-15
b. The Holy Spirit is providing direct inspired information that Elijah was alive during the reign of Jehoram.
c. 845 BC is year three of the sole reign of Jehoram, providing enough time for Jehoram to murder the royal family and become settled in his position.
d. “Beyond his critiques of Ahab and Ahaziah in 1-2 Kings, there is one reference to Elijah by the Chronicler (2 Chron 21:12), which mentions a letter that he wrote to King Jehoram of Judah, indicting him for idolatry and murder; but this brief detail is not attested in the books of Kings, nor does it easily fit with the most widely accepted chronology, according to which Elijah would have died before Jehoram’s reign.” (Dictionary of the Old Testament, p251)
e. It is to me noted that while there is only one reference to Elijah in the book of Chronicles, there are zero references to Elisha.
f. We must take the letter of Elijah to Jehoram king of Judah as genuine and of primary significance in the chronology.
6. The Famine of 2 Kings 4:38: 855 BC
a. We have little information about this famine. It must have been localized to the Ephraim area that included Gilgal. Gilgal was in the Jordan valley near Jericho.
b. The chronological/geographical reference, “When Elisha returned to Gilgal” likely refers to the regular circuit that Elijah and Elisha would take between the three prophet’s schools of Gilgal, Bethel and Jericho.
c. Connecting the “return to Gilgal” in 2 Ki 4:38 as a narrative continuance of 2 Kings 2:1 is unlikely because the story of the miraculous conception of the Shunammite’s Son in and his death span 5 years in 2 Kings 4:18.
d. The letter of Elijah in 845 BC in 2 Chron 21:12 was written during a famine and Elijah was taken up to heaven in a whirlwind at the end of the 7-year famine when the rains returned and he crossed over at high water as a miracle, like Joshua.
e. After Elijah was taken to heaven, the narrative in 2 Kings 2:23-25 has Elisha first going to Bethel, then Mt. Carmel, then he “returned to Samaria” (the city). That Samaria is one of the home bases of Elisha in 842 BC makes perfect sense!
7. Jezebel kills the prophets shortly after Ahab became king but before the beginning of Elijah’s 3.5-year drought.
a. Elijah predicts the 3.5-year drought soon after Jezebel began killing the prophets.
b. Obadiah was Ahab’s “master of the house” who protected the prophets by hiding them in caves etc. from Jezebel.
c. Elijah was sent to Obadiah at the end of the 3.5-year drought at which time the great showdown between the 850 prophets of baal vs. Elijah on Mt. Carmel.
d. Elijah fled to Mt. Sinai at the end of the 3.5-year drought.
e. Therefore the 3.5-year drought dates to 870-867 BC
8. The miraculous conception of the Shunammite woman provides several critical chronological keys: 2 Kings 4:8
a. Early in Elisha’s mission, he frequently visits Shunem where a woman and her husband build an upper room for him to sleep in.
b. Elisha promises the Shunammite will conceive a child
c. The child grows to about age 5 and dies, then Elisha raises her from the dead.
d. Gehazi is involved with both the first miracles of Elisha (widow’s oil and Shunammite conception) and the healing of Naaman. Josephus said that it was Naaman who killed Ahab with an arrow in 853 BC. This is a double indication that Gehazi served 7 years after Naboth was executed but before Ahab died.
9. Synchronism: Elijah began his ministry with the prediction of a 3.5-year drought and ends his ministry at the end of a 7-year drought predicted by Elisha (double portion 3.5 x 2 =7).
a. Elisha had a double portion so 3.5 x 2 = 7 years.
b. Therefore, Elijah began at the start of a 3.5-year drought and ended at the finish of a 7-year drought.
10. Elijah’s flight from Mt. Carmel to Beersheba dates to 867 BC, and Mt Sinai.
a. After spending some time (6 months) at Beersheba, Elijah fled to Mt. Sinai in 866 BC and spent time (“abode”) there as well.
b. We expect Elijah spend an entire year at Mt. Sinai and the great “Elijah what are you doing here” happened in 865 BC.
11. Elijah anointed Elisha in 865 BC and functioned as the servant of Elijah “poured water on his hands” for 23 years.
12. The 7-year drought recorded in 2 Ki 8:1-3 was predicted by Elisha: 849-842 BC
a. This 7-year drought began when Elisha warned the Shunammite woman and her household to flee to Philistia.
b. Ben-Hadad II sieges the city of Samaria during the 7-year drought.
c. At the end of the drought Joram king of Israel is a death edict to Elisha, who caused the drought, (2 Ki 6:31) when Joram witnessed cannibalism of two women eating their children. The four lepers leave the city to find the Aram camp is abandoned and the entire city rushes out to get the food left in the camp.
d. This ends the 7-year famine in 842 BC
13. Elisha purifies the Jericho spring water and kills the 42 rebel youths immediately after Elijah went to heaven in the tornado in 842 BC
14. Anointing of Hazael happened in 841 BC, one year after the famine ended.
a. After the 7-year drought ends the woman returns to Israel and is introduced to Joran king of Israel by the leprous and defrocked Naaman in 841 BC, the same time that Elijah is at Damascus anointing Hazael. Notice Elisha was not present, but Hazael reported the events and miracles of Elisha to the king.
b. Notice “Then… Elisha went to Damascus to anoint Hazael”: 2 Kings 8:7
15. Elisha dies in 795 BC during the reign of Jehoash king of Israel (798-782 BC)
a. See outline on Ancient Jewish Tombs
b. In 795 BC Elisha was buried and placed in a tomb.
c. In Between 795-4 BC when another burial was taking place, the Aram army attacked so they threw the dead body into Elijah’s tomb to make a quick get-away.
d. When the dead body contacted the bones of Elisha, the man was resurrected.
e.
The timing on this final miracle “from the grave” of
Elisha may have been up to a year after he died. In the first century, Jews
would place a dead body on a rock platform inside a rock cut tomb that featured
finger-like sections called Koch (singular, also called Kokh or loculus). Most
ancient tombs featured many kochim (plural of Kokh, also called loculi). Here
is a first century tomb excavated by Associates of Biblical research under the
direction of Dr. Bryant Wood in the AD 2000 excavation season that featured 7
loclui:

f.
Here is the tomb complex at Mareshah in Israel with the
author sitting in the middle loculus:

g.
This is the first century tomb of Helena, Queen of
Adiabene and Edessa located in Jerusalem. It features body decay slabs (1 year
process), body fluid drains and many loculi in which to store the ossuary bone
boxes. They also had rolling stone doors and set seals to protect the contents
from tampering. The tomb of Helena is typical of the kind of tomb with rolling
stone that Jesus of Nazareth was buried in. He would have been placed on a
stone slab as pictured below wrapped in white linen cloth. They also had many
oil lamp niches in the walls for light.


h. See outline on Ancient Jewish Tombs
B. Detailed Chronology and Timeline of Asa, Elijah and Elisha: 911 – 767 BC
|
Chronological reading |
Event |
|
|
911 BC |
1 Ki 15:8-24; 2 Chro 14-16 |
Asa becomes the 3rd king of Judea (911-870
BC) when Abijah dies in 912t-911n (911 BC). See outline on Abijah
king of Judea, the good king who turned to the Dark Side. (Abijah: 1
Kings 15:1-7; 2 Chron 13:1-22) |
|
911 BC |
Adad-nirari I becomes king of Assyria (911-891 BC) in the 1st regnal year of Asa king of Judah. |
|
|
910 BC |
1 Ki 15:25-31 |
Nadab becomes 2nd king of Israel when Jeroboam dies (910-909 BC) in the 2nd regnal year of king Asa |
|
909 BC |
1 Ki 15:32-16:7 |
Baasha becomes the 3rd king of Israel when Nadab dies in the 3rd regnal year of king Asa |
|
906 BC |
2 Chron 14:1 |
Asa had ten years of no war: 906-895 BC in the 6th to 15th regnal years of Asa king of Judah. The ten years started in year 6, not at the beginning of Asa’s reign. |
|
900 BC |
Ben-Hadad I (Idri) becomes king of Aram (900-860 BC) in the 10th regnal year of Asa king of Judah. |
|
|
2 Chron 15:19 Double chronological dating |
10 years of peace end: “No war until 35th year” (Dynastic divided kingdom since death of Solomon) = 896 BC: 15th year Asa = 35th year since Rehoboam. The text uses double dating. Sometimes the narrative counts from the start of the divided kingdom (ie. 35th year: 2 Chron 15:19; 16:1) and sometimes from the start of Asa’s reign. (ie. 15th year: 2 Chron 15:10). The two dating systems point to the same year. We know this is the case because Baasha died in 886 BC, which was the 25th regnal year of Asa’s reign. This simple observation solves an apparent chronological contradiction that had stumped Bible students for centuries. Details: Chronology of Kings of Judah and Israel. |
|
|
896 BC Jan. |
2 Chron 14:9-15 |
Battle of Mareshah: Zerah, the 1-million-man Ethiopian army attacks Judah 15th regnal year of Asa in February of the year Asa’s Great prayer |
|
896 BC April |
2 Chr 15:1-15 |
Prophet Azariah encourages Asa after he defeated the 1 million Ethiopian army to “be strong and do not lose courage, for there is reward for your work” in the removing of Idols from Judah in the 15th regnal year of Asa king of Judah. |
|
896 BC May |
2 Chron 15:9-15 |
Asa Reforms: In May, Asa removes idols and hosts Covenant festival. Asa removes his own mother named Maacah as queen mother because of her idolatry in the 15th regnal year of Asa king of Judah. |
|
896 BC Nov. |
2 Chron 16:1 |
Fortification of Ramah: Baasha fortifies Ramah in November of the 36th year = 896 BC after Tishri. 16th regnal year Asa = 36th year of since Rehoboam. |
|
895 BC spring |
2 Chron 16:2-20 |
Asa makes a treaty with Ben Hadad I to defeat Baasha in the 16th regnal year of Asa king of Judah. |
|
895t BC Nov. |
2 Chron 16:4; 1 Ki 15:18-20 |
Battle of Naphtali: Ben Hadad 1st attacks Ijon, Dan, Abel-maim and all the store cities of Naphtali. 17th regnal year of Asa in November (post Tishri). |
|
895 BC Nov. |
1 Ki 15:18-20 |
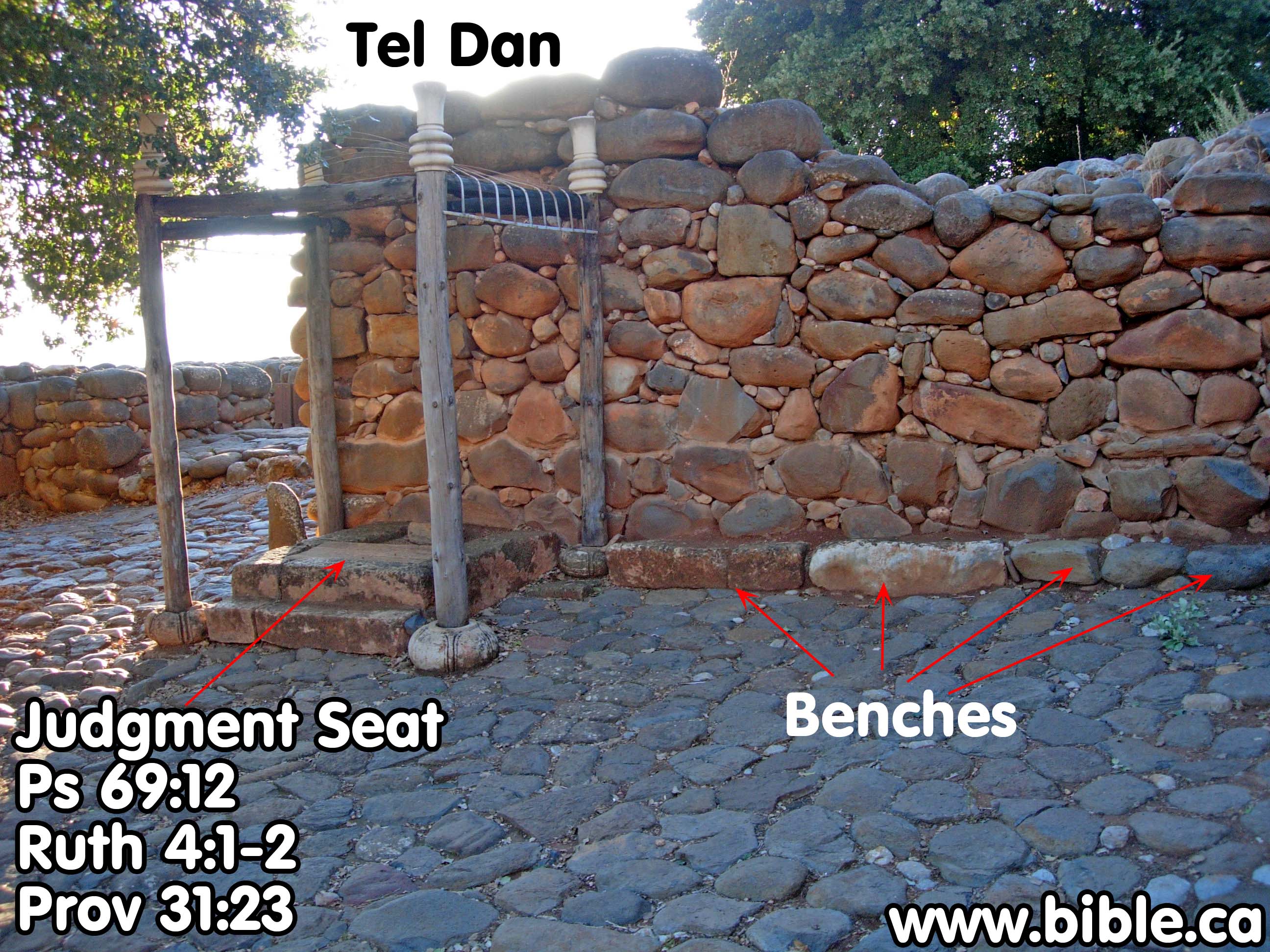
Tel Dan Archeological Destruction layer excavated from the Battle of Naphtali. The city gate at Dan with judgement seat and benches. Ancient city gates served 4 functions: J.E.W.S. J.E.W.S. = J = Justice E = Economics W = Worship S = Security |
|
894 BC spring |
1 Kings 15:22 |
Baasha withdraws from fortifying Ramah and Asa dismantles the fortifications at Ramah and builds Geba of Benjamin and Mizpah. |
|
894 BC spring |
2 Chron 14:6-7 |
Asa built fortified cities in Judah with walls, gates, bars. This statement is found in the introduction overview section of the story of Asa but chronologically occurred in 894 BC after Asa defeated the Ethiopians and Baasha king of Israel with the help of Ben-Hadad I. |
|
894 BC Nov. |
2 Chron 16:7 |
Prophecy of Hanani condemning Asa for his allegiance with Ben-Hadad I: “you have relied on the king of Aram and have not relied on the Lord your God”, whom Asa throws into prison in 894 BC (post Tishri) in Asa’s 18th regnal year. |
|
890 BC |
Tukulti-Ninurta II becomes king of Assyria (890-884 BC) in Asa’s 22nd regnal year |
|
|
885 BC |
1 Ki 16:1-5 |
Prophet Jehu son of Hanani condemns Baasha king of Israel for idolatry |
|
885 BC |
1 Kings 16:6-15 |
Elah and Zimri are coregent, rival kings of Israel after the death of Baasha in the 27th regnal year of Asa (=26th year as per 1 Kings 16:8). |
|
884 BC |
1 Kings 16:18 |
Zimri commits suicide by burning down the royal palace at Tizrah while inside |
|
884 BC |
1 Kings 16:16-28 |
Omri and Tibni are coregent, rival kings of Israel after the death of Zimri in the 28th regnal year of Asa king of Judah. (=27th year as per 1 Kings 16:10) |
|
883 BC |
Assurnasirpal II becomes king of Assyria (883-859 BC) in the 29th regnal year of Asa king of Judah. |
|
|
877 BC |
1 Kings 16:24 |
Founding of Samaria: Omri buys the land from Shemer and builds his palace on the hill and calls the new capital Samaria. After Zimri burned down the palace in Tizrah, Omri moves the capital to a virgin location and builds from scratch. |
|
877 BC |
Elijah begins ministry when Omri builds the palace in Samaria (Bible record is silent about this period but we know he was active before the great drought of 870 BC. |
|
|
873 BC |
chronological notes on kings |
Ahab becomes king of Israel when Omri dies and marries pagan Jezebel, daughter of Ethbaal king of the Sidonians in the 38th regnal year of Asa king of Judah. |
|
873 BC |
1 Ki 16:32 |
Ahab’s House of Baal Built by Ahab: 873 BC: 1 Ki 16:32 Destroyed by Jehu: 841 BC: 2 Ki 10:18-28 |
|
2 Chr 16:11-12; 2 Ki 1:17; 3:1 |
Jehoshaphat becomes coregent because of the foot disease of his father Asa in 873t-872t which is Asa’s 39th regnal year. |
|
|
872 BC |
1 Kings 18:3-4 |
Jezebel kills the good prophets but some are protected by Obadiah |
|
871 BC |
1 Ki 22:39 |
Ahab builds his “Ivory House” at Samaria. Carved Ivory found in Ahab’s palace at Samaria include: Woman at the Window, Human-headed sphinx, Winged guardian, Infant on a lotus, Cow and calf, Grazing stag |
|
2 Chron 16:13 |
Jehoshaphat becomes king of Judah 871t (870 BC). Asa dies in his 41st regnal year and is buried in tomb he dug, with perfume and huge mortuary bonfire. (not a cremation) |
|
|
870 BC |
Elijah begins ministry the year Asa died and Jehoshaphat becomes king (Bible record begins this year although he has been active 7 years earlier in 877 BC. |
|
|
870 BC |
1 Kings 17:1; Lk 4:25; James 5:17 |
Begin “bible recorded” ministry of Elijah: First recorded miracle: Predicts 3.5 year drought TYPE: Control over weather. Elijah’s 3.5-year drought: 1 Ki 17; Lk 4:25; James 5:17. Elisha caused 7-year famine: 2 Ki 6:31; 8:1-3 (double portion of Elijah’s 3.5 year famine). Jesus calmed the storm: Luke 8:22-25 |
|
870 BC |
1 Ki 17:1-7 |
Elijah moves to spring at Cherith river near Zerethan and Jabesh-Gilead where ravens provide food. Ravens never returned to the Ark: Gen 8:7 |
|
869 BC |
1 Ki 17:8-24 |
Elijah moves to live with widow of Zarephath near Sidon and performs miracles of multiplying flour and oil. Daily food from God was a pre-echo of weekly Manna in Exodus 16. Raises son from dead. TYPE: Asks gentile woman for water: Elijah: 1 Kings 17:10. Jesus asks Samaritan: Jn 4:7. TYPE: Multiply bread: “How can we feed so many… They shall eat and have some left over”: Elijah: 1 Kings 17:14; Elisha: 2 Kings 4:42-44. Jesus: Luke 9:17; John 6:9,13. TYPE: Raises only son of widow: Elijah: 1 Kings 17:17-24. Jesus: Luke 7:12-17. |
|
868 BC |
2 Chron 17:6-10 |
“Evangelist Jehoshaphat” takes “great pride” in spiritual things and sends royal officials, priests and Levites to all the cities of Judah to teach everyone the “Book of the Law”. Philistines and Arabs pay tribute. 1.16 million Judean army. |
|
867 BC |
1 Ki 18 |
Mt. Carmel: Elijah vs. 850 prophets of Baal Notice that just as Jezebel has executed the true prophets of YHWH, so too Elijah executed Jezebel’s 850 false prophets of Baal. TYPE: Chose God or satan! “How long will you hesitate between two opinions?” Joshua said this in Josh 24:15. Elijah said this on Mt Carmel: 1 Kings 18:21. Jesus: Matt 6:24 TYPE: 12 pitchers of water: Elijah poured 12 pitchers of water over the 12 stones of the altar: 1 Kings 18:34. Jesus had 12-18 “measures of water” poured into into 6 stone vessels: John 2:7-9 TYPE: “God who answers by fire”: Elijah on Mt. Carmel: 1 Kings 18:24, 38. Jesus sends tongues of fire on Pentecost: Acts 2. TYPE: Beam me up Scotty! Miracle of supernatural transportation: Elijah supernaturally outran Ahab to Jezreel: 1 Kings 18:46. Jesus and the disciples in the boat were instantly transported to the shore John 6:21. Philip was instantly transported to Azotus after baptizing the Eunuch: Acts 8:39-40. |
|
866 BC |
1 Kings 19 |
Jezebel issues death threat. Elijah flees to Beersheba, where angels provide food for 40 days. Mt. Sinai and lives in a cave for anywhere from a month to a year. John the Baptist lived in another the cave of Elijah located near Bethany beyond the Jordan river in modern Jordan. You can visit that cave today.
In AD 36, at his conversion, Paul fled Damascus for fear of being killed by Jews (Acts 22:18) and went to Mt. Sinai then returned the same year to Damascus (Galatians 1:17). Paul likely stood in the cave of Elijah on Mt. Sinai and Paul even quotes the famous words spoken to Elijah, who like Paul, had fled there out of fear: Romans 11:2-5. Paul returned to Damascus for three years without fear, then went up to Jerusalem for the first time.
TYPE: Enemies issue death threat: Jezebel issues death threat to Elijah: 1 Ki 19:2. Ben Hadad II tries to arrest or kill Elisha: 2 Ki 6:12-14; Jehoram king of Israel issued death threat because Elisha caused 7-year famine: 2 Ki 6:31; 8:1-3. Jesus had many death threats and attempts to kill him: Luke 4:29; John 7:19; 8:37; 11:53; 19:7. TYPE: Supernatural provision of food: Angels served him food in wilderness when physically exhausted: Elijah: 1 Kings 19:5-7. Jesus: Matthew 4:11. TYPE: Flees into wilderness after death threats: Elijah fled to Mt. Sinai: 1 Kings 19:3. Jesus fled to Ephraim (Khirbet El-Maqatir) John 11:53-54. TYPE: Fasted for 40 days in wilderness: Elijah: Angel gave food at the start of 40 days then he didn’t eat until reaching Sinai: 1 Kings 19:5-7. Jesus fasted for 40 days then angels gave him food: Matthew 4:2. TYPE: Angels encouraged him in time of emotional distress: Elijah at Beersheba: 1 Kings 19:7. Jesus in Garden of Gethsemane the night he was arrested: Luke 22:43. |
|
865 BC |
1 Kings 19:19-21 |
Elijah leaves Mt Sinai to anoint Elisha at age 20 years old. (same age as Joshua at Mt. Sinai in 1446 BC) TYPE: Please Excuse me: Plowing then say goodbye to family. Elijah found Elisha plowing who asked to say goodbye and was permitted: 1 Kings 19:20–21. Jesus did not accept Elisha’s excuse: Luke 9:61-62 |
|
Note |
1 Kings Chapters 20 and 21 are reversed in the Septuagint (LXX) and are followed as correct over the Masoretic Text (MT). |
|
|
862 BC |
1 Kings 21 |
Naboth’s Vineyard, Elijah condemns Repentance of Ahab. God’s grace is unmeasurable that He would be moved to reward this tiny show of repentance in light of the great evil Ahab did. God even confirmed his grace by rewarding Ahab with a victory against Ben-Hadad II in the Siege of Samaria I in 857 BC and the Battle of Aphek in 856 BC TYPE: Murder to gain possession of vineyard: Elijah sent to condemn Ahab in Naboth’s vineyard: 1 Kings 21. In parable of the vineyard the Jews kill Jesus (on the cross) to gain possession of the vineyard: Luke 20:9-18. |
|
861 BC |
2 Ki 4:1-17 |
Elisha’s first miracles: widow’s oil; Shunammite woman builds house for Elisha as an itinerate miracle worker. Shunammite woman conceives a son miraculously. TYPE: Itinerant miracle workers: Elijah, Elisha and Jesus were all traveling miracle workers. John the Baptist came in the “power and spirit of Elijah” yet performed no miracle. A puzzle, except John’s power was in bringing people to repentance, which is the primary work of Elijah during the pagan northern tribes: Jn 10:41. TYPE: Miraculous payment of debt: Elisha pays widow’s debt with oil: 2 Kings 4:1-7. Jesus pays tax debt with coin from mouth of fish: Matthew 17:24-27. TYPE: Others prepared an upper room: Elisha in Shunem: 2 Ki 4:10-11. In Jerusalem for Jesus to sleep and the last supper: “Where is MY guest room”: Mk 14:13-15 TYPE: Miraculous conception: Elisha: Conception after menopause: “she has no son and her husband is old”: 2 Ki 4:13-17. John the Baptist: Conception after menopause: Luke 1:7,18. Jesus’ virgin birth: Mt 1:18. |
|
860 BC |
Ben-Hadad [irdi] II becomes king of Aram, 860-841 BC when Ben-Hadad I dies. |
|
|
858 BC |
Shalmaneser III becomes king of Assyria: 858-824 BC when Assurnasirpal II king of Assyria dies (883-859 BC) |
|
|
857 BC |
1 Kings 20:1-25 |
Siege of Samaria I: Ahab defeats drunken Ben-Hadad II while he and 32 kings were in the temporary shelters outside Samaria during the siege. It was high noon and being drunk at this time indicated how certain they were of both safety from harm and victory in battle. Notice the 7000 men lead the battle echoing what God told Elijah on Mt. Sinai that he was not the last faithful man on earth! |
|
856 BC |
2 Ki 4:18-37 |
Elisha raises Shunammite’s dead son age 5 years TYPE: Person falls at feet crying, wanting miracle, disciples of master dissuade: Shunamite falls at feet of Elisha over dead son, Gehazi objects: 2 Kings 4:27. Jarius falls at feet of Jesus, disciples object: Mark 5:22,35. Mary at feet of Jesus over Lazarus who died: John 11:32. TYPE: Raises dead child: Elisha raises 5-year-old boy: 2 Kings 4:18-37. Jesus raises 12-year-old daughter: Mark 5:22-43 TYPE: Faithless disciples of the master could not perform miracle on boy: Gehazi unable to raise boy from dead, Elisha raises child: 2 Kings 4:29-31. Jesus’ disciples unable to cure boy: Mt 17:14-20 |
|
856BC |
1 Kings 20:26-43 |
Battle of Aphek: whose walls fell like Jericho and killed 27,000 (east coast of Sea of Galilee): Ahab defeats Ben-Hadad II then releases him. TYPE: Disguised himself so not to be recognized: One of the prophets asked to be injured then covered his eyes for Ahab: 1 Kings 20:41. John was “not recognized” as Elijah: Mt 17:12. Jesus was not recognized on the road to Emmaus: Luke 24:16; Mary at the tomb: John 20:14; Disciples on beach: Jn 21:4. TYPE: Life and death: Elijah confronted Ahab of his sin in Baal worship and a death decree was issued: 1 Ki 20:42-43. John the Baptist confronted Philip of his sin in Mt 14:4 and was beheaded then buried in Samaria beside Ahab’s ancient palace at the Byzantine church of John the Baptist that marks the original grave spot. |
|
2 Kings 4:38 |
Famine: See notes above on this famine and placing it in 855 BC. We have little information about this famine. It must have been localized to the Ephraim area that included Gilgal. Gilgal was in the Jordan valley near Jericho. Connecting the “return to Gilgal” in 2 Ki 4:38 as a narrative continuance of 2 Kings 2:1 is unlikely because: 1. In 2 Kings 2:23-25 Elisha goes to Bethel, then Mt. Carmel, then he “returned to Samaria” (the city). 2. The story of the miraculous conception of the Shunammite’s Son and his death, span 5 years in 2 Kings 4:18. |
|
|
855 BC |
2 Ki 4:38-44 |
Elisha’s miracles of the Poisonous stew, multiplies bread during famine TYPE: Immune from poison: Elisha: prophets unharmed by eating poisonous stew: 2 Ki 4:38-41. Jesus promised the disciples: Mark 16:18. Paul bitten by poisonous snake: Acts 28:2-6. TYPE: Multiply bread: “How can we feed so many… They shall eat and have some left over”: Elijah: 1 Kings 17:14; Elisha: 2 Kings 4:42-44. Jesus: Luke 9:17; John 6:9,13. |
|
854 BC |
2 Ki 4 |
Elisha heals Naaman, dips 7x in Jordan 1. The famine of 855 BC likely continued down to the time of the healing of Naaman, which may be why Naaman said, “the famine-ravished, dried-up muddy waters of the Jordan are not as good as the full running waters of the two rivers of Damascus”. (paraphrase) 2. Gehazi’s leprosy because of greed, lying and faithlessness. Gehazi was unable to raise the dead Shunammite’s son. Gehazi was a faithless traitor, liar and thief just like Judas. TYPE: Leprosy cured: Naaman cured by Elisha who struck dishonest Gehazi with leprosy 2 Ki 5:27. Jesus cured lepers: Mt 8:1-4; Mk 14:3; The ten lepers and the Samaritan leper: Luke 17:17. TYPE: Lying, faithless, traitorous money-grubbing, materialistic, servant for silver money/coins: Gehazi betrayed for silver money: 2 Ki 5:23; lied: 2 Ki 5:25, money: 2 Ki 5:26. The first coins in Israel date to 378 BC. Gehazi’s leprosy: Gehazi was faithless and unable to raise the dead Shunammite’s son. Gehazi was a faithless traitor, liar and thief just like Judas. Judas betrayed for 30 silver coins: Mt 26:15-16. |
|
853 BC |
4 Shalmaneser III inscriptions:
|
Battle of Qarqar: Shalmaneser’s 6th yr. vs. Ben-Hadad + Ahab: Shalmaneser’s Kurkh Monolith says Ahab sent 2,000 chariots, 10,000 men which contributed to Shalmaneser’s defeat.
853 BC: “In the sixth year of my reign” (Black Obelisk) “On the fourteenth day of the month Iyyar, in the eponymy of Daiiān-Aššur, I moved out from Nineveh, crossed the Tigris … I approached the city Qarqar. I razed, destroyed, (and) burned the city Qarqar, his royal city. An alliance had been formed of these twelve kings: 1,200 chariots, 1,200 cavalry, (and) 20,000 troops of Hadad-ezer (Adadidri) [Ben-Hadad II], the Damascene; 700 chariots, 700 cavalry, (and) 10,000 troops of Irhulënu, the Hamatite; 2,000 chariots (and) 10,000 troops of Ahab (Ahabbu) the Israelite (Sir'alaia); 500 troops of Byblos; 1,000 troops of Egypt; 10 chariots (and) 10,000 troops of the land Irqanatu; 200 troops of Matinu-ba’al of the city Arvad; 200 troops of the land Usanätu; 30 chariots (and) [N],000 troops of Adunu-ba'al of the land Sianu; 1,000 camels of Gindibu of the Arabs; [N] hundred troops (Line ii 95) of Ba’asa, the man of Bit-Ruhubi, the Ammonite. They attacked to [wage] war and battle against me. With the supreme forces which Aššur, my lord, had given to me (and) with the mighty weapons which the divine standard, which goes before me, had granted me I fought with them. I defeated them from the city Qarqar as far as the city Gilzau.” (Kurkh Monolith) “I fought with them (and) defeated them. I captured from them their chariotry, cavalry, (and) military equipment (and) put to the sword 25,000 of their fighting men.” (Marble Tablets) “I laid low like sheep 29,000 of his brave warriors (and) threw the remnant of his troops into the Orontes. They fled to save their lives.” (Basalt Statue) “To save their lives they ran away. They boarded boats (and) went out upon the sea.” (Twin Bulls) |
|
853 BC |
2 Chro 18:1-34; 1 Ki 22:28; Josephus Ant. 8.414 |
Battle of Ramoth-gilead I After Shalmaneser III defeated both Ben-Hadad II and Ahab in the Battle of Qarqar months earlier, Ahab was encouraged to turn against Ben-Hadad II and retake Ramoth-gilead. Jehoshaphat and Ahab form an allegiance to recapture Ramoth-gilead against Ben-Hadad II. Seer Micaiah son of Imlah, predicts the death of Ahab. Josephus said that Naaman was the Aram solder who kills Ahab with arrow after being healed of leprosy by Elisha. See exact parallel stories of Ahab and Josiah below. It is puzzling why Jehoshaphat would go to battle after Micaiah, the true prophet of YHWH, predicted defeat!
Josephus records Naaman killed Ahab: “So when the Syrians, upon their joining battle with the Israelites, saw Jehoshaphat stand before the army, and conjectured that he was Ahab, they fell violently upon him, (414) and encompassed him round: but when they were near, and knew that it was not he, they all returned back; and while the fight lasted from the morning light till late in the evening, and the Syrians were conquerors, they killed nobody, as their king had commanded them; and when they sought to kill Ahab alone, but could not find him, there was a young nobleman belonging to king Benhadad, whose name was Naaman; he drew his bow against the enemy, and wounded the king through his breastplate, in his lungs. (415) Upon this Ahab resolved not to make his mischance known to his army, lest they should run away; but he bid the driver of his chariot to turn it back, and carry him out of the battle, because he was sorely and mortally wounded. However, he sat in his chariot and endured the pain till sunset, and then he fainted away and died.” (Antiquities 8.413–415) |
|
853 BC |
chronological notes on kings |
Jehoram’s coregency begins during battle of Ramoth-Gilead I against Aram |
|
853 BC |
1 Ki 22:40 |
Ahaziah becomes king of Israel when Ahab dies, See chronological notes on kings |
|
853 BC |
2 Ki 1:1 |
Moab Rebels against Israel |
|
853 BC |
2 Ki 1:1-16 |
Ahaziah, king of Israel falls through the roof at Samaria. Elijah kills 2 sets of 50 soldiers sent to bring him to Ahaziah and says he will die. TYPE: Hairy with leather belt: Elijah: 2 Kings 1:8. The prophet who anointed Jehu king of Israel as “crazy or mad” in 2 Kings 9:11. In Mt 3:4; Zech 13:4 John the Baptist dressed in a costume worn by prophets of the 9th century BC. His dress was as distinct, recognizable and historic as the Jewish Hassidic dress today. The black hats, shirt and pants and beards with a long twirl of hair is a costume that imitates 18th century Germany. TYPE: Three sets of men sent, first two killed: Ahaziah king of Israel sent three sets of 50 to Elisha: 2 Kings 1:9-16. Jesus and the parable of the landowner: Matthew 21:34-37. |
|
853 BC |
2 Chr 19:1-4 |
Prophet Jehu son of Hanani condemns Jehoshaphat for allegiance with Israel in the Battle of Ramoth-gilead I. Jehoshaphat sinned by ignoring God’s warning through Micaiah, the true prophet of YHWH, not to go to battle! Why Jehoshaphat would ignore God’s warning is a mystery! |
|
853 BC |
2 Chron 19:4–11 |
“Evangelist Jehoshaphat”, takes the rebuke of Jehu son of Hanani to heart and during the last 5 year of his life, he travels personally throughout Judah teaching them the bible, turning the hearts of his subjects back to God and warns the judges he has appointed to be fair and just. Jehoram’s coregency is confirmed these 5 years as he takes over the state matters and his father in his old age becomes an itinerate evangelist of the Mosaic Law. |
|
852 BC |
2 Chr 20 |
Battle of Engedi: Jehoshaphat’s great prayer answered by seer Jahaziel. Moab & Ammon and Edom kill themselves without any fighting from Judah. |
|
852 BC |
2 Chron 20:36-37 |
Eliezer condemns Ezion-Geber shipbuilding joint venture between Jehoshaphat and Ahaziah king of Israel |
|
852 BC |
2 Kings 1:1-16 |
Joram (Jehoram) becomes king of Israel when Ahaziah dies |
|
851 BC |
2 Ki 6:1-7 |
Elisha recovers axe-head. TYPE: Defy gravity: Elisha causes iron axe-head float: 2 Kings 6:6. Jesus and peter walk on water: Mt 14:25-29. |
|
850 BC |
Battle of Dothan: Ben-Hadad II tries to arrest or kill Elisha: Elisha blinds Aram army at Dothan, marches to Samaria. Jehoram king of Israel wants to kill them but Elisha feeds the army and sets them free. Echoes Jesus and the woman caught in adultery of John 8. In spite of healing Naaman of Leprosy, the miracle of blindness and the mercy in releasing the army, Ben-Hadad II, attacks Israel again 8 years later in 842 BC in the Siege of Samaria II (2 King 6:24ff) at the end of the 7-year drought of Elisha (849-842 BC) TYPE: Opened eyes of disciples to see glory of God on the mountain: Elisha’s eyes were opened and shown the angel chariots that protected the mountain: 2 Ki 6:17.Jesus showed glorified Moses and Elijah on the mountain: Mt 17:1-3. TYPE: Angels at disposal: Elisha in the Battle of Dothan: 2 Kings 6:17. Jesus at the temptation: Mt 4:6-7. Jesus at his arrest could have called 12 legions of angels: Mt 26:53. TYPE: Miracle of blindness and sight. Elisha strikes Aram army with blindness: 2 Ki 6:12-14. Jesus restores the site of blind man: Jn 9. TYPE: Sinful captives released in mercy when others wanted to condemn and kill: Jehoram, king of Israel wanted to kill the “blinded Aram army” but Elisha set them free: 2 Ki 6:22. Woman caught in adultery: Jn 8:11; “he has sent me to proclaim release to the captives, and recovery of sight to the blind” Lk 4:18. |
|
|
849 BC |
2 Kings 8:1-2 |
7-YEAR DROUGHT STARTS in the last year of Jehoshaphat king of Judah. Elisha sends the Shunammite woman who miraculously conceived a son and her family to live with the Philistines for the 7 years. TYPE: Control over weather. Elijah’s 3.5-year drought: 1 Ki 17; Lk 4:25; James 5:17. Elisha caused 7-year famine: 2 Ki 6:31; 8:1-3 (double portion of Elijah’s 3.5 year famine). Jesus calmed the storm: Luke 8:22-25 |
|
849 BC |
3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions:
|
Battle of Carchemish: Shalmaneser III vs. Ben-Hadad II + 12 kings Composite text of 3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 849 BC: “In the tenth year of my reign, I crossed the Euphrates for the eighth time. (Black Obelisk) “I razed, destroyed, (and) burned the cities of Sangara, the Carchemishite. (Twin Bulls) “Moving on from the cities of the Carchemishite I approached the cities of Aramu (and) captured Arnê, his royal city, together with one hundred cities in its environs.” (Marble Tablets) “I razed, destroyed, (and) burned (it) together with one hundred cities in its environs. I massacred them (and) plundered them. At that time, Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri), the Damascene, (and) Irhulenu, the Hamatite, together with twelve kings on the shore of the sea, trusting in their united forces, attacked me to wage war and battle. I fought with them (and) defeated them. I took from them their chariotry, cavalry, and military equipment. To save their lives they ran away.” (Twin Bulls) |
|
849 BC |
2 Ki 3:4-27 |
Battle of Moab I: In the first year of the 7-year drought, Jehoshaphat king of Judah, Jehoram king of Israel and Edom decide to attack Mesha king of Moab. Moab had rebelled after the death of Ahab king of Israel in 853 BC. Jehoshaphat had just defeated Moab in 852 BC in the Battle of Engedi when Moab and Ammon attacked Judah in the Battle of Engedi three years earlier. Jehoshaphat was rebuked twice for his allegiances with two previous kings of Israel (Ahab in the battle of Ramoth-gilead I and Ahaziah in the shipbuilding venture at Ezion-geber). It is a puzzle why Jehoshaphat would AGAIN agree to another military cooperation with a wicked king of Jehoram of Israel who 7 years later issues a death edict against Elisha in 843 BC. Perhaps Jehoshaphat’s victory against Moab in the Battle of Engedi gave him confidence that such an allegiance was approved by God. Elisha is called and he miraculously commands the holes of the land of Edom to be filled with water during drought, which looked like blood to the Moabites who come out to see but are killed by the trilogy of kings. The king of Moab sacrifices his son and the Moabites repel the offensive. |
|
848 BC |
2 Chron 21:1-4 chronological notes on kings |
Jehoram becomes king of Judah when Jehoshaphat dies, and kills off his brothers to secure the throne. |
|
848 BC |
3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions:
|
Battle of Hamath I: Shalmaneser III vs. Ben-Hadad II Composite text of 3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 484 BC: “In my eleventh regnal year I crossed the Euphrates for the ninth time. I captured ninety-seven cities of Sangara (and) one hundred cities of Aramu.” (Marble Tablets) “At that time Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri), the Damascene, (and) Irhulënu, the Hamatite, together with twelve kings on the shore of the sea, trusting in their united forces, attacked me to wage war and battle. I fought with them (and) defeated them. I put to the sword 10,000 of their fighting men. I took from them their chariotry, cavalry, and military equipment.” (Twin Bulls) “I was successful in overthrowing them.” (Black Obelisk) |
|
847 BC |
2 Chro 21:8-10 |
Edom appoints a king for themselves and rebels against Judah along with the city of Libnah (Tel Burna, Josh 10:29). Jehoram, king of Judah attacks Edom. |
|
846 BC |
2 Ki 8:21; 2 Chro 21:9 |
Battle of Edom: After Edom appoints a king and Jehoram king of Judah comes to Zair inside Edomite territory. The Edomites ambushed and surround the Judean camp at night. Judah attacks and kills many Edomites the quickly escapes back to Judah. The location of the battle was in the Transjordan territory of Edom because Edom’s first incursion into Judah was after the first attack of Nebuchanezzar in 605 BC. The MT reads “Zair” and the LXX reads “Siōr. Therefore the two most likely readings mean Seir, as in the Edomite Mt. Seir located just north east of Elat and Ezion-geber or Zoar where lot fled just south east of the southern tip of the salt sea. “A perhaps more plausible solution is identifying Zair with Zoar (tsoʿar [צֹעַר]; Gen 13:10; 14:2, 8; 19:22–23, 30), at the southeastern tip of the Dead Sea. All three names—Zair, Zior, and Zoar—are related to a Hebrew word meaning “small, young” (tsaʿir)” (New Interpreter’s Dictionary of the Bible, Vol 5, Page 954, 2009 AD) |
|
845 BC |
Ben-Hadad II inscriptions: |
Melqart stele erected at Aleppo by Ben-Hadad II. The stele was erected as a kind of “rabbit’s foot” lucky charm to invoke the assistance of the pagan god named “Melqart” in the Battle of Hamath II against Shalmaneser III. Text of Ben-Hadad Melqart inscription: “The stele which Bir-Hadad, son of ‘Ezer, the Damascene, son of the king of Aram, erected to his Lord Melqart, to whom he made a vow and who heard his voice.” |
|
845 BC |
3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions:
|
Battle of Hamath II with Ben-Hadad II and 12 kings. Shalmaneser III, year 14: (Melqart stele erected at Aleppo by Ben-Hadad II) Composite text of 3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 945 BC: “In the fourteenth year of my reign … I crossed the Euphrates.” (Black Obelisk) … “in flood with 120,000 troops. At that time Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri), the Damascene, (and) Irhulënu, the Hamatite, together with twelve kings on the shore of the sea, above and below, mustered their troops which were too numerous to be counted.” (Twin Bulls) … “They attacked me, I fought with them, (and) defeated them. I took away their chariotry, cavalry, (and) military equipment. To save their lives they ran away.” (Marble Tablets) |
|
845 BC |
2 Chro 21:12-15 |
LETTER OF ELIJAH: Elijah’s letter condemning Jehoram for murdering royal family. Jehoram will lose wealth, wives, sons for one year (2 Chron 21:16-17) then two years of sickness until death in 841 BC |
|
842 BC |
2 Kings 6:25; 7:6 |
Siege of Samaria II at the end of the 7-year famine of Elisha: Ben-Hadad I flees when God creates the sound of a great army, 4 lepers find Aram camp abandoned then report the abandoned Aramean camp to the city of Samaria. The entire city rushes out and plunders the Aramean camp. This ends the Famine. |
|
842 BC |
2 Ki 8:3 |
7-YEAR DROUGHT ENDS: After the Siege of Samaria II the rains begin to fall flooding the Jordan river. |
|
842 BC |
2 Ki 2:1-12 |
Elijah goes to heaven in whirlwind probably on Nisan 14, Passover. Three prophet schools of Elijah: Gilgal, Bethel, Jericho. (see also: 2 Kings 4:38) In 1025 BC, David fled to Samuel’s prophet’s school called “Raioth” at Ramah: 1 Sam 19:18-20:1. Elisha will replace Elijah as the “master” of these three prophet schools. 50 prophets accompany Elijah and Elisha but wait on the western shore of the Jordan river. Elijah and Elisha cross on dry ground and Elisha witnesses the whirlwind and Elijah disappears. Elisha crosses back on dry ground. This is the same crossing point as Joshua in 1406 BC (564 years earlier) and where John the Baptist baptized Jesus in AD 29 (870 years later). It is also an echo of when Moses parted the Red Sea at the Straits of Tiran. See detailed outline on this crossing location. TYPE: Double portion: 2 Kings 2:9 of Elisha. Christ and his disciples had double portion: Isaiah 61:1-7 TYPE: Joshua’s crossing point of the Jordan on dry ground: Elijah crossed on dry ground at same spot as Joshua: 2 Kings 2:8. Elisha crossed on dry ground at same spot as Joshua: 2 Kings 2:14. John Baptized at the same spot Joshua crossed: John 1:28. Jesus was baptized at the crossing point of Joshua, Elijah and Elisha. You can visit this exact place today in Israel. TYPE: Same of start of ministry location at Jordan: Both Elisha and Christ had the same starting location their ministry where Joshua crossed the Jordan and John was baptizing. |
|
842 BC |
2 Ki 2:19-25 |
The prophets spend 3 days looking for Elijah in vain. Elisha purifies Jericho spring water. Elisha sends two mother bears to kills 42 youths who mocked the bald headed of 43-year-old Elisha. TYPE: Living waters: Elijah purified the death of the spring waters of Jericho into waters of life forever: 2 Kings 2:21. Today you still drink of this same pure spring water at Jericho. Jesus offered living water at Samaritan well: John 4:10; John 7:38. |
|
841 BC |
2 Kings 8:3-6 |
The Shunammite woman (who miraculously conceived a son) and her family return from the land of the Philistines after the 7-year famine of Elisha ended. |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 8:7; (see 1 Ki 19:15) |
Elisha travels to Damascus and anoints Hazael who smothers Ben-Hadad II and becomes king in his place. Strangely, Ben-Hadad II king of Aram, who tried to kill Elisha 9 years earlier in 850 BC in the Battle of Dothan, now asks Elisha if he will live or die. Elisha anoints Hazael king of Aram who reigned 841-800 BC. It is amazing that the Basalt Statue of Shalmaneser III accurately records how Hazael usurped the royal bloodline as an outsider: “Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri) [Ben-Hadad II] passed away (and) Haza'el, son of a nobody, took the throne.” (Basalt Statue) The Assyrians highly treasured the importance of a royal dynastic continuance in kings from father to son to son and Hazael caught the attention of Shalmaneser III as an interloper who became king. Obviously it irked Shalmaneser III enough that he commented on it. The old Ben-Hadad II was sick on his deathbed and sent Hazael to seek the answer from God if he would live or die. Although Elisha told Hazael that Ben-Hadad II would surely die, Hazael lied to the king that he would live. For the next 24 hours Ben-Hadad II may have been praising and thanking YHWH for the false hope generated through the lie of Hazael that he would live. At least his last 24 hours were filled with peace, joy and thankfulness. Today, sometimes we withhold information from our loved ones that they will soon die, in order to let them not be troubled about their imminent death. |
|
841 BC |
2 Chro 21:18-20 |
Ahaziah (or Azariah: 2 Kin 8:29) becomes king of Judea for one regnal year, when Jehoram dies after a two-year sickness. Ahaziah was injured by an arrow during the Battle of Ramoth-gilead II Jehoram king of Judah is given a commoner’s burial outside the area of the Tombs of the Kings in the Kidron Valley on the east side of the City of David and the west side of the Mount of Olives. See chronological notes on kings |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 8:28-29 Hazael Stele found at Tel Dan |
Battle of Ramoth-gilead II recorded in Stele of Hazael: Ahaziah king of Judah and Jehoram king of Israel form an allegiance to fight Hazael at Ramoth-Gilead. Such allegiances have been condemned under Asa and Jehoshaphat. The Arameans wound Jehoram (or Joram) king of Israel either in direct combat, a sling or an arrow. It is unknown how he was injured. The Hazael inscription describes the battle of Ramoth-gilead II: It is interesting the Hazael claims to kill both kings of Judah and Israel, when in fact he only insured Jehoram king of Israel. Scripture tells us that it was Jehu who actually killed them both. However, royal annals of ancient kings often bragged or took credit for things they had not accomplished directly. What is important is that the Stele of Hazael confirms the Bible record that both kings died the same year after the same battle of Ramoth-gilead II. Keep in mind that Hazael was a “God ordained” executioner of the two wicked idol worshipping kings. This is what Elijah had been told at Mt. Sinai years earlier. So Hazael was operating a divinely authorized mission of YHWH. What you read in the book, you find in the ground. 841 BC: “I killed Joram son of Ahab and Ahaziah, son of Jehoram of the house of David” (Tel Dan Victory Stele of Hazael). Hazael captures Tel Dan and sets up his victory stele. This is the second time Tel Dan has been destroyed by a king of Aram. Ben-Hadad I also destroyed Tel Dan in 895 BC. See: Tel Dan Excavations from the time of Ben-Hadad I. See also the Victory Stele of Hazael more famously known as the “house of David” stele. |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 9:1-15 |
Jehu son of Nimishi is the commander of the Israeli army under king Jehoram who has returned to Jezreel after being injured in the battle of Ramoth-gilead II. As Jehu is stationed at Ramoth-gilead during the continued fight against Hazael after Jeoram was injured, Elisha sends one of the prophets (known) to anoint Jehu the son of Jehoshaphat (not the same as Jehoshaphat the King of Judah) the son of Nimshi at Ramoth-gilead during the battle of Ramoth-gilead II. The prophet instructs Jehu to murder the house of Ahab and Jezebel which would include Jehoram, the current king of Israel. Jehu immediately races at full speed to Jezreel before word reaches Jehoram king of Israel that Jehu was anointed king in his place. The note in 2 Kings 9:11 that the prophet was described as “crazy or mad” indicates that like Elijah and John the Baptist, the prophets from the three schools of Gilgal, Bethel and Jericho dressed in peculiar ways that were contrary to the norms of the day. Elijah had a peculiar dress as did John the Baptist: “He was a hairy man with a leather girdle bound about his loins.” And he said, “It is Elijah the Tishbite.”" (2 Kings 1:8) |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 9:16-26 |
Jehu Kills Jorah king of Israel and becomes king. Jehu kills Joram in Naboth’s vineyard at Jezreel. It is fitting that the house of Ahab would be “cut off” in the infamous vineyard of Naboth. Ahaziah king of Judah had come to visit Joram king of Israel in the vineyard of Naboth. The famous quote, “the driving is like the driving of Jehu the son of Nimshi, for he drives furiously” describes the speed Jehu made on the 40 km trip west from Ramoth-gilead to Jezreel. The two kings look for Jehu and find him waiting in Naboth’s vineyard. Jehu shot Jehoram king of Israel with an arrow from behind, in the heart, while he was fleeing in his chariot and killed him. |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 9:27-28; |
Jehu kills Ahaziah king of Judah Several days or weeks pass between the initial time that Jehu kills Joram at Jezreel at which time Ahaziah king of Judah flees, and the time Ahaziah is executed by Jehu at Megiddo which is 10 km NW of Jezreel. Before Jehu leaves Jezreel (and while Ahaziah is on the run from Jehu’s men who are perusing him), he also kills Jezebel, Ahab’s house, and sends letters to Samaria to send the 70 heads of Ahabs sons to Jezreel. Then Jehu moves south to Samaria and kills all the Baal worshippers. We are not told if he went to Megiddo first, then to Samaria.
An apparent difference of events surrounding the death of Ahaziah in the accounts of Kings versus Chronicles is easily solved. In 2 Ki 9:27 Ahaziah is shot at Ibleam and he then fled to Megiddo and died there. In 2 Chro 22:8-9 Ahaziah is captured hiding in the city of Samaria and brought to Jehu at an unspecified location and put to death.
Adding the Septuagint to each reading: 2 Kings 9:27–28: (MT + LXX) "When Ahaziah the king of Judah saw this, he fled by the way of the garden house (the road to Beth-haggan, LXX). And Jehu pursued him and said, “Shoot him too, in the chariot.” So they shot him at the ascent of Gur (Ai, LXX), which is at Ibleam. But he fled to Megiddo and died there." (2 Kings 9:27–28)
2 Chro 22:8-9: (MT + LXX) “He also sought Ahaziah (He said to seek for Ahaziah, LXX), and they caught him while he was hiding in Samaria (as he was being treated in Samaria, LXX); they brought him to Jehu, put him to death and buried him. For they said, “He is the son of Jehoshaphat, who sought the Lord with all his heart.” So there was no one of the house of Ahaziah to retain the power of the kingdom." (2 Chronicles 22:8–9)
Splicing the two passages together and adding the Septuagint (LXX) Composite reading (2 Kings 9:27-28 + 2 Chro 22:8-9 + LXX): "When Ahaziah the king of Judah saw this, he fled by the way of the garden house (the road to Beth-haggan, LXX). And Jehu pursued him and said, “Shoot him too, in the chariot.” So they shot him at the ascent of Gur (Ai, LXX), which is at Ibleam. But he [was trying to] flee to Megiddo and died [there- not at Megiddo] [but fled to Samaria after being shot instead of Megiddo].” (2 Kings 9:27–28) “Jehu also sought Ahaziah (He said to seek for Ahaziah, LXX), and they caught him while he was hiding in Samaria (as he was being treated in Samaria, LXX); they brought him to Jehu [doesn’t say where Jehu was], put him to death (even though he had already been shot at Ibleam earlier] and buried him [in Jerusalem]." (2 Chronicles 22:8–9)
The actual sequence of events when Ahaziah king of Judah was killed are: 1. Ahaziah king of Judah fled Naboth’s vineyard in Jezreel and Jehu’s men shoot and injure Ahaziah at Ibleam (10 km SE of Jezreel). 2. Ahaziah escapes and reaches the city of Samaria. (20 km due SE of Ibleam) 3. While Ahaziah is fleeing and while in Jezreel, Jehu kills Jezebel, Ahab’s household, and receives the 70 heads of Ahab’s sons sent from Samaria to Jezreel. 4. Jehu travels 10 km north to Megiddo. 5. Jehu’s men find and capture Ahaziah being treated for his injuries in Samaria. 6. Ahaziah is taken to Jehu in Megiddo (35 km north of Samaria) and is put to death by Jehu who had already traveled 10 km NW from Jezreel to Megiddo. 7. Ahaziah is taken to Jerusalem and buried. 8. Jehu then travels south from Megiddo to Samaria. |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 9:30-37 |
Jehu kills Jezebel wife of Ahab king of Israel in Jezreel "When Jehu came to Jezreel, Jezebel heard of it, and she painted her eyes and adorned her head and looked out the window [at the city gate]." (2 Kings 9:30)
Jezebel was likely often seen sitting in this same city gate window adorned as a pagan priestess prostitute. All who entered the city had likely seen her in this window with painted eyes.
“Reminiscent of the Egyptian goddess Isis, the “woman in the window,” the most common of the Phoenician ivory motifs, alludes to the cult of Astarte, in which the goddess Astarte lived in a Phoenician palace as a sacred prostitute. From ninth- or eighth-century B.C. Nimrud, the delicate ivory is only four inches tall.” (British Museum) Ivory excavated from Ahab’s Palace in Samaria
Jezebel in the gate tower of Jezreel with “painted eyes looking through the window” (2 Ki 9:30) is a common pagan motif found on Ivory carvings in Samaria and Egyptian stone stele and wall paintings, etc. The woman is thought to be a sacred prostitute, which fits the story line perfectly. Jezebel may have been preparing herself for a fitting symbol before she died, or to save her life either through carnal seduction or respect for the divine. Jezebel’s statement “Is it well, Zimri, your master’s murderer?” is one last slap at Jehu by likening him to Zimri who killed Elah, was king for only 7 days, until he committed suicide by burning the royal palace down on top of himself.
Although Jezebel is not referenced in Chronicles, she is in Revelation which echos the actual life and influence of the real Jezebel. “I will kill her children” echoes the Jehu killed all the children of the house of Ahab.
"‘But I have this against you, that you tolerate the woman Jezebel, who calls herself a prophetess, and she teaches and leads My bond-servants astray so that they commit acts of immorality and eat things sacrificed to idols. ‘I gave her time to repent, and she does not want to repent of her immorality. ‘Behold, I will throw her on a bed of sickness, and those who commit adultery with her into great tribulation, unless they repent of her deeds. ‘And I will kill her children with pestilence, and all the churches will know that I am He who searches the minds and hearts; and I will give to each one of you according to your deeds." (Revelation 2:20-23) |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 10:1-11 |
Jehu beheads 70 of Ahab’s sons in Samaria and has the heads sent to Jezreel 70 of Ahab’s sons were beheaded and put into two piles at the gates of Jezreel. Such war practices are common in the ancient world including during the dark ages. The Muslims commonly practice beheading today and stack heads in a pile, which they merely adopted from the ancient Jews and other contemporary kings of the 7th century. |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 10:12-14 |
Jehu kills 42 of relatives of Ahaziah king of Judah at the “pit of Beth-eked”, which is located between Jezreel and Samaria. |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 10:15-17 |
The Rechabites: Jehu meets the famous “Jehonadab the son of Rechab” who rides with him to Samaria where Jehu killed the rest of Ahab’s relatives, man, woman and child. Jehonadab, the son of Rechab, are a priestly scribal family that date back to the time of King David: (1 Chro 2:55) The sons of Rechab are used by Jeremiah in 605 BC (Jer 35:1-19) as an exemplary example of how children obey their fathers. The metaphor is that if an earthly father is obeyed by his children, how much more the heavenly father.
The Rechabites were defined by obeying extra-biblical commandments: "But they said, “We will not drink wine, for Jonadab the son of Rechab, our father, commanded us, saying, ‘You shall not drink wine, you or your sons, forever. ‘You shall not build a house, and you shall not sow seed, and you shall not plant a vineyard or own one; but in tents you shall dwell all your days, that you may live many days in the land where you sojourn.’" (Jeremiah 35:6–7)
This human tradition family was not breaking any Mosaic laws or sinning, they had just set a collection of rules for themselves to follow forever.
It is important that Jeremiah does not endorse the traditions of the Rechabites, but instead commends their obedience to such rules as an example for others to follow. |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 10:18-28 |
Ahab’s House of Baal destroyed by Jehu in Samaria House of Baal built by Ahab: 873 BC: 1 Ki 16:32 Ahab’s house of Baal destroyed by Jehu: 841 BC: 2 Ki 10:18-28 Jehu kills all the prophets of Baal by calling for them to all come and sacrifice in the house of Baal. Jehu eradicates prophets of Baal from Israel and burns house of Baal built by Ahab. |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 11:1-3 2 Chro 22:10-12 |
Athaliah (Daughter of Jezebel and Ahab, granddaughter of Omri king of Israel) becomes queen of Judah after Jehu kills Ahaziah. Athaliah kills all her own children and grandchildren but infant Joash is hidden in the temple of Solomon for 6 years. Infant Joash, son of king Ahaziah was hidden in the temple by his aunt Jehosheba (sister of Ahaziah) who was also married to Jehoiada the High Priest. (2 Chro 22:11; 24:6)
Filicidal Idolatrous Queen Athaliah (aka Jezebel #2): Athaliah was the wife of Jehoram, the mother of wicked King Ahaziah whom Jehu killed and the granddaughter of Omri king of Israel. (2 Ki 11:1-3; 2 Chro 22:10-12) Like Jezebel her mother, Athaliah built a house of Baal, except this was in Judah. (2 Chro 23:17) She stole the sacred things from Solomon’s temple and used them for Baal worship: 2 Chron 24:7. Like Jezebel, Athaliah was a ruthless murderer of all her own royal children (filicide) just to secure the throne for herself for six short years. The influence that Athaliah was the daughter of Jezebel and granddaughter of pagan king Omri of Israel caused great evil in Judah. |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 10:29-31 |
Jehu continues to worship the two calves at Bethel and Dan: Apparently, Jehu was obedient to God in killing Jehoram king of Israel, Ahaziah king of Judah, Jezebel and prophets of Baal in order to selfishly secure his own throne. Although he “eradicated Baal from Israel” it was for carnal selfish reasons rather than faith. We know this because he continued to worship Jeroboam’s two golden calves at Bethel and Dan. So, to Jehu, his pagan god of choice was a golden calf not Baal: 2 Kings 10:29-31
"However, as for the sins of Jeroboam the son of Nebat, which he made Israel sin, from these Jehu did not depart, even the golden calves that were at Bethel and that were at Dan. … But Jehu was not careful to walk in the law of the Lord, the God of Israel, with all his heart; he did not depart from the sins of Jeroboam, which he made Israel sin.” (2 Kings 10:29–31) |
|
841 BC |
2 Ki 10:32-33 |
Jehu is defeated by Shalmaneser III, Hazael and Mesha of Moab “In those days the Lord began to cut off portions from Israel; and Hazael defeated them throughout the territory of Israel: from the Jordan eastward, all the land of Gilead, the Gadites and the Reubenites and the Manassites, from Aroer, which is by the valley of the Arnon, even Gilead and Bashan." (2 Kings 10:32-33)
After killing Jehoram king of Israel and Ahaziah king of Judah Jehu lost two battles: 1. Shalmaneser III attacked and defeated Hazael, then demanded that Jehu send him tribute as a new vassal king of Assyria. 2. Mesha king of Moab began attacking cities in Moabite territory that were controlled by Judah. This is witnessed in the Mesha Stele (Moabite stone). Incredibly, the Moabite stone says, “, I took the vessels of YHWH”. Mesha may have attacked Jerusalem and looted Solomon’s temple since Queen Athaliah ruled for six years after 841 BC and it was likely a period of military weakness. These holy vessels might have been captured in Judean controlled cities in Moab. |
|
841 BC |
5 Shalmaneser III inscriptions:
|
Siege of Damascus: Shalmaneser III defeats Ben-Hadad II, Jehu pays tribute
“In my 18th year (841 BC) ... I received tribute from the people of Tyre (and) Sidon (and) from Jehu (Iaua) of the house of Omri (Humrî). (Lines I"-27") (Twin Bulls of Shalmaneser III)
“I received tribute from Jehu, [Iaúa] house of Omri. [Bīt-Ḫumrî]: silver, gold, a gold bowl, a gold tureen, gold vessels, gold pails, tin, the staff of the king’s hand and spears.” (Inscription below Jehu bowing, Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser III)
Jehu bows to Shalmaneser III and pays him tribute:
“Jehu did not depart, even the golden calves that were at Bethel and that were at Dan” Composite text of 5 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 841 BC: “In my eighteenth regnal year I crossed the Euphrates for the sixteenth time.” (Black Obelisk) “Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri) [Ben-Hadad II] passed away (and) Haza'el, son of a nobody, took the throne. (Basalt Statue) … “Hazael of Damascus, trusting in the might of his soldiers, carried out an extensive muster of his troops … I fought with him (and) defeated him. I put to the sword 16,000 of his fighting men (and) took away from him 1,121 of his chariots (and) 470 of his cavalry with his military camp.” (Twin Bulls) “To save (line 15") his life he ran away (but) I pursued him. I imprisoned him in Damascus, his royal city, (and) cut down his gardens. I marched to Mount Haurānu (and) razed, destroyed, (and) (line 20") burned cities without number. I carried off more booty than could be counted. I marched to Mount Ba’lira’asi, which is a cape (jutting out into) the sea, (and) erected my royal statue there. At that time I received (line 25") tribute from the people of Tyre (and) Sidon (and) from Jehu (Iaua) of the house of Omri (Humrî). (Lines I"-27") (Twin Bulls) “To save his life he ran away (but) I pursued him. I imprisoned him in Damascus, his royal city, cut down his gardens, (and) burned his shocks” (Marble Tablets) “At that time I received tribute from the people of Tyre, Sidon, (and) from Jehu (laua) of the house of Omri (Humrî).” (Alabaster Statue) |
|
841 BC |
Moabite Stele 2 Kings 10:32-33 |
Battle of Moab II: Moabite Stele: “Israel is ruined”, King Mesha retakes Ataroth, Nebo, Jahaz from Israel”
Mesha, king of Moab saw “Israel is ruined” because its king was killed at the end of a 7-year famine/drought and Judah’s king was killed and now governed by a woman (Queen Athaliah) for the six years after 841 BC.
Partial text of Mesha inscription: 841 BC: “I am Mesha the king of Moab… Omri was the king of Israel, and he oppressed Moab for many days, And his son Ahab) succeeded him, and he said “I will oppress Moab!” In my days (941 BC) I looked down on him and on his house, and Israel has gone to ruin. … And Chemosh said to me: “Go, take Nebo from Israel!” … I took it, and I killed [its] whole population, seven thousand male citizens … And from there, I took the vessels of YHWH” (Mesha Stone, 841 BC) |
|
841 BC |
Begin Iron Age IIB Archaeological |
End of Archaeological Age IIA (1010-841 BC) Iron Age IIA begins with the rule of David in Hebron in 1010 BC and ends in the conquest of Jehu in 841 BC. 1. Archaeologists recognize a new assemblage of pottery and objects came into use at this time which is attributed to the rise of Jehu in 841 BC. 2. Jehu Killed Jorah king of Israel and became King in his place in 841 BC. 3. Jehu killed Ahaziah the King of Judah and Jezebel widow of Ahab in 841 BC. 4. Begin Iron Age IIB in 841 BC |
|
839 BC |
Kuntillet Ajrud Fortress and Ostraca on Pithos Jar: Partial text of inscription: “YHWH of Samaria and his wife”. (Kuntillet Ajrud ostraca) This illustrates the idolatry at Samaria that mixed the worship of YHWH and paganism where the God of Abraham is worshipped alongside of the wife of the God of Abraham. This mirrors the pagan view of multiple gods with their goddess wives and god children. The fortress of Kuntillet Ajrud located far south in the Judean/Simeon Negev near the border with Egypt was likely controlled by the powers in the ten northern tribes under Jehu. This was a period when Judea was weak, being governed by Queen Athaliah with little support of her local Judeans since he had killed off all her own children to secure the throne. When her one remaining grandson reached 7 years old, she was executed and Jehoiada the high priest governed behind the young king. That this is the time the ostraca of the fortress of Kuntillet Ajrud were written “YHWH of Samaria and his wife”, with the emphasis that this is ruled by Samaria NOT Jerusalem, fits 839 BC perfectly!
835 BC: "So all the people of the land rejoiced and the city was quiet. For they had put Athaliah to death with the sword at the king’s house." (2 Kings 11:20) |
|
|
838 BC |
Shalmaneser III inscriptions: |
Battle of Aram: Shalmaneser III defeats Hazael again Text of Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser III inscription: 838 BC: “In the twenty-first year of my reign, I crossed the Euphrates for the twenty-first time. I advanced against the cities of Hazael of Aram. I captured four of his cities. I received the gifts of the Tyrians, Sidonians, and Gebalites [Byblos].” (Black Obelisk) |
|
835 BC |
2 Ki 11:2-21; 2 Chro 23:1-15 |
7-year-old Joash (Jehoash) becomes king of Judea 835-796 BC after Athaliah dies See chronological notes on kings.
It was the wife of Jehoiada the High priest who hid Joash in the temple for 6 years. Jehoiada was the brother in law to Ahaziah, the father of Joash. (2 Chro 22:11; 24:6) Jehoiada became shadow king behind young Joash. It is clear that all the reforms for good in Judah were the result of Jehoiada, NOT Joash because when Jehoiada died, Joash began worshipping idols.
"Jehoash did right in the sight of the all his days in which Jehoiada the priest instructed him." (2 Kings 12:2)
Jehoiada the high priest arranges to make Joash king: "Then he brought the king’s [7 year old] son out [of Solomon’s Temple] and put the crown on him and gave him the testimony; and they made him king and anointed him, and they clapped their hands and said, “Long live the king!” … the king was standing by the pillar, according to the custom, with the captains and the trumpeters beside the king; and all the people of the land rejoiced and blew trumpets." (2 Kings 11:12) |
|
835 BC |
2 Ki 11:17-18; 2 Chro 23:16-21 |
People’s oath to serve God and Athaliah’s House of Baal torn down All the people commit to worship YHWH and tear down Athaliah’s house of Baal "Then Jehoiada made a covenant between the Lord and the king and the people, that they would be the Lord’s people, also between the king and the people. All the people of the land went to the house of Baal, and tore it down; his altars and his images they broke in pieces thoroughly, and killed Mattan the priest of Baal before the altars. And the priest appointed officers over the house of the Lord." (2 Kings 11:17-18)
"For the sons of the wicked Athaliah had broken into the house of God and even used the holy things of the house of the for the Baals." (2 Chronicles 24:7)
Jehoiada restores the spiritual order established by David (2 Chron 23:18): See full outline on the New Spiritual order of David. |
|
Ostraca of Elisha found in the home town of Elisha
|
Ostraca of Elisha: Discovered in 2013 AD in professional 3-dimentional archeological excavations at Tel Rehov, which is the home town of Elisha in the Bible called Abel-Meholah which is located 10 km SE of Beth-Shean near the Jordan river. "The Lord said to Elijah [at Mt. Sinai], “Go, return on your way to the wilderness of Damascus, and when you have arrived, you shall anoint Hazael king over Aram; and Jehu the son of Nimshi you shall anoint king over Israel; and Elisha the son of Shaphat of Abel-meholah you shall anoint as prophet in your place." (1 Kings 19:15–16) While the anointing of Elisha took place in 865 BC and the Ostraca is dated to 830 BC (35 years later), this documents the Bible story perfectly. The home town of Elisha would be a famous place during and after his lifetime. To find an ostraca with the name of Elisha on it, in the home town of Elisha in the Bible is a stunning proof that “what you read in the book, you find in the ground”. |
|
|
815 BC |
2 Ki 12:1-5; 2 Chron 24:1-5 |
Jehoiada gets Joash (age 29) to order priests to repair the Temple of Solomon In the 22nd year of Joash king of Judah (age 29) commanded that the temple be repaired. It is clear that Jehoiada the high priest was the force behind this renovation ordered by king Joash. |
|
814 BC |
2 Ki 13:1 |
Jehoahaz (Joash) becomes king of Israel 814-798 BC after Jehu dies See chronological notes on kings |
|
814 BC |
2 Ki 12:6-16; 2 Chron 24:6-14 |
Temple of Solomon repairs start when Joash is 30 years old. In the 23rd year of Joash king of Judah, the priests had still not begun repairs to the temple so the king issues new commands that the priests must use all money collected for the people to repair the temple and they can have none of it themselves. Incredibly, the priests decide to no longer accept money from the people but will also NOT do any repairs to the temple:
"So the priests agreed that they would take no more money from the people, nor repair the damages of the house." (2 Kings 12:8)
The faithless priests only source of money was the service fees from guilt and sin offerings of the people. (2 Kings 12:16)
Religious practice stripped of true faith and spirituality The priests were unmotivated and faithless because they collected the money from the people but did no repairs. Instead they just pocketed the extra cash for themselves! It is incredible that the lazy priests had no interest in repairing the very temple they served. It was a classic case of religious ritual stripped of any genuine faith. Jehoiada the high priest was the only true spiritual force at this time and he used the king’s power for the good of God’s work.
Jehoiada the priest creates a secure wooden money deposit box beside the altar so the people can donate their money directly to the repair of the Temple, bypassing the faithless, worthless priests. This proves that the common Jews did enter the outer tabernacle and stand directly beside the alter of burnt offerings. Further confirmation of this is that only the worthy common Jew was permitted inside the temple: "He stationed the gatekeepers of the house of the Lord, so that no one would enter who was in any way unclean." (2 Chronicles 23:19)
Repairs to the temple were completed and the workmen hired were faithful as stewards in the money they received without deception. |
|
810 BC |
Infant Adad-nirari III coregent with his mother Semiramis: Young Adad-nirari III becomes king of Assyria but his mother “Semiramis” is coregent with him for 6 years. We do not know how old he was when he became king, but the dynastic father son transmission of kings was as strong in Assyria as it was in Judah. Here we have two kings (Joash of Judah and Adad-nirari III) who ascended the throne as infants while their mothers (Athaliah, Semiramis) ruled the kingdom for them for 6 years. What is even more amazing is that they were king at the same period of time with an overlapping governorship of 14 years. This may have created an affinity between the Hebrews and Assyria as the two child kings governed their parts of the world at the same time.
Joash king of Judah and Adad-nirari III were: 1. Both Infants when their fathers died 2. Both had coregent mothers (Athaliah, Semiramis) 3. Both had coregencies of 6 years
Summary of Adad-Nirari III’s reign: 1. Six-year coregency with mother “Semiramis”: 810-806 BC 2. First functioning year as sole monarch: 806 BC 3. 5th year of reign as sole monarch on Stele: 799 BC 4. 4-year Fulfilment of 2 Ki 13:5: 799 BC (Jehoahaz/Israel) - 796 BC (Joash/Israel) 5. Dies and his son Shalmaneser IV becomes king of Assyria |
|
|
~808 BC |
2 Chro 24:15-16 |
Jehoiada the high priest dies age 130. His son Zechariah becomes high priest in his place. |
|
~808 BC |
2 Chron 24:17-19 |
Newly restored Solomon’s temple abandoned: People worship idols YWHW Temple Worship abandoned for idol worship of Asherim and Baal |
|
~808 BC |
2 Chron 24:19, 27 |
God sends many prophets to warn of Idolatry: After the death of Jehoiada the high priest who was the spiritual force behind Joash, God sends many prophets and finally sends Zechariah, the son of Jehoiada and Joash kills him in the temple.
"As to … the many oracles against him and the rebuilding of the house of God, behold, they are written in the treatise of the Book of the Kings." (2 Chronicles 24:27) |
|
~805 BC |
2 Chron 24:20-22 |
Joash kills prophet Zechariah, the son of the high priest Zechariah was likely the acting high priest.
The prophetic message of condemnation to Joash by Zechariah, son of Jehoiada the high priest, triggers Joash king of Judah, to kill the prophet in the court of the temple.
Jesus speaks of the written prophet Zechariah (520-518 BC) who was killed in the same way: "so that upon you may fall the guilt of all the righteous blood shed on earth, from the blood of righteous Abel to the blood of Zechariah, the son of Berechiah, whom you murdered between the temple and the altar." (Mt 23:35)
While the two stories are separated by 300 years and differ a bit in the details, they were killed for the same reasons: People of darkness get angry at people of light when they expose and condemn their wickedness.
Almost like Jesus’ Parable of the Vineyard owner: The caretakers kill the many prophets and finally the son of the high priest! (Mark 12:1) |
|
~804 BC |
2 Ki 12:17–18 2 Chro 24:23-24 |
Battle of Gath: Hazael captures Gath Probably triggered by the death of Jehu, Hazael king of Aram in Damascus captures Gath and is intent on attacking Jerusalem. Joash king of Judah sends tribute which appeases Hazael who calls off the attack.
"Then Hazael king of Aram went up and fought against Gath and captured it, and Hazael set his face to go up to Jerusalem. Jehoash king of Judah took all the sacred things that Jehoshaphat and Jehoram and Ahaziah, his fathers, kings of Judah, had dedicated, and his own sacred things and all the gold that was found among the treasuries of the house of the Lord and of the king’s house, and sent them to Hazael king of Aram. Then he went away from Jerusalem." (2 Kings 12:17-18) |
|
~804 BC |
2 Chro 24:25 |
Joash king of Judah injured and bedridden by Hazael for 8 years until his murder in 796 BC "When they [Hazael] had departed from him (for they left him very sick) (2 Chro 24:25)
Josephus records how Joash was bedridden after Hazael attacked Gath: ”However, it was not long before the king suffered punishment for his transgressions, for when Hazael, king of Syria, made an irruption into his country, and when he had overthrown Gath, and spoiled it, he made an expedition against Jerusalem; upon which Jehoash was afraid, and emptied all the treasures of God, and of the kings [before him], and took down the gifts that had been dedicated [in the temple], and sent them to the king of Syria, (171) and procured so much by them, that he was not besieged, nor his kingdom quite endangered; but Hazael was induced, by the greatness of the sum of money, not to bring his army against Jerusalem; yet Jehoash fell into a severe distemper, and was set upon by his friends, in order to revenge the death of Zechariah, the son of Jehoiada. These laid snares for the king, and slew him.” |
|
804 BC |
Adad-nirair III becomes sole regent when his mother Semiramis dies Summary of Adad-nirari III’s reign: 1. Six-year coregency with mother “Semiramis”: 810-806 BC 2. First functioning year as sole monarch: 806 BC 3. 5th year of reign as sole monarch on Stele: 799 BC 4. 4-year Fulfilment of 2 Ki 13:5: 799 BC (Jehoahaz/Israel) - 796 BC (Joash/Israel) 5. Dies and his son Shalmaneser IV becomes king of Assyria |
|
|
804 BC |
|
Adad-nirair III sets up four statues of Nebu/Nebo in Calah (Nimrod)
The inscription records the equivalent to the “Lord’s prayer” to a pagan god: "To the god Nebo who is heroic, exalted, surpassing in wisdom, mighty prince whose command is supreme, master of the arts, guardian of all heaven and earth, all knowing, whose ear is open [ie. to prayer] who writes the book of man's life and destiny, merciful, approachable, who depopulate and repopulate the land [determines the boundaries of man's habitation.] lord of lords, whose might has no equal, without whom no counsel is given in heaven, merciful, compassionate, kindly forgiving. Trust in the god Nebo! Do not trust in another god." (Trust Nebo Alone Statue of Adad-nardi III, 804 BC) |
|
799 BC |
Battle of Damascus I: Adad-nirari III (Assyria) attacks Ben-Hadad III (Mar) king in Damascus. Adad-nirari III starts 3 years of attacks on Aram in 5th year of sole reign of Adad-nirari III after coregency with mother Semiramis ended in 804 BC bringing relief to Israel and beginning the fulfillment of 2 Ki 13:5.
“As we know from the eponym chronicle, there were several campaigns to the west, between 805 and 796 BC, and the description on this stele [Saba’a Stele of Adad-nirari III] is just a brief summary of these events. " (Assyrian Rulers of the Early First Millennium BC, Adad-Nirari III, A. Kirk Grayson, p 208, A.0.104.6, 1996 AD)
God’s two stage fulfillment of 2 Kings 13:5: "The Lord gave Israel a deliverer, so that they escaped from under the hand of the Arameans; and the sons of Israel lived in their tents as formerly." 1. First stage: the prayer and humbling of Jehoahaz king of Israel (814-798 BC) was after Hazael died in 800 BC, so the prayer occurred in 799 and the deliverance continued into the last year of his life in 798 BC. 2. Second stage happened in 796 BC and is witnessed in the stele of Adad-nirairi III and the Bible: "Then Jehoash the son of Jehoahaz took again from the hand of Ben-hadad the son of Hazael the cities which he had taken in war from the hand of Jehoahaz his father. Three times Joash defeated him and recovered the cities of Israel." (2 Kings 13:25) |
|
|
798 BC |
chronological notes on kings |
Jehoash becomes king of Israel after Jehu dies. |
|
796 BC |
chronological notes on kings |
Amaziah becomes king of Judah after Joash is murdered in his sickbed after being bedridden for 8 years. |
|
796 BC |
|
Battle of Damascus II "Several events converged at the beginning of the eighth century to catapult Israel and Judah into prominence. The defeat of Aram-Damascus by Adad-nirari III about 796 bce liberated Israel from Aramean oppression." (The Eighth, the Greatest of Centuries? P. J. King, Journal of Biblical Literature, 108, p3, 1989 AD)
Rimah Joash Conquest stele inscription: “In one year I subdued all the lands of Amurru & Hatti (Syria and Israel). I imposed tribute of Mari [Ben-Hadad III], the Damascene. I received the tribute of Joash [lit. Iu'asu], the Samaritan, and tribute of Tyre & Sidon.” (Rimah Joash conquest stele of Adad-nirari III)
Saba’a Conquest Stele inscription: “I confined Mari [Ben Hadad III] in Damascus and he gave me 100 talents of gold and 1,000 talents of silver as tribute.” (Saba'a conquest stele of Adad-nirari III)
|
|
795 BC |
2 Ki 13:14-20 |
Elisha dies of disease 95 years old after serving 70 years as prophet Jehoahaz (Joash) king of Israel repeats Elisha’s own words he spoke when Elijah went to heaven in a whirlwind: “My father, my father, the chariots of Israel and its horsemen” 2 Ki 13:14. Elisha gets Joash king of Israel to shoot Arrows and strike arrows on the ground as a symbol of the defeat of Aram. |
|
795 BC |
Stele of Zakkur, King of Hamath |
Battle of Hamath III: After his defeat by Adad-Nirari III of Assyria, Ben-Hadad III attacks Hamath but again is defeated by Zakkur king of Hamath. Notice how king Zakkur trusts in his pagan god:
Inscription of the Stele of Zakkur: “I am Zakkur, king of Hamath and Luʿash. I was a humble but Baʿlshamayn [my other god] [raised] me and stood beside me, and Baʿlshamayn made me king over Hazrach [Hamath]. Then Ben-Hadad [III], son of Hazael, king of Aram, united against me s[even]teen kings: Ben-Hadad [III] and his army, Bar-Gush and his army, the king of Que and his army, the king of ʿAmuq and his army, the king of Gurgum and his army, the king of Samʾal and his army, the king of Meliz and his army [ ] seven[teen], they and their armies. All these kings laid siege to Hazrach. They raised a wall higher than the wall of Hazrach, they dug a ditch deeper than [its] ditch. Now I raised my hands to Baʿlshamayn and Baʿlshamayn answered me. Baʿlshamayn [spoke] to me through seers and diviners. Baʿlshamayn said to me, “Do not be afraid! Since I have made [you king, I will stand] beside you. I will save you from all [these kings who] have besieged you.” [Baʿlsha-mayn] also said to [me, “] all these kings who have [besieged you ] and this wall [ ].” (Stele of Zakkur, King of Hamath)
Stele of Zakkur, King of Hamath |
|
794 BC |
1 Ki 13:21 |
Elisha’s last miracle from the grave: Dead man thrown on top of Elisha’s dead body in the tomb and is raised from dead.
TYPE: Dead raised after death: Body thrown onto Elisha’s bones was resurrected: 2 Ki 13:21; Josephus Ant. 9.183. Jerusalem saints resurrected from tombs at death of Christ: Mt 27:52.
Josephus records the Death of Elijah: “It also happened, that at that time certain robbers cast a man, whom they had slain, into Elisha’s grave, and upon his dead body coming close to Elisha’s body, it revived again. And thus far have we enlarged about the actions of Elisha the prophet, both such as he did while he was alive, and how he had divine power after his death also.” (Josephus Antiquities 9.183)
Jesus is the True Resurrection: This echoes the moment Jesus died at 3 pm on the 3 April 33 AD that many were resurrected in nearby tombs in Jerusalem. Jesus is truly the Lord of the Resurrection and the Life:
"And Jesus cried out again with a loud voice, and yielded up His spirit. And behold, the veil of the temple was torn in two from top to bottom; and the earth shook and the rocks were split. The tombs were opened, and many bodies of the saints who had fallen asleep were raised; and coming out of the tombs after His resurrection they entered the holy city and appeared to many. Now the centurion, and those who were with him keeping guard over Jesus, when they saw the earthquake and the things that were happening, became very frightened and said, “Truly this was the Son of God!”" (Matthew 27:50–54) |
|
793 BC |
2 Kings 14:7; 2 Chro 25:6-16 |
Battle of Kadesh Barnea: (Sela, Joktheel, Petra) Amaziah king of Judah hires 100,000 Israeli warriors to fight Edom but a prophet condemns him and orders the king to dismiss the solders and just forfeit the money the warriors were paid. The Israeli warriors are insulted and loot Judean cities on the way back home and kill 3000 Judeans.
Meanwhile, Amaziah defeats Edom in the Valley of Salt at the south end of the Salt sea, then captures Kadesh and renames is Joktheel which means “God nourishes”. This is a fitting name for the place the Hebrews spent 38 years with Moses. Kadesh Barnea is wrongly located at Qudeirat south of Beersheba 27 km inside the promised land on every Bible map since 1916 AD. See outline on Kadesh Barnea at Petra.
Amaziah worships Edomite gods in Jerusalem: King Amaziah brings back and worships the gods of defeated Edom in Jerusalem. A prophet condemns him but the king threatens to kill the prophet, who says, “God is going to destroy you”. |
|
793 BC |
chronological notes on kings 2 Chro 25:13 |
Jehoash king of Israel appoints his son Jeroboam II as coregent king: The anger generated by the Israeli soldiers who each got paid their talent without having to fight, but then they looted the cities of Judah and killed 3000 Judeans, caused Jehoash to wisely appoint his son at this time in the event of war. Indeed, just 3 years later, Judah and Israel were at war in the Battle of Beth Shemesh. |
|
790 BC |
2 Ki 14:7-14; 2 Chro 25:17-24 |
Battle of Beth Shemesh: Amaziah king of Judah wanted revenge for the looting of the Israeli solders he hired and dismissed with full pay. After winning the Battle of Kadesh Barnea, Amaziah felt confident he would defeat Israel, given the prophet had told him to dismiss the Israeli soldiers because they were a cursed of God. But Amaziah has started worshipping the God’s of defeated Edom and he too is now cursed of God.
Jehoash warns Amaziah not to fight: Idol worshipping Jehoash king of Israel even warns Amaziah he will be defeated. This is exactly what happened to Josiah in 609 BC, when the idol worshipping Pharaoh Neco II warned him not to fight or he would die. Jehoash captures Amaziah, tears down 225 meters of the Jerusalem walls, loots the Temple of Solomon and the kings house. Amaziah is released but Jehoash takes many additional hostages to prevent retaliation and returns to Samaria. These were probably released once the king of Israel returned home safely. Amaziah never repents for the next 23 years until he is killed at Lachish: When Amaziah threatened the “man of God” it cost him dearly. Like king Asa before him he snubbed God for no reason. We know Amaziah never repented of his sins or returned to God because his own officials wanted to kill him, so he fled to Lachish but was captured there and killed in 767 BC |
|
790 BC |
chronological notes on kings |
Amaziah appoints his son Uzziah (Azariah) as coregent at age 16. |
|
767 BC |
chronological notes on Kings 2 Chro 26:1-3 |
Uzziah (Azariah) becomes sole monarch after his father dies. Reign of Uzziah: 1. Became king at age 16 in 790 BC 2. 23 years coregent with his father Amaziah: 790-767 BC 3. 16 years sole king: 767-750 BC 4. 11 years coregent with his son Jotham: 750-740 BC 5. Total years: 51 Uzziah had military successes with God’s help, but he became proud and offered incense in the Temple and God struck him with leprosy: 2 Chronicles 26:16-21 |
|
|
V. Master List of 25 Wars During the Time of Asa, Elijah and Elisha: 857-838 BC
|
25 Wars During the Time of Elijah and Elisha: 857-838 BC |
|||
|
War |
Date |
Text |
Battle |
|
1. |
896 BC |
2 Chron 14:9-15 |
Battle of Mareshah: Zerah, the Ethiopian attacks Judah 15th regnal year of Asa in February of the year |
|
2. |
896 BC |
2 Chron 16:1 |
Fortification of Ramah: Baasha fortifies Ramah in November of the 36th year = 896 BC after Tishri. 16th regnal year Asa = 36th year since Rehoboam. |
|
3. |
895t BC |
2 Chron 16:4; 1 Ki 15:18-20 |
Battle of Naphtali: Ben Hadad 1st attacks Ijon, Dan, Abel-maim and all the store cities of Naphtali. 17th regnal year of Asa in November. |
|
4. |
857 BC |
1 Kings 20:1-25 |
Siege of Samaria I: Ahab defeats Ben-Hadad II |
|
5. |
856BC |
1 Kings 20:26-43 |
Battle of Aphek: whose walls fell like Jericho and killed 27,000 (east coast of Sea of Galilee): Ahab defeats Ben-Hadad II. |
|
6. |
853 BC |
1 Ki 22 |
Battle of Ramoth-gilead I Jehosaphat and Ahab. |
|
7. |
853 BC |
4 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 4. Twin Bulls |
Battle of Qarqar: Shalmaneser’s 6th yr. vs. Ben-Hadad + Ahab: Shalmaneser’s Kurkh Monolith says Ahab sent 2,000 chariots, 10,000 men which contributed to Shalmaneser’s defeat. |
|
8. |
852 BC |
2 Chr 20 |
Battle of Engedi: Jehoshaphat defeats Moab & Ammon. Seer Jahaziel |
|
9. |
850 BC |
2 Ki 6:12-14 |
Battle of Dothan: Ben Hadad II tries to arrest or kill Elisha: Elisha blinds Aram army at Dothan, marches to Samaria. |
|
10. |
849 BC |
3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 2. Twin Bulls |
Battle of Carchemish: Shalmaneser III vs. Ben-Hadad + 12 kings |
|
11. |
849 BC |
2 Ki 3:4-27 |
Battle of Moab I: Judah, Israel, Edom vs. Mesha. Elisha’s water miracle during drought that looked like blood |
|
12. |
848 BC |
3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 2. Twin Bulls |
Battle of Hamath I: Shalmaneser III vs. Ben-Hadad II |
|
13. |
846 BC |
2 Ki 8:21; 2 Chro 21:9 |
Battle of Edom: After Edom appoints a king and Jehoram king of Judah comes to Zair inside Edomite territory. The Edomites ambushed and surround the Judean camp at night. Judah attacks and kills many Edomites the quickly escapes back to Judah. |
|
14. |
845 BC |
3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 2. Twin Bulls |
Battle of Hamath II with Ben-Hadad II and 12 kings. Shalmaneser III, year 14: (Melqart stele erected at Aleppo by Ben-Hadad II) |
|
15. |
842 BC |
2 Kings 6:25; 7:6 |
Siege of Samaria II: during famine: Ben-Hadad flees, 4 lepers find Aram camp abandoned. |
|
16. |
841 BC |
2 Kings 8:28 |
Battle of Ramoth-gilead II: Hazael wounds Joram king of Judah. |
|
17. |
841 BC |
5 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 3. Twin Bulls |
Siege of Damascus: Shalmaneser III defeats Ben-Hadad II, Jehu pays tribute “In my 18th year (841 BC) ... I received the tribute of ... Jehu, son of Omri” (Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser III) |
|
18. |
841 BC |
Moabite Stele 2 Kings 10:32-33 1. Mesha Stele |
Battle of Moab II: Moabite Stele: “Israel is ruined”, King Mesha retakes Ataroth, Nebo, Jahaz from Israel |
|
19. |
838 BC |
Shalmaneser III inscriptions: |
Battle of Aram: Shalmaneser III defeats Hazael. Jehu bows and pays tribute. |
|
20. |
804 BC |
2 Ki 12:17; 2 Chro 24:23 |
Battle of Gath: With God’s help Hazael king of Aram captures Gath with a very small army then threatens Jerusalem, and kills many of the officials. When Hazael came to Jerusalem Joash paid large tribute from the temple treasuries and sacred items of silver and gold. |
|
21. |
799 BC |
2 Ki 13:5 |
Battle of Damascus I Adad-nirari III delivers Israel from Ben-Hadad III. |
|
22. |
796 BC |
See outline on Adad-nirari III
|
Battle of Damascus II This is the historic complete and final submission of Aram and Ben-Hadad III (Mari) to the Assyrian powers. From this point forward Assyria will grow in power, be rebuked by Jonah, repent, only to take the entire nation of Israel (ten northern tribes) into Assyria where they will become extinct forever. 1. “I received tribute of Ben-Hadad III of Damascus and Jehoash the Samaritan” (Rimah Joash conquest stele) 2. “I crossed the Euphrates in flood. … I commanded [my troops to march to Damascus]. I [confined] Mari [Ben Hadad III] in Damascus [... He brought to me] 100 talents of gold (and) 1,000 talents of silver as tribute. (Saba'a conquest stele) |
|
23. |
795 BC |
Stele of Zakkur, King of Hamath |
Battle of Hamath III: Ben-Hadad III defeated in his attack on Zakkur king of Hamath with a coalition of 12 kings. Zakkur calls upon his pagan god for support and help. After being defeated by Adad-nirari III twice previously in the Battle of Damascus I (799 BC) and the Battle of Damascus II (796 BC), this is the third defeat of Ben-Hadad III (Mari) in his offensive attack on Hamath. It is likely that Ben-Hadad III was looking for an easy/soft target to replenish his wealth after paying huge tribute to Adad-nirari III king of Assyria. |
|
24. |
793 BC |
2 Kings 14:7; 2 Chro 25:6-16 |
Battle of Kadesh Barnea: (Sela, Joktheel, Petra) Amaziah king of Judah hires 100,000 mercenaries from Israel to assist in his attack of Edom but a prophet orders him to dismiss them and send them home to Samaria. The soldiers loot the cities of Judah and kill 3000 on the way home. Meanwhile, Amaziah successfully defeats Edom at the southern shore of the Salt Sea and captures Sela, which is ancient Kadesh Barnea where Israel spent 38 years with Moses in the wilderness. Kadesh Barnea is wrongly located at Qudeirat south of Beersheba 27 km inside the promised land on every Bible map since 1916. See: Kadesh Barnea at Petra. After obeying the prophet of God and winning the war with Edom, Amaziah shockingly brings back the pagan gods of defeated Edom to Jerusalem and begins worshipping them |
|
25. |
790 BC |
2 Ki 14:7-14; 2 Chro 25:17-24 |
Battle of Beth Shemesh Amaziah king of Judah seeks revenge for the 100,000 soldiers of Israel who looted Judah and murdered 3000 Judeans. Although Joash king of Israel is now a vassal of king Adad-nirair III of Assyria, he has been delivered from the constant attacks of the king Ben-Hadad III of Aram. Joash king of Israel warns Amaziah not to attack Israel. Perhaps it never crossed Amaziah’s mind that he would be fighting against the same 100,000 soldiers whom he had hired for a talent of silver each, then dismissed at the command of the prophet of God. Amaziah was captured at Beth Shemesh by Joash king of Israel, who went to Jerusalem, tore down 25 meters of the city wall, looted Solomon’s temple and the king’s palace, and return to Samaria with hostages. Amaziah was released and the hostages were ensured safe passage by Joash back to Samaria his capital city. Amaziah was defeated because he abandoned YHWH for the gods of Edom, then threatened to kill the prophet who rebuked him. |
|
25 Wars 900 – 795 BC |
|||
|
War |
Name of Battle |
Date |
Text |
|
1. |
Battle of Mareshah: Zerah, the Ethiopian attacks Judah |
896 BC |
2 Chron 14:9-15 |
|
2. |
Fortification of Ramah: Baasha fortifies |
896 BC |
2 Chron 16:1 |
|
3. |
Battle of Naphtali: Ben Hadad 1st Naphtali |
895 BC |
2 Chron 16:4; 1 Ki 15:18-20 |
|
4. |
Siege of Samaria I: Ahab defeats Ben-Hadad II |
857 BC |
1 Kings 20:1-25 |
|
5. |
Battle of Aphek: Ahab defeats Ben-Hadad II. |
856BC |
1 Kings 20:26-43 |
|
6. |
Battle of Ramoth-gilead I Jehosaphat and Ahab vs. Ben-Hadad II |
853 BC |
1 Ki 22 |
|
7. |
Battle of Qarqar: Shalmaneser III defeats Ben-Hadad II, Ahab |
853 BC |
4 Shalmaneser III inscriptions 1. Kurkh Monolith 2. Basalt Statue 3. Black Obelisk 4. Twin Bulls 5. Marble Tablets |
|
8. |
Battle of Engedi: Jehoshaphat defeats Moab & Ammon |
852 BC |
2 Chr 20 |
|
9. |
Battle of Dothan: Elisha blinds Aram |
850 BC |
2 Ki 6:12-14 |
|
10. |
Battle of Carchemish: Shalmaneser III vs. Ben-Hadad + 12 kings
|
849 BC |
3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 1. Black Obelisk 2. Twin Bulls 3. Marble Tablets |
|
11. |
Battle of Moab I: Judah, Israel, Edom vs. Mesha |
849 BC |
2 Ki 3:4-27 |
|
12. |
Battle of Hamath I: Shalmaneser III vs. Ben-Hadad II |
848 BC |
3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 1. Black Obelisk 2. Twin Bulls 3. Marble Tablets |
|
13. |
Battle of Edom: Judah attacks Edom |
846 BC |
2 Ki 8:21; 2 Chro 21:9 |
|
14. |
Battle of Hamath II Shalmaneser III defeats Ben-Hadad II + 12 kings |
845 BC |
3 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 1. Black Obelisk 2. Twin Bulls 3. Marble Tablets |
|
15. |
Siege of Samaria II: Ben-Hadad II flees |
842 BC |
2 Kings 6:25; 7:6 |
|
16. |
Battle of Ramoth-gilead II: Hazael wounds Joram king of Judah. |
841 BC |
2 Kings 8:28 |
|
17. |
Siege of Damascus: Shalmaneser III defeats Ben-Hadad II, Jehu |
841 BC |
5 Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 1. Basalt Statue 2. Black Obelisk 3. Twin Bulls 4. Marble Tablets 5. Alabaster Statue |
|
18. |
Battle of Moab II: Mesha retakes Ataroth, Nebo, Jahaz from Israel |
841 BC |
Moabite Stele 2 Kings 10:32-33 1. Mesha Stele |
|
19. |
Battle of Aram: Shalmaneser III defeats Hazael. Jehu bows and pays tribute. |
838 BC |
Shalmaneser III inscriptions: 1. Black Obelisk |
|
20. |
Battle of Gath: Hazael king of Aram captures Gath |
804 BC |
2 Ki 12:17; 2 Chro 24:23 |
|
21. |
Battle of Damascus I: Adad-nirari III delivers Israel from Ben-Hadad III. |
799 BC |
2 Ki 13:5 |
|
22. |
Battle of Damascus II: Adad-nirari III fully defeats Ben-Hadad III |
796 BC |
See outline on Adad-nirari III 1. Rimah Joash conquest stele 2. Saba'a conquest stele |
|
23. |
Battle of Hamath III: Zakkur king of Hamath defeats Ben-Hadad III |
795 BC |
Stele of Zakkur, King of Hamath |
|
24. |
Battle of Kadesh Barnea: Amaziah defeats Edom |
793 BC |
2 Kings 14:7; 2 Chro 25:6-16 |
|
25. |
Battle of Beth Shemesh: Joash king of Israel defeats Amaziah |
790 BC |
2 Ki 14:7-14; 2 Chro 25:17-24 |
|
|
VI. Asa king of Judah: 911-870 BC
A. Chronological summary of events during the reign of Asa:
|
Chronological timeline of Asa king of Judah |
|||
|
Date |
Asa Regnal year |
Event |
Chronological reading of scripture |
|
912t-911n (911 BC) |
1st year |
Asa Becomes king of Judah (911-870 BC) |
1 Ki 15:9-24; 2 Chro 14-16 |
|
910 BC |
2nd year |
Nadab becomes king of Israel (910-909 BC) |
1 Ki 15:25-31 |
|
909 BC |
3rd year |
Baasha becomes king of Israel |
1 Ki 15:32-16:7 |
|
906-895 BC |
6-15th year |
Ten years of no war |
2 Chron 14:1 |
|
900 BC |
10th year |
Ben Hadad 1st becomes king of Aram (900-860 BC) |
|
|
897t BC (Oct) |
15th year |
Prophecy of Azariah |
2 Chron 15:1-7 |
|
896 BC |
15th year Asa = 35th year of Rehoboam |
No war until 35th year (Dynastic divided kingdom since death of Solomon) = 896 BC |
2 Chron 15:19 |
|
896 BC (Feb) |
15th year |
Battle of Mareshah Zerah, the Ethiopian attacks Judah |
2 Chron 14:9-15 |
|
896 BC (May) |
15th year |
Covenant festival, queen mother removed |
2 Chron 15:9-15 |
|
896 BC (Nov) |
16th year Asa = 36th year of Rehoboam |
Fortification of Ramah Baasha fortifies Ramah in 36th year = 896 BC after Tishri |
2 Chron 16:1 |
|
16th year |
Asa makes treaty with Ben Hadad I, who breaks treaty with Samaria |
2 Chron 16:2-3 |
|
|
895t BC (Nov) |
17th year |
Battle of Naphtali Ben Hadad 1st attacks Ijon, Dan, Abel-maim and all the store cities of Naphtali |
2 Chron 16:4; 1 Ki 15:18-20 |
|
894t BC (Nov) |
18th year |
Prophecy of Hanani, whom Asa throws into prison. |
2 Chron 16:7 |
|
890 BC |
22nd year |
Tukulti-Ninurta II becomes king of Assyria (890-884 BC) |
|
|
873t-872t |
39th year |
Asa stricken with diseased feet, Jehoshaphat is made co-regent for two years. |
2 Chron 16:11 |
|
871t (870 BC) |
41st year |
Asa dies, buried in tomb he dug, with perfume and huge bonfire |
2 Chron 16:13 |
B. Parallels between Asa and Josiah:
|
Asa and Josiah parallels |
||
|
|
ASA 911-870 BC (41 years) |
JOSIAH 640-609 BC (31 years) |
|
Bible was ignored, Idol worship rampant |
"For many days Israel was without the true God and without a teaching priest and without law." (2 Chronicles 15:3) |
No bible. Idols in temple of Solomon. |
|
Sought God and Removed idols on his own |
"Asa did good and right in the sight of the Lord his God, for he removed the foreign altars and high places, tore down the sacred pillars, cut down the Asherim," (2 Chronicles 14:2-3) |
"For in the eighth year of his reign while he was still a youth, he began to seek the God of his father David; and in the twelfth year he began to purge Judah and Jerusalem of the high places, the Asherim, the carved images and the molten images." (2 Chronicles 34:3) |
|
Was reassured by a prophet |
"Now the Spirit of God came on Azariah the son of Oded, and he went out to meet Asa and said to him, “Listen to me, Asa, and all Judah and Benjamin: the Lord is with you when you are with Him. And if you seek Him, He will let you find Him; but if you forsake Him, He will forsake you." (2 Chronicles 15:1-2) |
Found book of Law of Moses, enquired of God. "Hilkiah responded and said to Shaphan the scribe, “I have found the book of the law in the house of the Lord.” And Hilkiah gave the book to Shaphan." (2 Chronicles 34:15) "Go, inquire of the Lord for me and for those who are left in Israel and in Judah, concerning the words of the book which has been found; for great is the wrath of the Lord which is poured out on us because our fathers have not observed the word of the Lord, to do according to all that is written in this book." (2 Chronicles 34:21) "“Because your heart was tender and you humbled yourself before God when you heard His words against this place and against its inhabitants, and because you humbled yourself before Me, tore your clothes and wept before Me, I truly have heard you,” declares the Lord. “Behold, I will gather you to your fathers and you shall be gathered to your grave in peace, so your eyes will not see all the evil which I will bring on this place and on its inhabitants.” ’ ” And they brought back word to the king." (2 Chronicles 34:27–28) |
|
Accelerated reforms after divine reassurance |
"Now when Asa heard these words and the prophecy which Azariah the son of Oded the prophet spoke, he took courage and removed the abominable idols from all the land of Judah and Benjamin and from the cities which he had captured in the hill country of Ephraim. He then restored the altar of the Lord which was in front of the porch of the Lord." (2 Chronicles 15:8) |
"Josiah removed all the
abominations from all the lands belonging to the sons of Israel, and made all
who were present in Israel to serve the Lord their God. Throughout his
lifetime they did not turn from following the Lord God of their fathers."
(2 Chronicles 34:33) |
|
Challenges prophet of God at end of life |
"At that time Hanani the seer came to Asa king of Judah and said to him, “Because you have relied on the king of Aram and have not relied on the Lord your God, therefore the army of the king of Aram has escaped out of your hand. “Were not the Ethiopians and the Lubim an immense army with very many chariots and horsemen? Yet because you relied on the Lord, He delivered them into your hand. “For the eyes of the Lord move to and fro throughout the earth that He may strongly support those whose heart is completely His. You have acted foolishly in this. Indeed, from now on you will surely have wars.” Then Asa was angry with the seer and put him in prison, for he was enraged at him for this. And Asa oppressed some of the people at the same time." (2 Chronicles 16:7–10) |
"But Neco sent messengers to him, saying, “What have we to do with each other, O King of Judah? I am not coming against you today but against the house with which I am at war, and God has ordered me to hurry. Stop for your own sake from interfering with God who is with me, so that He will not destroy you.”" (2 Chronicles 35:21) |
|
Death and disease are the result. |
"In the thirty-ninth year of his reign Asa became diseased in his feet. His disease was severe, yet even in his disease he did not seek the Lord, but the physicians." (2 Chronicles 16:12) |
"However, Josiah would not turn away from him, but disguised himself in order to make war with him; nor did he listen to the words of Neco from the mouth of God, but came to make war on the plain of Megiddo. The archers shot King Josiah, and the king said to his servants, “Take me away, for I am badly wounded.”" (2 Chronicles 35:22–23) |
|
|
VII. The Ahab/Josiah parallels:
In one of the strangest stories in the Bible, wicked idolatrous King Neco II of Egypt warns the "righteous promised child" Josiah to go home and not to fight against him. Josiah did not believe that YHWH had indeed directly communicated with and send Neco II on a special military mission to defeat Nebuchadnezzar in the Battle of Carchemish. Josiah was killed before the battle of Carchemish at Megiddo by an arrow shot by Neco II’s army at Megiddo.
This story of Josiah is eerily similar to that of wicked Ahab, king of Israel.
1. Josiah and Ahab Differences:
a. Ahab was a king of the ten northern tribes of Israel whose capital was Samaria and Josiah was the king of Judah whose capital was Jerusalem.
b. Ahab was one of the wickedest kings of the Bible while Josiah was one of the most righteous.
2. Josiah and Ahab Similarities:
a. Both were kings
b. Both Ahab and Josiah were warned by God not to go to battle.
c. Both disobeyed a prophet of God.
d. Both disguised themselves and went to war.
e. Both were killed by an arrow.
f. Both said the identical words: "take me away I am severely wounded."
|
Ahab and Josiah parallels |
|
|
Ahab |
Josiah |
|
One of Israel's most evil kings |
One of Judah's most righteous kings |
|
Did what was evil in God's eyes |
Did what was right in God's eyes |
|
Had a history of listening to false prophets |
Had a history of rejecting false prophets |
|
"Micaiah said, “If you [Ahab] indeed return safely, the Lord has not spoken by me.” And he said, “Listen, all you people.”" (2 Chronicles 18:27) |
"But Neco sent messengers to him, saying, “What have we to do with each other, O King of Judah? I am not coming against you today but against the house with which I am at war, and God has ordered me to hurry. Stop for your own sake from interfering with God who is with me, so that He will not destroy you.” (2 Chronicles 35:21) |
|
"The king of Israel said to Jehoshaphat, “I will disguise myself and go into battle, but you put on your robes.” So the king of Israel disguised himself, and they went into battle." (2 Chronicles 18:29) |
"However, Josiah would not turn away from him, but disguised himself in order to make war with him; nor did he listen to the words of Neco from the mouth of God, but came to make war on the plain of Megiddo." (2 Chronicles 35:22) |
|
"A certain man drew his bow at random and struck the king of Israel in a joint of the armor. So he said to the driver of the chariot, “Turn around and take me out of the fight, for I am severely wounded.”" (2 Chronicles 18:33) |
"The archers shot King Josiah, and the king said to his servants, “Take me away, for I am badly wounded.”" (2 Chronicles 35:23) |
|
Probably said after he died: "How could I be so stupid" |
Probably said after he died: "What just happened? I am confused." This likely the same thing that Jonathan said when he was killed on Mt. Gilboah with his father Saul. |
|
|
VIII. Overview of the Kingdom of Aram dynasty:
A. Dynasty of Ben-Hadad I and Ben-Hadad II and Ben-Hadad III
1. The Aram dynasty is as follows:
a. Ben-Hadad I: 900-860 BC (son of Tab-Rimmon, son of Hezion)
b. Ben-Hadad II: 860-841 BC (son of Ben-Hadad I)
c. Hazael: 841-800 BC (usurped the throne, dynasty broken.)
d. Ben-Hadad III: 800-770 BC (son of Hazael)
2. Ben-Hadad I (900-860 BC) conquered Dan in 895 BC.
3. Elijah healed Naaman the leper, who was the army commander for Ben-Hadad II, and had accomplished many victories (2 Ki 5:1).
4. Ahab was victorious in 857 BC by repelling Ben-Hadad II's (860-841 BC) invasion of Samaria.
5. Ben-Hadad II was again defeated the following year (856 BC, 1 Kings 20:26-30) at Aphek (east coast of sea of Galilee).
6. Three years later (853 BC) Ben-Hadad II is named "Adad-’idri" in the Kurkh Monolith of Shalmaneser III (Battle of Qarqar) as having 1200 manned chariots and 20,000 soldiers in an alliance with Ahab (who had 2000 chariots and 10,000 soldiers) to defeat Shalmaneser III in 853 BC.
7. Later in 853 BC, Ahab and Jehoshaphat joined in an alliance against Ben-Hadad II at Ramoth-Gilead (1 Ki 22:1-40) in which Ahab was killed. Ben-Hadad II is named as an adversary in the annals of Shalmaneser III in the western campaigns in the years 849, 848, and 845 BC.
8. Around 850 BC, Ben-Hadad II attacked Joram, king of Israel in Samaria (2 Kings 6:24) but God struck them with insanity (panic: 2 Kings 7:6) and they fled back to Aram.
9. In 841 BC Mesha, king of Moab, mentions the "house of David" in the "Mesha stele"
10. In the year 841 BC, five different events happen:
a. In 841 BC Hazael usurps the throne in 2 Kings 8:7-15 by smothering him with a wet towel.
b. 841 BC is also the 18th year of Shalmaneser III who actually records that Hazael was not royal blood but a commoner (son of nobody) who seized the throne in a coup from Ben-Hadad II.
c. In 841 BC, Jehu king of Israel (841-814 BC) fatally injured Joram king of Israel. A few weeks later Jehu murders both Joram and Ahaziah, king of Judah in 2 Kings 9:24-28.
11. Ben-hadad III is "Mari" in three stele of Adad-nirari III, king of Assyria: See Conquest stele of Adad-nirari III, king of Assyria
d. There are several inscriptions that reference Mari that have been discovered in archeology.
e. The many inscriptions of Mari show it to be a title like King, Pharaoh or President or Prime Minister and is not a personal name.
f. Both Hazael and his son Ben-hadad III were called "mr'(n)": Mari.
g. "Page identifies IMa-ri-’i mātImeri-šú as Ben-hadad [III], the son of Hazael (Iraq 30 (1968): 149–150). The inscribed ivory from Arslan Tash states: הזאל למדאן showing that Hazael, king of Damascus had the title mr’(n). Since Hazael had the title, it is likely that his son Ben-hadad also held it on becoming monarch. Hazael ruled ‘all the days of Jehoahaz’ (2 Kings 13:22), which implies that he died either in the same year as Jehoahaz or later. Since Ia’asu is probably Joash, Mari’ may be either Hazael, or more probably his son Ben-hadad (2 Kings 13:25). Page suggests that since no verse in the Old Testament records either Adad-nirari’s intervention in Damascus or tribute given to the Assyrian monarch by Joash (or Jehoahaz for that matter), the Israelite king (Joash) took his chance by siding with the Assyrians when the Assyrians appeared at the gate of Damascus. Joash’s gift was then recorded by the Assyrian scribes (p. 150). (Ancient Conquest Accounts: A Study in Ancient Near Eastern and Biblical History Writing, K. Lawson Younger Jr., Vol. 98, p 122, footnote 103, 1990 AD)
h. "Hazael was the scourge of Israel in the reigns of Joram, Jehu and Jehoahaz, fighting against Shalmaneser again in 837; with Joram at Ramoth Gilead in 843/2 (2 Kgs 8:28) and Jehoahaz (13:22). In old age he was a vassal of Adad-nirari III (c. 805/798) who referred to him as mari’. This could be a title (‘my Lord’) or a personal name, abbreviation of Mari’-Hadad, for an inscribed ivory from Arslan Tash (Til Barsip) reads ‘lord Hazael’ (mr’n ḥz’l). His name is also found on an ivory from Nimrud and written on a bead captured by Shalmaneser. A possible representation of him appears on another ivory (IBD, p. 612). He was succeeded by his son Bir-Hadad (Ben-Hadad III) who ruled c. 796–770 bc (13:24). The Aramaic Zakir stela inscription reads ‘Bar-Hadad bar (son of) Hazael, king of Aram’." (1 and 2 Kings: an introduction and commentary TOTC, p 227, 1993 AD)
i. "More difficult is Mari of Damascus. Mari can be simply the Aramaic title, ‘my lord’ rather than a personal name. It has been suggested that the Assyrians referred to the Aramaean leader by this term because they were uncertain as to who he was. The Arslan Tash ivory might suggest that this was Hazael: ‘[]xx ‘m’ to our lord (mr’n) Hazael in the year [of the tak]ing of Ḥ[].’ A similar message is found on the Hazael booty inscriptions which seems to read something along the lines of the following: ‘That which Hadad (?) gave to our lord (mr’n) Hazael from Umeq in the year that our lord crossed over the river’. Others, however, would identify Mari with Bar-Hadad son of Hazael." (Ahab Agonistes: The Rise and Fall of the Omri Dynasty, L. L. Grabbe, p76, 2007 AD)
B. Dynasty of Hazael and his son, Ben-Hadad III: 841-800 BC
1. 841 BC was a busy year for Hazael that included his anointing by Elisha as king of Aram, fatally injuring Joram king of Israel and erecting his Victory stele at Tel Dan.
a. In 841 BC Elisha goes to anoint Hazael. Hazael has been sent by Ben-Hadad II to enquire if he will recover from a sickness. Elisha had previously healed Naaman, the army commander of Beh-Hadad II.
b. In 841 BC Hazael fatally wounds Joram, king of Israel. A short time later Jehu kills both Joram and Hazael.
c. In 841 BC Hazael puts the "Tel Dan Stele" with the "House of David" inscription outside the city gate of Dan where the pagan temple of Jonathan, grandson of Moses and Jeroboam had pagan altars.
2. In 814 BC (23rd year of Jehoash king of Judah) Hazael conquers Gath and threatens to attack Jerusalem but Jehoash gives Hazael tribute.
a. According to the chronology of Kings Chart, it appears that the 23rd year of Joash is 812 BC, when in fact it is 814 BC. 814 BC is the 23rd year of Joash when you have the correct understanding of inclusive vs non-inclusive counting and the new years in Tishri (t) and Nisan (n). "Joash of Judah began in 836t; his reign was by non-accession reckoning, so his ‘23rd’ year was 836t – 22 (acc) = 814t. Jehoahaz son of Jehu began in that year, 814t, more specifically in 814t/813n. The trouble is when people look at the Bible numbers and think in terms of BC years without making the correct translation between the two calendar systems. Joash began in 835n/835t. This was 836t by Judean official reckoning, but it was, in our reckoning, in the 6-month period on or after Nisan 1 of 935 BC. (Rodger Young, email, 2014 AD)
3. 841-770 BC Aram controlled much of northern Israel's land because of their idolatry. It wasn't until Hazael died that Joash began to recapture some of this lost territory from the Arameans.
4. 800-770 BC: Hazael dies: “When Hazael king of Aram died, Ben-hadad his son became king in his place. Then Jehoash the son of Jehoahaz took again from the hand of Ben-hadad the son of Hazael the cities which he had taken in war from the hand of Jehoahaz his father. Three times Joash defeated him and recovered the cities of Israel.” (2 Kings 13:24-25)
5. 755 BC: Judgement against Hazael: “Thus says the Lord, “For three transgressions of Damascus and for four I will not revoke its punishment, Because they threshed Gilead with implements of sharp iron. “So I will send fire upon the house of Hazael. And it will consume the citadels of Ben-hadad.” (Amos 1:3-4)
6. See also: Stele of Zakkur, king of Hamath that name Ben-Hadad III: 795 BC:
a. A war between Hamath and Ben-Hadat III (Mari), son of Hazael, and a coalition of 17 kings.
b. See: Zakkur monument

7. See also: A
collection of 6 stela, tablets and statues that name Ben-Hadad III: 796 BC

a. Adad-Nirari III, King of Assyria (810-783) "The Unknown Deliverer of Israel of 2 Kings 13:5
b. "YHWH gave Israel a deliverer, so they escaped from under Aram [Ben-Hadad III]" (2 Kings 13:5)
c. A stunning collection of six (6) stela, statues and inscriptions fully document how God used Assyrian king Adad-Nirari III, as the one who delivered Josiah, king of Israel, out of the hand of the Ben-Hadad III, king of Aram at Damascus in 2 Kings 13:4-5. 796 BC
d. Ben-Hadad III named on the Stela of Adad-Nirari III, King of Assyria (810-783 BC)
|
Adad-Nirari III (810 - 783 BC) "The unknown deliverer" |
||
|
2 Kings 13:5 |
||
|
"YHWH gave Israel King Joash (Israel) |
a deliverer King Adad-nirari III (Assyria) |
they escaped Aram" King Ben Hadad III (Aram) |
|
|
IX. Archeological excavations and inscriptions: What you read in the book you find in the ground!
A. Tel Dan Archeological Destruction layer: Excavations Tel Dan Excavations
1. Archeological excavations dating to 895 BC from the Battle of Naphtali have found a massive destruction layer confirming the Bible story as real history.
2.
Ben-Hadad I destroyed the city after making a treaty
with Asa king of Judah in an effort to defeat Baasha king of Israel when he
fortified Bethel: (1 Ki 15:18-20)

B. The seal of Jezebel, wife of Ahab, king of Judah
1. View the Seal of Jezebel
2. The bible story of Jezebel: 1 Kings 16:31; 21:25; Rev 2:20
a. As the foreign wife of Ahab, king of Israel, Jezebel was influential from 873-841 BC.
b. Jehu king of Israel had Jezebel thrown out of a tower to her death in 841 BC
3. About the seal:
a. The grey opal seal names Jezebel in Paleo-Hebrew along with Egyptian hieroglyphics .
b. The rare seal was discovered on the black market in 1962 AD and donated to the Israel Museum shortly thereafter.
C. The Stele of Hazael (more famously known as the “House of David stele/inscription”):
3. In 841 BC, Ben-Hadad II king of Aram, who tried to kill Elisha 9 years earlier in 850 BC, ironically now asks this same Elisha if he will live or die. Elisha anoints Hazael king of Aram. 841-800 BC. Hazael murders Ben-Hadad II king of Aram and becomes king in his place. (2 Ki 8:7; 1 Ki 19:15) See outline on Hazael
4. Hazael Stele found at Tel Dan: “I killed Joram son of Ahab and Ahaziah, son of Jehoram of the house of David”. Hazael captures Tel Dan and sets up his victory stele. This is the second time Tel Dan has been destroyed by a king of Aram. Ben-Hadad I also destroyed Tel Dan in 895 BC. See: Tel Dan Excavations from the time of Ben-Hadad I.See also the Victory Stele of Hazael more famously known as the “house of David” stele.
D. Stele of Mesha (Moabite Stone) 841 BC
1. Mesha was king of Moab in 841 BC
2. He records several Bible kings, names YHWH and Samaria
3. He also confirms the devastation suffered by Israel in 841 BC recorded in the Bible when he says, “Israel is ruined” (2 Kings 10:32-33)
4. King Mesha also retakes the cities of Ataroth, Nebo, Jahaz from Israel
5. See detailed outline: Mesha Stele
E. Archeological inscriptions of Ben-Hadad II, king of Aram: 858 – 828 BC
5. Ben-Hadad II is mentioned in the Bible frequently and was a direct force in shaping the kingdoms of Judah and Israel during his lifetime.
6. In 845 BC (Shalmaneser III, year 14, the Battle of Hamath II was fought by Ben-Hadad II and 12 kings against Shalmaneser III during the time of Jehoram king of Israel.
7. The Melqart Stele was erected at Aleppo by Ben-Hadad II as a “lucky charm/rabbits foot” to his God Melqart in order to get the stone pagan god’s help in defeating Shalmaneser III in the Battle of Hamath II (845 BC).
8. Melqart Stele failed to appease the pagan god Melqart because Ben-Hadad II was soundly defeated by Shalmaneser III.
9.
Ben-Hadad II, king of Aram, set up the Melqart Stele near Aleppo
where the Battle of Hamath II was
fought against Shalmaneser III.

F. Archeological inscriptions of Shalmaneser III, king of Assyria: 858 – 828 BC
1. Nine Inscriptions of Shalmaneser III:
a. Shalmaneser III had direct contact with all the kings of Judah and Israel during his lifetime.
b. The Akkadian cuneiform inscriptions on his stele, statues and tables name “Ahab the Israelite”, the house of Omri, Jehu, Sidon, Tyre, Ben-Hadad II king of Aram and Hazael who smothered him on his death bed as Elisha predicted.
c. Many of his important inscriptions were diaries of annual military campaigns which are directly mentioned in the Bible.
d. Shalmaneser III directly confirms the Bible story by calling Hazael “the son of nobody”. Ancient inscriptions confirm that royal succession from father to son of both kingdoms of Aram and Assyria was very important. Shalmaneser III specifically notes that Hazael was not part of the any royal dynasty and this is why he called him the “son of nobody” on his basalt annals statue.
|
9 Inscriptions of Shalmaneser III |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Full Text of the Battle of Qarqar in 853 BC from inscriptions by Shalmaneser III (853 = year 6, Eponymy of Daiiān-Aššur)
a. “On the fourteenth day of the month Iyyar, in the eponymy of Daiiān-Aššur, I moved out from Nineveh, crossed the Tigris, (and) approached the cities of Giammu on the River Balih. They were frightened of my lordly fearfulness (and) the flash of my fierce weapons and with their own weapons they killed Giammu, their master. I entered the cities Sahlala and Tīl-ša-turahi. I took my gods into his palaces and celebrated in his palaces. I opened his storage area (and) saw his treasure. I carried off his possessions (and) property (and) brought (them) to my city, Aššur. (Lines ii 78b-81a) Moving on from the city Sahlala I approached the city Kār-Shalmaneser. I crossed the Euphrates, which was in flood, for a second time in rafts (made of inflated) goatskins. In the city Ana- Aššur-utēr-asbat, which is by the opposite bank of the Euphrates on the River Sagura (and) which the people of the land Hatti call the city Pitru, in (this city) I received tribute from kings on the opposite bank of the Euphrates, from Sangara the Carchemishite, from Kundašpu the Kummuhite, from Aramu, the man of Bīt-Agūsi, from Lalla the Melidite, from Haiiänu the man of Bït-Gabbari, from Qalparuda the Patinean, (and) from Qalparuda the Gurgumite: silver, gold, tin, bronze, (and) bronze casseroles. (Lines ii 81b-86a) Moving on from the Euphrates I approached Aleppo (Halman). They were afraid to do battle with me (and) submitted to me. I received their tribute of silver (and) gold (and) made sacrifices before the god Adad of Aleppo (galman). Moving on from Aleppo (Halman) I approached cities of Irhulënu, the Hamatite. I captured the cities Adennu, Pargâ, (and) Arganâ, his royal cities. I brought forth his captives, property, (and) palace possessions, (and) burned his palaces, (Lines ii 86b-89a) Moving on from the city Arganâ I approached the city Qarqar. I razed, destroyed, (and) burned the city Qarqar, his royal city. An alliance had been formed of (lit. "he/it had taken as his allies") these twelve kings: 1,200 chariots, 1,200 cavalry, (and) 20,000 troops of Hadad-ezer (Adadidri) [Ben-Hadad II], the Damascene; 700 chariots, 700 cavalry, (and) 10,000 troops of Irhulënu, the Hamatite; 2,000 chariots (and) 10,000 troops of Ahab (Ahabbu) the Israelite (Sir'alaia); 500 troops of Byblos; 1,000 troops of Egypt; 10 chariots (and) 10,000 troops of the land Irqanatu; 200 troops of Matinu-ba’al of the city Arvad; 200 troops of the land Usanätu; 30 chariots (and) [N],000 troops of Adunu-ba'al of the land Sianu; 1,000 camels of Gindibu of the Arabs; [N] hundred troops (Line ii 95) of Ba’asa, the man of Bit-Ruhubi, the Ammonite. They attacked to [wage] war and battle against me. With the supreme forces which Aššur, my lord, had given to me (and) with the mighty weapons which the divine standard, which goes before me, had granted me I fought with them. I defeated them from the city Qarqar as far as the city Gilzau. I felled with the sword 14,000 troops, their fighting men, (and) rained down upon them destruction (lit. "flood") as the god Adad would. I filled the plain with their spread out (lit. "I spread out") corpses (and) <felled> their extensive troops with the sword. I made their blood flow in the wadis. (Line ii 100) The plain was too small to lay the (incredible number of) their bodies (lit. "lives") flat; the extensive area was not sufficient (lit. "vanished") to accommodate burying (all of) them. I dammed up the Orontes River with their bodies like a bridge. In the midst of this battle I took away from them chariots, cavalry, (and) teams of horses.” (Lines ii 89b-102) (Kurkh Monolith)
b. “I defeated Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri), the Damascene, together with twelve princes who were his allies. I laid low like sheep 29,000 of his brave warriors (and) threw the remnant of his troops into the Orontes. They fled to save their lives.” (Statue Front, lines 14-24, Year 6, 853 BC) (Basalt Statue)
c. “In the sixth year of my reign, I drew near to the cities on the banks of the Balih. They slew Giammu, governor of their cities. I entered Til-Mâr-ahi. The Euphrates I crossed at its flood. I received gifts from all the kings of Hatti. At that time Hadad-ezer [Ben-Hadad II] of Aram, Irhuleni the Hamathite, together with the kings of Hatti and the seacoast, relied on each other's strength and came out against me to offer battle (make battle and war). At the command of Assur, the great lor, my lord, I fought with them, I accomplished their defeat. I took from them their chariots, their cavalry, and their weapons of war. I slew 20,500 of their warriors with the sword. (Lines 54-62) (Black Obelisk)
d. “In my sixth regnal year I moved out from Nineveh and approached the cities on the banks of the River Balih. They became frightened in the face of my mighty weapons and [killed] Giammu, [their city] ruler. I entered the city Til-turahi (and) claimed the city as my own. Moving on from the banks of the River Balih [I crossed the Euphrates in flood]. (line 15') I received [tribute] from the kings of the land Hatti. Moving on from the land Hatti I approached Aleppo (Halman) (and) made sacrifices [before the god Adad] of Aleppo (Halman). Moving on from Aleppo (Halman) I approached the city Qarqar. Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri) [Ben-Hadad II], the Damascene, Irhulënu, the Hamatite, together with twelve kings on the shore of the sea, trusting in their united forces, attacked me to wage war and battle. I fought with them. I put to the sword 25,000 of their fighting men (and) captured from them their chariotry, cavalry, (and) military equipment. To save their lives they ran away. I boarded boats (and) went out upon the sea.” (Lines 12'b-19') (Twin Bulls)
e. “In my sixth regnal year I approached the cities on the banks of the River Balih. They killed Giammu, their city ruler. I entered the city Til-turahi. I crossed the Euphrates in flood (and) received tribute from the kings of the land Hatti. Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri) [Ben-Hadad II], the Damascene, Irhulënu, the Hamatite, together with twelve kings on the shore of the sea, (Column II, line 20) trusting in their united forces, attacked me to wage war and battle. I fought with them (and) defeated them. I captured from them their chariotry, cavalry, (and) military equipment (and) put to the sword 25,000 of their fighting men.” (Column II, lines 13-25) (Marble Tablets)
3. Full Text of the Battle of Carchemish in 849 BC from inscriptions by Shalmaneser III (849 BC=Year 10)
a. “In the tenth year of my reign, I crossed the Euphrates for the eighth time. I captured the cities of Sangara of Carchemish. I advanced against the cities of Arame. I captured Arnê, his royal city, together with 100 of his small cities.” (Lines 85-86) (Black Obelisk)
b. “In my tenth regnal year I crossed the Euphrates for the eighth time. I razed, destroyed, (and) burned the cities of Sangara, the Carchemishite. Moving on from the cities of the Carchemishite I approached the cities of Aramu (and) captured the city Arnê, his royal city. I razed, destroyed, (and) burned (it) together with one hundred cities in its environs. I massacred them (and) plundered them. At that time, Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri), the Damascene, (and) Irhulenu, the Hamatite, together with twelve kings on the shore of the sea, trusting in their united forces, attacked me to wage war and battle. I fought with them (and) defeated them. I took from them their chariotry, cavalry, and military equipment. To save their lives they ran away.” (Lines 29'b-34') (Twin Bulls)
c. “In my tenth regnal year I crossed the Euphrates for the eighth time. <I captured> the cities of Sangara, the Carchemishite. Moving on from the cities of the Carchemishite I approached the cities of Aramu (and) captured Arnê, his royal city, together with one hundred cities in its environs.” (Column II, lines 45-50) (Marble Tablets)
4. Full Text of the Battle of Hamath I in 848 BC from inscriptions by Shalmaneser III (848 BC=Year 11)
a. “In the eleventh year of my reign, I crossed the euphrates for the ninth time. I captured countless cities. I descended upon cities of the land of Hamath. I captured 89 cities. Hadad-ezer [Ben-Hadad II] of Aram and twelve kings of the land of Hatti stood by each other. I was successful in overthrowing them.” (Lines 87-89) (Black Obelisk)
b. “In my eleventh regnal year I moved out from Nineveh (and) crossed the Euphrates in flood for the ninth time. I captured ninety-seven cities of Sangara. I captured, razed, destroyed, (and) burned one hundred cities of Aramu. I took to the slopes of the Amanus range, crossed Mount laraqu, (and) descended to the cities of the people of Hamat. I captured the city Aštammaku, together with ninetynine (other) cities. I massacred their (inhabitants) (and) plundered them. At that time Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri), the Damascene, (and) Irhulënu, the Hamatite, together with twelve kings on the shore of the sea, trusting in their united forces, attacked me to wage war and battle. I fought with them (and) defeated them. I put to the sword 10,000 of their fighting men. I took from them their chariotry, cavalry, and military equipment. On my return I captured Aparāzu, the fortified city of Aramu. At that time I received tribute from Qalparunda the Patinean: silver, gold, tin, horses, oxen, sheep, (and) linen garments. I went (back) up the Amanus range (and) cut beams of cedar.” (Lines 35'-41'a) (Twin Bulls)
c. “In my eleventh regnal year I crossed the Euphrates for the ninth time. I captured ninety-seven cities of Sangara (and) one hundred cities of Aramu. I took to the slopes of the Amanus range, (Column II, line 55) crossed Mount Iaraqu, (and) descended to the cities of the people of Hamath. I captured the city Abšimaku (Aštammaku?), together with eighty-nine cities. At that time (Column III, line 1) Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri) [Ben-Hadad II], the Damascene, (and) Irhulënu, the Hamatite, together with twelve kings on the shore of the sea, trusting in their united forces, (attacked me) and I fought with them (and) defeated them. I put to the sword [10] ,000 of their fighting men.” (Column II, line 51 – column III, line 5) (Marble Tablets)
5. Full Text of the Battle of Hamath II in 845 BC from inscriptions by Shalmaneser III (845 BC=Year 14)
a. Note: The Melqart Stele was erected by Ben-Hadad II in preparation for this battle.
b. “In the fourteenth year of my reign, I mustered my land. I crossed the Euphrates. Twelve kings advanced to meet me. I battled with them and successfully overthrew them.” (Lines 92-93) (Black Obelisk)
c. “In my fourteenth regnal year I mustered (the troops of my) extensive land in countless numbers (and) crossed the Euphrates in flood with 120,000 troops. At that time Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri), the Damascene, (and) Irhulënu, the Hamatite, together with twelve kings on the shore of the sea, above and below, mustered their troops which were too numerous to be counted. They attacked me, I fought with them, (and) defeated them. I destroyed their chariotry (and) cavalry — (and) took away their military equipment. To save their lives they ran away.” (Lines 44b-47a) (Twin Bulls)
d. “In my fourteenth regnal year I mustered (the troops of my) extensive land in countless numbers (and) crossed the Euphrates in flood with 120,000 of my troops. At that time Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri) [Ben-Hadad II], the Damascene, (and) Irhulënu, the Hamatite, together with twelve kings on the shore of the sea, (Column III, line 20) above and below, mustered their troops, which were too numerous to be counted. They attacked me, I fought with them, (and) defeated them. I took away their chariotry, cavalry, (and) military equipment. To save their lives they ran away.” (Column III, lines 14-25) (Marble Tablets)
6. Full Text of the Siege of Damascus in 841 BC from inscriptions by Shalmaneser III (841 BC=Year 18)
a. “Hadad-ezer (Adad-idri) [Ben-Hadad II] passed away (and) Haza'el, son of a nobody, took the throne. He mustered his numerous troops (and) moved against me to wage war and battle. I fought with him (and) defeated him. I took away from him his walled camp. He fled to save his life (and) I pursued (him) as far as Damascus, his royal city, (ii 1) [I cut down his] gardens. [...] The gods Anu and A[dad ...] peace [...] I received tax [...] (Statue Front, lines 25-35, continued onto left hip, Lines 1-6, Year 18, 841 BC) (Basalt Statue)
b. “In my eighteenth regnal year I crossed the Euphrates for the sixteenth time. Hazael of Damascus attacked to do battle. I captured from him 1,121 of his chariots (and) 470 of his cavalry, together with his camp. (Lines 97b-99a) (Black Obelisk)
c. “In my eighteenth regnal year I crossed the Euphrates for the sixteenth time. Hazael of Damascus, trusting in the might of his soldiers, (line 5") carried out an extensive muster of his troops. He fortified Mount Saniru, the mountain peak, which is before Mount Lebanon. I fought with him (and) defeated him. (line 10") I put to the sword 16,000 of his fighting men (and) took away from him 1,121 of his chariots (and) 470 of his cavalry with his military camp. To save (line 15") his life he ran away (but) I pursued him. I imprisoned him in Damascus, his royal city, (and) cut down his gardens. I marched to Mount Haurānu (and) razed, destroyed, (and) (line 20") burned cities without number. I carried off more booty than could be counted. I marched to Mount Ba’lira’asi, which is a cape (jutting out into) the sea, (and) erected my royal statue there. At that time I received (line 25") tribute from the people of Tyre (and) Sidon (and) from Jehu (Iaua) of the house of Omri (Humrî). (Lines I"-27") (Twin Bulls)
d. “In my eighteenth regnal year I crossed the Euphrates for the sixteenth time. Hazael of Damascus, trusting in the might of his soldiers, carried out an extensive muster of his troops, (Column III, line 50) He fortified Mount Saniru, the mountain peak, which is before Mount Lebanon. I put to the sword 16,020 of his fighting men (and) took away from him 1,121 of his chariots (and) 470 of his cavalry with his military camp, (Column IV, line 1) To save his life he ran away (but) I pursued him. I imprisoned him in Damascus, his royal city, cut down his gardens, (and) burned his shocks, (Column IV, line 5) I marched to Mount Haurānu (and) razed, destroyed, burned, (and) plundered cities without number. I marched to Mount Ba’lira’asi, which is a cape (jutting out into) the sea before the land of Tyre, (and) (Column IV, line 10) erected my royal statue there. I received tribute from Ba’ali-manzeri of Tyre (and) from Jehu (Iāu) of the house of Omri (Humri). On my return I ascended Mount Lebanon (and) erected my royal statue with the statue of Tiglathpileser, a strong king who preceded me.” (Column III, line 45b – Column IV, line 15a) (Marble Tablets)
e. “In my eighteenth regnal year I crossed the Euphrates for the sixteenth time. Hazael of Damascus, trusting in the might of his soldiers, carried out an extensive muster of his troops. He fortified Mount Saniru, the mountain peak which is before Mount Lebanon. I fought with him (and) defeated him. I put to the sword 16,000 of his fighting men (and) took away from him 1,121 of his chariots (and) 470 of his cavalry with his military camp. (Lines 25) To save his life he ran away (but) I pursued (him). I imprisoned him in Damascus, his royal city, (and) cut down his gardens. I marched to Mount Haurānu (and) razed, destroyed, burned, (and) plundered cities without number. I marched to Mount Ba’lira’asi, which is a cape (jutting out into) the sea, (and) erected my royal statue there. At that time I received tribute from the people of Tyre, Sidon, (and) from Jehu (laua) of the house of Omri (Humrî).” (Lines 21-30a) (Alabaster Statue)
7. Full Text of the Battle of Aram 838 BC from inscriptions by Shalmaneser III (838 BC=Year 21)
a. “In the twenty-first year of my reign, I crossed the Euphrates for the twenty-first time. I advanced against the cities of Hazael of Aram. I captured four of his cities. I received the gifts of the Tyrians, Sidonians, and Gebalites [Byblos].” (Lines 102-104) (Black Obelisk)
G. Archeological inscriptions from the Kuntillet Ajrud Fortress in the Negev: 839 BC
1. See full outline on Kuntillet Ajrud ostraca
2. Kuntillet Ajrud was one of the border fortresses built by Solomon on the Egyptian-Judean/Simeon border.
a. There are several levels of occupation.
b. The ostraca used here dates to 839 BC.
3. All the inscriptions found at Kuntillet Ajrud paint a sad picture of a mixing of paganism with pure monotheistic Judaism.
4. Kuntillet Ajrud Ostraca on Pithos Jar #1:
a. Pictured above, it is the earliest known text of Numbers 4:24-26 known on earth.
b. It predates the Silver Scroll by over 140 years!
c.
See
details about the Silver Scroll from Ketef Hinnom

5. Kuntillet Ajrud Ostraca on Pithos Jar #2:
a. Text: “YHWH of Samaria and his wife”.
b. This illustrates the idolatry at Samaria that mixed the worship of YHWH and paganism where the God of Abraham is worshipped along side of the wife of the God of Abraham.
c. This mirrors the pagan view of multiple gods with their goddess wives and god children.
H. Ostraca of Elisha found in the home town of Elisha: 830 BC: Elisha Ostraca
1. See details: Elisha Ostraca
2. Ostraca of Elisha: Discovered in 2013 AD in professional 3-dimentional archeological excavations at Tel Rehov, which is the home town of Elisha in the Bible called Abel-Meholah which is located 10 km SE of Beth-Shean near the Jordan river.
3. The home town of Elisha would be a famous place during and after his lifetime.
a. "The Lord said to Elijah [at Mt. Sinai], “Go, return on your way to the wilderness of Damascus, and when you have arrived, you shall anoint Hazael king over Aram; and Jehu the son of Nimshi you shall anoint king over Israel; and Elisha the son of Shaphat of Abel-meholah you shall anoint as prophet in your place." (1 Kings 19:15–16)
b. While the anointing of Elisha took place in 865 BC and the Ostraca is dated to 830 BC (35 years later), this documents the Bible story perfectly.
4. To find an ostraca with the name of Elisha on it, in the home town of Elisha in the Bible is a stunning proof that “what you read in the book, you find in the ground”.
5. See also: Excavations at Tel Rehov where the Elisha ostraca was found in 2013 AD
I. Inscriptions of Adad-nirari III: 810-783 BC
1. See outline on Adad-nirari III
2.
Trust Nebu/Nebo Alone Statues:

a. Adad-nirair III sets up four statues of Nebu/Nebo in Calah (Nimrod)
c. The inscription records the equivalent to the “Lord’s prayer” to a pagan god:"To the god Nebo who is heroic, exalted, surpassing in wisdom, mighty prince whose command is supreme, master of the arts, guardian of all heaven and earth, all knowing, whose ear is open [ie. to prayer] who writes the book of man's life and destiny, merciful, approachable, who depopulate and repopulate the land [determines the boundaries of man's habitation.] lord of lords, whose might has no equal, without whom no counsel is given in heaven, merciful, compassionate, kindly forgiving. Trust in the god Nebo! Do not trust in another god." (Trust Nebo Alone Statue of Adad-nardi III, 804 BC)
3.
Rimah Joash Conquest stele of the Battle of Damascus II

a. See outline Rimah Joash conquest stele
b. Rimah Joash Conquest stele inscription: “In one year I subdued all the lands of Amurru & Hatti (Syria and Israel). I imposed tribute of Mari [Ben-Hadad III], the Damascene. I received the tribute of Joash [lit. Iu'asu], the Samaritan, and tribute of Tyre & Sidon.” (Rimah Joash conquest stele of Adad-nirari III)
4.
Saba’a Conquest Stele inscription of the Battle of Damascus II

a. Saba’a Conquest Stele inscription: “I confined Mari [Ben Hadad III] in Damascus and he gave me 100 talents of gold and 1,000 talents of silver as tribute.” (Saba'a conquest stele of Adad-nirari III)
b. See outline: Saba'a conquest stele
J. Inscriptions of Zakkur king of Hamath and the Battle of Hamath III: 795 BC
1. After his defeat by Adad-Nirari III of Assyria, Ben-Hadad III attacks Hamath but again is defeated by Zakkur king of Hamath.
2. Notice how king Zakkur trusts in his pagan god.
3. Inscription of the Stele of Zakkur: “I am Zakkur, king of Hamath and Luʿash. I was a humble but Baʿlshamayn [my other god] [raised] me and stood beside me, and Baʿlshamayn made me king over Hazrach [Hamath]. Then Ben-Hadad [III], son of Hazael, king of Aram, united against me s[even]teen kings: Ben-Hadad [III] and his army, Bar-Gush and his army, the king of Que and his army, the king of ʿAmuq and his army, the king of Gurgum and his army, the king of Samʾal and his army, the king of Meliz and his army [ ] seven[teen], they and their armies. All these kings laid siege to Hazrach. They raised a wall higher than the wall of Hazrach, they dug a ditch deeper than [its] ditch. Now I raised my hands to Baʿlshamayn and Baʿlshamayn answered me. Baʿlshamayn [spoke] to me through seers and diviners. Baʿlshamayn said to me, “Do not be afraid! Since I have made [you king, I will stand] beside you. I will save you from all [these kings who] have besieged you.” [Baʿlsha-mayn] also said to [me, “] all these kings who have [besieged you ] and this wall [ ].” (Stele of Zakkur, King of Hamath)
4.
The Stele was found in Afis:

5. See outline on Stele of Zakkur, King of Hamath
|
|
1. The 9th century BC (899-800 BC) was a very turbulent period for Israel and Judah
a. There were 25 different wars fought that included Israel or Judah or both.
b. The Hebrews fought the Assyrians, the Arameans, the Moabites, the Ethiopians and each other!
2. Elijah comes on the world stage at when Omri builds his palace in Samaria in 877 BC. Jezebel builds (through Ahab) the house of Baal in 872 BC. The first recorded event of Elijah was in 870 BC when he made the prediction of the 3.5-year drought.
a. The drought begins the year of the death of Asa and shortly after Jezebel starts murdering the righteous priests of YHWH.
b. Elisha’s “double measure” of Elijah’s ministry is seen in: Elijah had a 35-year ministry and Elisha 70-year ministry. Elijah predicted a 3.5-year drought and Elisha predicted a 7-year drought.
3. A series of major efforts of restoration back to the Bible and the removing of idolatry occurred
a. Asa king of Judah took great steps in stamping out idolatry during his long 41-year reign, most of which was free of any kind of war or outside disturbance.
b. Elijah has the great showdown on Mt. Carmel and kills the 850 false prophets of Baal.
c. Jehu killed the two idolatrous kings of Israel and Judah and the notorious Jezebel.
d. Jehu “eradicated Baal out of Israel." (2 Kings 10:28)
e. Jehoiada the high priest destroys the “House of Baal” in Judea that Athaliah had set up when Joash was king of Israel. (835 BC)
4. Many oral prophets but none of the written prophets
a. None of the books of the Bible were written during the period of 900-800 BC
b. The first written prophet after this period was Amos that dates to 762 BC as the first of a series of written and oral prophets warning the ten northern tribes to repent or go into extinction in Assyria in 723 BC.
c. Written prophets of the 8th century after the death of Elisha:
i. Amos: 762 BC
ii. Jonah 759 BC
iii. Hosea: 750 BC
iv. Isaiah: 740-700 BC
v. Micah: 735 BC
5. Asa was the first in a series of Judean kings who were condemned by God through oral prophets for their allegiances with Samaria (10 northern tribes, headed in Samaria) and other pagan foreign nations.
a. Asa was condemned for his allegiances with Ben-Hadad I to defeat Baasha
b. Jehoshaphat was condemned for his allegiances with Ahab to defeat Ben-Hadad II.
6. 25 Archeological confirmations of the Bible names, places and events from inscriptions, ostraca, seals, statues and annals tables.
a. Tel Dan Excavations confirm Ben-Hadad I destroyed the city in 895 BC just as the Bible says: 1 Ki 15:18-20
b. Seal of Jezebel, wife of Ahab, king of Judah
c. Victory Stele of Hazael king of Aram or “House of David stele/inscription”: 941 BC
d. Mesha Stele (Moabite Stone) 841 BC
e. Melqart Stele inscription of Ben-Hadad II, king of Aram: 845 BC
f. Nine inscriptions of Shalmaneser III, king of Assyria: 858 – 828 BC
i. Kurkh Monolith 852 BC
ii. Basalt Statue 833 BC
iii. Black Obelisk 827 BC
iv. Bronze Gates 847 BC
v. Basalt Throne 849 BC
vi. Clay Brick 858-839 BC
vii. Twin Bulls 840 BC
viii. Marble Tablets 838 BC
ix. Alabaster Statue 838 BC
g. Kuntillet Ajrud ostraca “Fortress in the Negev”: 839 BC
h. Silver Scroll from Ketef Hinnom: 725-650 BC
i. Elisha of Ostraca: 830 BC found in the home town of Elisha
j. Excavations at Tel Rehov where the Elisha ostraca was found in 2013 AD
k. Six inscriptions of Adad-nirari III Adad-nirari III Inscriptions of Adad-nirari III: 810-783 BC
i. Dynastic door sill stone: 804 BC
ii. Trust Nebo Alone Statue: 804 BC
iii. Hindanu Stele: 797 BC
iv. Rimah Joash conquest stele: 796 BC
v. Omri-land conquest stele: 796 BC
vi. Saba'a conquest stele: 796 BC
l. Stele of Zakkur king of Hamath: 795 BC
What you read in the book you find in the ground!
|
Why not attend a Bible believing church in your own home town
|
Steve Rudd: Contact the author for comments, input or corrections.